
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Makoto Tsuda2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 1959-1968
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
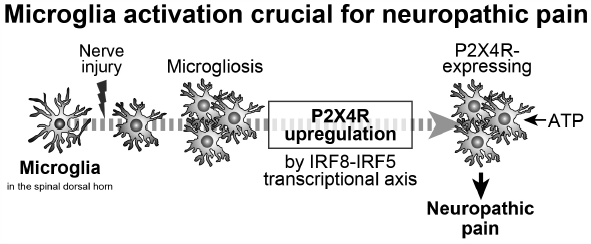
ジャーナル フリー HTMLPain is a defense system that responds rapidly to harmful internal and external stimuli through the somatosensory neuronal pathway. However, damage to the nervous system through cancer, diabetes, infection, autoimmune disease, chemotherapy or trauma often leads to neuropathic pain, a debilitating chronic pain condition. Neuropathic pain is not simply a temporal continuum of acute nociceptive signals from the periphery, but rather due to pathologically altered functions in the nervous system, which shift the net neuronal excitatory balance toward excitation. Although alterations were long thought to be a result of changes in neurons, but an increasing body of evidence over the past decades indicates the necessity and sufficiency of microglia, the tissue-resident macrophages of the spinal cord and brain, for nerve injury-induced malfunction of the nervous system. In this review article, I describe our current understanding of the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the role of microglia in the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain and discuss the therapeutic potential of microglia from recent advances in the development of new drugs targeting microglia.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1020K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1020K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Rajendran Harishkumar, Lakki Pramod Kumar Reddy, Shivam H. Karadkar, M ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 1969-1976
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
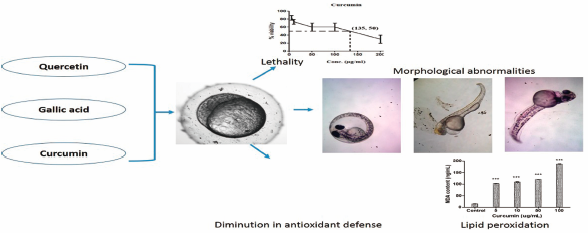
ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn recent years, numerous research outcomes were established on various naturally occurring compounds that have been shown to have beneficial antioxidant and other biological activities. Antioxidant defence mechanism plays a vital role in combating various diseases mainly due to oxidative stress. However, various models have been utilized to identify their bioactivities using these compounds (quercetin, gallic acid and curcumin). Their toxicity level also has to be explored to determine the threshold levels on the usage of these compounds. In this study, we investigated the lethal concentration of these compounds and abnormalities, biochemical and morphological changes in zebrafish embryo (Danio rerio). Toxicity level was evaluated by calculating the LD50 on the embryonic stages at 24, 48 and 72 h. Antioxidant parameters such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione (GSH) and biological assays such as lipid peroxidation, protein estimation were performed. Microscopic evaluations were also observed to find out morphological abnormalities. However, these naturally derived compounds are reported to have their protective and curative role in many health complications. From the above assays, we are studying the effect of the drugs in both biochemical and molecular way in the zebrafish model organism.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2293K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2293K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Akihiro Inamura, Sanae Muraoka-Hirayama, Koichi Sakurai2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 1977-1987
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLGemcitabine (2,2-difluorodeoxycytidine nucleic acid), an anticancer drug exhibiting a potent ability to kill cancer cells, is a frontline chemotherapy drug. Although some chemotherapeutic medicines are known to induce nuclear DNA damage, no investigation into mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage currently exists. When we treated insulinoma pancreatic β-cells (line INS-1) with high mitochondrial activity with gemcitabine for 24 h, the mtDNA contents were decreased. Gemcitabine induced a decrease in the number of mitochondria and the average potential of mitochondrial membrane in the cell but increased the superoxide anion radical levels. We observed that treatment with gemcitabine to induce cell death accompanied by autophagy-related protein markers, Atg5 and Atg7; these were significantly prevented by the autophagy inhibitors. The localization of Atg5 co-occurred with the location of mitochondria with membranes having high potential and mitophagy in cells treated with gemcitabine. The occurrence of mitophagy was inhibited by the inhibitors of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Our results led us to the conclusion that gemcitabine induced cell death through mitophagy with the loss of mtDNA. These findings may provide a rationale for the combination of mtDNA damage with mitophagy in future clinical applications for cancer cells.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (6179K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (6179K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Eun Ho Shin, Moonhang Kim, Binika Hada, Chang Taek Oh, Min Jung Jang, ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 1988-1995
