- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1397-1411
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1648K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1412-1418
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/21PDF形式でダウンロード (1327K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1419-1423
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1148K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1424-1431
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (727K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1432-1436
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (690K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1437-1447
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/18PDF形式でダウンロード (2526K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1448-1454
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (10864K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1455-1460
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/28PDF形式でダウンロード (285K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1461-1467
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (915K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1468-1474
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (665K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1475-1481
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (591K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1482-1487
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (583K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1488-1495
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3076K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1496-1507
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1496-1507
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
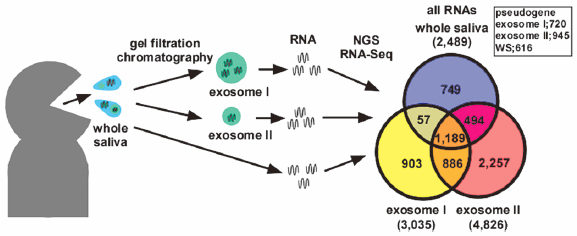
Editor's pickIn their report, Ogawa et al. described next-generation sequencing of protein-coding and long non-protein-coding RNAs in two types of exosomes derived from human whole saliva. Exosomes are small extracellular vesicle released from variety types of cells. They contain proteins and nucleic acids transferred to recipient cells. Human whole saliva contains two types of exosomes (exosomes I and II) that are different in size, proteome and small RNA transcriptome. In this study, they investigated the compositions of protein-coding RNAs and long non-protein-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) of exosome I, exosome II and whole saliva by next-generation sequencing technology. Interestingly, lncRNAs of pseudogenes were abundant in exosomes and whole saliva. Their results may highlight a new function of exosomes in regulation of gene expression.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1001K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1508-1513
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/17PDF形式でダウンロード (282K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1514-1522
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/06/18PDF形式でダウンロード (1206K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1523-1530
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/07/21PDF形式でダウンロード (3216K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1531-1537
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (899K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1538-1543
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2016/07/07PDF形式でダウンロード (517K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1544-1548
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (538K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1549-1554
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (321K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1555-1558
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1832K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1559-1563
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (756K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1564-1567
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (401K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2016 年 39 巻 9 号 p. 1568
発行日: 2016/09/01
公開日: 2016/09/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (230K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|