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLRich in bioactive substances such as amino acids and peptides, Laennec (human placenta hydrolysate) has been widely used to control various types of musculoskeletal pain. However, the effects of Laennec on tendon and ligament injuries are not clearly understood. In the present study, Laennec was tested to identify its in vivo effects on ligament injury in an animal model and its in vitro effects on tendon-derived fibrocytes. A total of 99 Sprague Dawley rats were divided into the negative control (normal) group (n = 11) and the ligament injury group (n = 88). The ligament injury group was subdivided into normal saline-treated group, Laennec-treated group, polydeoxyribonucleotide-treated group, and 20% dextrose-treated group. Ligaments were collected at 1 week and 4 weeks after treatment. Histologic and biomechanical properties were analyzed. In vitro effects of Laennec and polydeoxyribonucleotide on fibrocytes were also analyzed. Although all other treatment groups showed increased inflammatory cells, the Laennec-treated group maintained cell counts and activated macrophage levels that were similar to the normal group. Unlike the saline-treated group and dextrose-treated group, the Laennec-treated group had low levels of degenerative changes at 4 weeks after treatment. Supportively, in vitro results showed that the Laennec-treated group had increased collagen type I, scleraxis (Scx) and tenomodulin (Tnmd) expression (p < 0.05). Our study demonstrates that Laennec treatment enhances wound healing of damaged ligament by suppressing immune responses and reducing degenerative changes of damaged ligament. In addition, we found that Laennec induces the gene expression of type I collagen, Scx and Tnmd in fibrocytes, suggesting that Laennec may facilitate regeneration of damaged ligaments. Therefore, we expect that Laennec can be a useful drug to treat injured ligament.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2977K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2977K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hirokazu Wakuda, Takashi Okura, Kana Maruyama-Fumoto, Satomi Kagota, Y ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 1996-2001
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
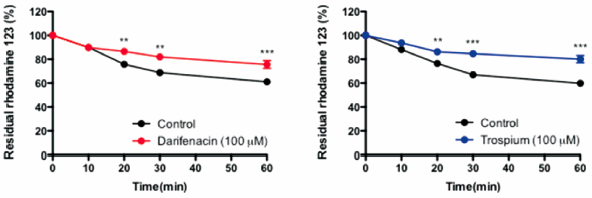
ジャーナル フリー HTMLWe evaluated the effects of anticholinergic drugs principally used for the therapy of overactive bladder (OAB) on the activity of P-glycoprotein, an efflux transport protein, in Caco-2 cells. The time-dependent changes in the fluorescence of residual rhodamine 123, a P-glycoprotein activity marker, in the apical region of Caco-2 cells were measured in the presence of anticholinergic drugs using time-lapse confocal laser scanning microscopy. The effect of anticholinergic drugs on human P-glycoprotein ATPase activity was also measured. The fluorescence of residual rhodamine 123 in untreated Caco-2 cells decreased over time. The gradual decrease in the fluorescence was significantly inhibited by treatment with cyclosporine A, darifenacin, and trospium. In contrast, oxybutynin, N-desethyl-oxybutynin (DEOB), propiverine, and its active metabolites (M-1, M-2), imidafenacin, solifenacin, or tolterodine had little effect on the efflux of rhodamine 123. P-Glycoprotein ATPase activity was increased by darifenacin. Darifenacin and trospium reduced the rhodamine 123 transfer across the apical cell membrane. These data suggest that darifenacin and trospium interact with P-glycoprotein. Additionally, darifenacin influenced P-glycoprotein ATPase activity. These results suggest that darifenacin may be a substrate of P-glycoprotein. This study is the first paper to test simultaneously the effects of 10 anticholinergic drugs used currently for the therapy of OAB, on the P-glycoprotein.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (556K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (556K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Deokbae Park2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2002-2008
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLMetformin, a widely prescribed anti-diabetic drug, also exerts anti-cancer effects in different types of cancers. Although a number of molecular mechanisms have been suggested, the metabolic features underlying metformin’s anti-cancer activity is not fully understood enough. Because cancer cells have been known to prefer inefficient aerobic glycolysis to support their proliferation, it is important to clarify by which metformin affects metabolism to suppress the proliferation of cancer cells. Here, we report the metabolic changes induced by metformin and its relevance to the induction of apoptosis in H4II rat hepatocellular carcinoma cells. H4IIE cells were treated with metformin and other reagents in culture media with various nutritional compositions. Glutamine as well as pyruvate enhanced the viability of H4IIE cells in glucose-deprived conditions. Protective effects of glucose and pyruvate were comparable at same concentrations (5 mM). Metformin induced apoptosis irrespective of any nutritional conditions. Glucose consumption and lactate production were stimulated by metformin. Inhibition of glycolysis by 2-deoxyglucose suppressed the metformin-induced lactate production but additively enhanced metformin’s pro-apoptotic effect. These results indicate that metformin does not interfere but accelerate glycolysis. Unexpectedly, the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was markedly stimulated by metformin. A potent antioxidant, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) suppressed all pro-apoptotic changes as well as ROS generation induced by metformin. Taken together, metformin does not interfere with glycolysis but promotes apoptosis by enhancing oxidative stress.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1332K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1332K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hikari Iba, Takuya Watanabe, Kanae Matsuzawa, Maki Saimiya, Masako Tan ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2009-2015
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe traditional herbal medicines yokukansan (YKS) and yokukansankachimpihange (YKSCH) are prescribed for neurosis, insomnia or night crying and irritability in children. YKSCH comprises YKS and two additional herbs, a chimpi and a hange, and is used to treat digestive function deficiencies. However, the differences between the effects of YKS and YKSCH on brain function are unclear. The present study examined the effects of YKS and YKSCH on aggressive behavior in mice reared under a social isolation (SI) condition. Mice were housed individually for 6 weeks. YKS and YKSCH were administered orally for 2 weeks before aggression tests. SI increased aggressive behavior against naïve mice, and YKS, but not YKSCH, significantly attenuated this aggressive behavior. Because serotonin (5-HT)2A and 5-HT3A receptor antagonists are reported to have anti-aggressive effects, the mRNA levels of these receptors were examined. YKS attenuated the SI-induced increase in 5-HT2A and 5-HT3A receptor mRNA in the amygdala. On the other hand, YKSCH attenuated the SI-induced increase in 5-HT1A receptor mRNA. YKS and YKSCH did not affect 5-HT and its metabolite 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid content in the amygdala. However, YKSCH increased the mRNA level of arginine vasopressin (AVP), which is a neuropeptide that has been implicated in aggression, in the amygdala. These results suggest that YKS ameliorates aggressive behavior by decreasing 5-HT2A and 5-HT3A receptor expression. The YKSCH-induced increase in AVP may disrupt the anti-aggressive effect of YKS. YKS may be more effective than YKSCH for treating irritability if digestive function deficiencies are not considered.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (504K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (504K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Norihito Kanai, Aiko Shono, Akifumi Kushiyama, Manabu Akazawa2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2016-2023
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLMedication therapy management by tracking patients with risk of progression to type 2 diabetes has not been investigated in Japan. We aimed to assess the characteristics of these patients and their early medications. Claims (n = 190507) and health checkup data (n = 106984) between April 2005 and March 2015 in Japan were selected. We selected patients aged ≥40 years with fasting plasma glucose levels of 100–125 mg/dL or glycated hemoglobin A1c values of 5.7–6.4%. The early-medication group comprised patients who received hypoglycemic medications within 6 months after their first clinic visit, while the no-medication group comprised patients who did not receive any hypoglycemic medications. Main outcome measures were characteristics and early hypoglycemic medications of patients at risk of progression to type 2 diabetes. Of 5676 individuals, hypoglycemic medications were initiated in 276 (5%). The early-medication group had a higher proportion of individuals with a body mass index ≥25 kg/m2 and current smokers and drinkers than the no-medication group. Approximately 83% of patients in the early-medication group were prescribed a single hypoglycemic medication, and since 2010, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors were prescribed to one-third of these patients. In our population, early hypoglycemic medication was initiated within 6 months of the first clinic visit, indicating that initiation took place earlier than recommended by current guidelines. Early hypoglycemic medications, especially dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors with low risks of hypoglycemia, might be prescribed based on patient characteristics. Further epidemiological studies are needed to confirm the suitability of early hypoglycemic medication.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (657K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (657K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masashi Muroi, Norihiko Ogura, Hikaru Mizumura, Jun Aketagawa, Toshio ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2024-2037
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/10/05ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Assays using lysate reagents prepared from horseshoe crab hemocyte extract (limulus amoebocyte lysate, LAL) are commonly and widely used to detect and measure endotoxin in parenteral drugs and medical devices. However, lysate reagents suffer from lot-to-lot variations leading to possible fluctuations in testing. Also, this continued usage of lysate reagents leads to the possible decline of the horseshoe crab population. Recently, a new recombinant chromogenic reagent, PyroSmart, consisting of three recombinant factors was introduced to the market. There are now three recombinant products; two with recombinant factor C reagents and PyroSmart with the complete recombinant LAL system. We evaluated the applicability of the reagent to the harmonized bacterial endotoxins test in the United States, European and Japanese pharmacopeias. The recombinant product showed equivalent potency of thirteen endotoxins from different bacterial strains to conventional chromogenic lysate reagents as long as their assay modes are identical. All analytical characteristics or assay parameters of the reagent satisfied the acceptance criteria which are set for the use for the bacterial endotoxins test filed in the pharmacopeias. All of 109 parenteral drugs tested can be measured with PyroSmart within respective maximum allowable dilutions. The lot-to-lot variation in recovery of endotoxin added in the parenteral drugs for PyroSmart was equal to or less than those of six limulus lysate reagents. In conclusion, the present study suggests that the recombinant reagent, PyroSmart, provide a good alternative to the LAL reagents with better lot-to-lot variation.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (607K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (607K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Rodi Abdalkader, Johan Unga, Fumiyoshi Yamashita, Kazuo Maruyama, Mits ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2038-2044
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/09/25ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn this study, we have prepared perfluorohexane (PFH)-based acoustic nanodroplets (PFH-NDs) and evaluated their theranostic characteristics. Nile Red (NR) was incorporated into PFH-NDs as a model of hydrophobic drugs (NR-PFH-NDs). The mean particle diameters of PFH-NDs and NR-PFH-NDs were 205 ± 1.8 nm and 346.3 ± 6 nm, respectively. There was no significant PFH leakage from PFH-NDs during 90 min incubation at 37°C in the presence of 10% rat serum. The in vitro ultrasonography showed that the phase transition of PFH-NDs from liquid droplets to gassed bubbles could be induced by therapeutic low-intensity ultrasound with a frequency of 1 MHz and an intensity of 5 W/cm2. Irradiation of ultrasound in combination with NR-PFH-NDs enhanced uptake of NR in murine adenocarcinoma cells (C26). After intravenous injection of PFH-NDs to mice, PFH gradually disappeared from blood circulation with an elimination half-life of 43.3 min. Intravenous injection of PFH-NDs also resulted in significant contrast enhancement in the mouse carotid artery upon therapeutic low-intensity ultrasound irradiation. These results suggest the potential of PFH-NDs as a novel contrast agent for further theranostic applications.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4559K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4559K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Mari Hara Nakano, Chihiro Udagawa, Arata Shimo, Yasuyuki Kojima, Reiko ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2045-2053
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/10/09ジャーナル フリー HTML
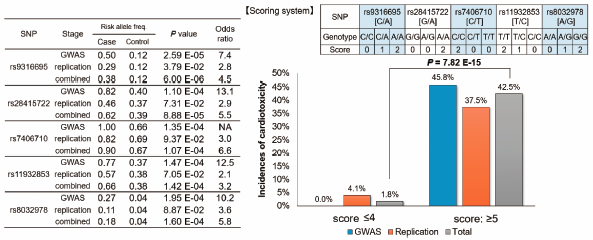
電子付録Trastuzumab has been administered to patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive cancer, however, the cardiotoxicity is identified as one of the life-threatening toxicities. Clinically useful biomarker for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity has been expected to be developed. To identify a novel genetic marker(s) determining the risk of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity, we performed a first genome-wide association study (GWAS) in Japanese population. We enrolled 481 patients who had been treated with trastuzumab and carried out a GWAS using 11 cases (with cardiotoxicity) and 257 controls (without cardiotoxicity). Top 100 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which revealed the smallest p values in GWAS (p = 7.60 × 10−7 − 2.01 × 10−4) were further examined using replication samples consisted of 14 cases and 199 controls. The combined analysis of the GWAS and replication study indicated possible association of five loci with trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity (rs9316695 on chromosome 13q14.3, rs28415722 on chromosome 15q26.3, rs7406710 on chromosome 17q25.3, rs11932853 on chromosome 4q25, and rs8032978 on chromosome 15q26.3, Pcombined = 6.00 × 10−6, 8.88 × 10−5, 1.07 × 10−4, 1.42 × 10−4, 1.60 × 10−4, respectively). Furthermore, we developed a risk prediction model for trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity using the five marker SNPs. The incidence of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity in patients with risk score ≥5 was significantly higher (42.5%) compared to that in patients with score ≤ 4 (1.8%) (p = 7.82 × 10−15, odds ratio = 40.0). These findings suggest the potential to improve the ability of physicians to avoid the trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity for patients with HER2-positive cancer.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2114K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2114K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hiroko Kobayashi, Takeshi Sangawa, Katsuki Takebe, Naomi Motoyoshi, Ta ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2054-2061
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLRNase He1 is a guanylic acid-specific ribonuclease of the RNase T1 family from Hericium erinaceus (Japanese name: Yamabushitake). Its RNA degrading activity is strongly inhibited by Zn2+, similar to other T1 family RNases. However, RNase He1 shows little inhibition of human tumor cell proliferation, unlike RNase Po1, another T1 family RNase from Pleurotus ostreatus (Japanese name: Hiratake). Here, we determined the three-dimensional X-ray crystal structure of RNase He1 in complex with Zn, which revealed that Zn binding most likely prevents substrate entry into the active site due to steric hindrance. This could explain why RNase He1 and other T1 family RNases are inhibited by Zn. The X-ray crystal structures revealed that RNase He1 and RNase Po1 are almost identical in their catalytic sites and in the cysteine residues involved in disulfide bonds that increase their stability. However, our comparison of the electrostatic potentials of their molecular surfaces revealed that RNase He1 is negative whereas RNase Po1 is positive; thus, RNase He1 may not be able to electrostatically bind to the plasma membrane, potentially explaining why it does not exhibit antitumor activity. Hence, we suggest that the cationic characteristics of RNase Po1 are critical to the anti-tumor properties of the protein.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5675K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5675K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masaki Tashiro, Takafumi Naito, Chikoto Yamamoto, Shin-Ya Katoh, Junic ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2062-2068
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
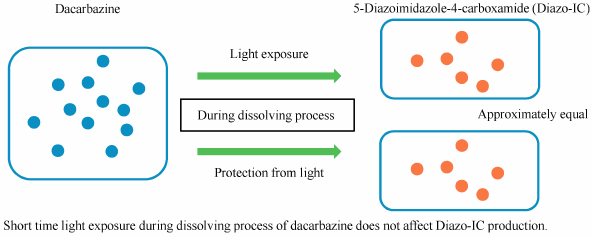
ジャーナル フリー HTMLDacarbazine (DTIC) is converted to the photo-degradation product 4-diazoimidazole-5-carboxamide (Diazo-IC) by light. Diazo-IC production is often responsible for the pain reactions observed during peripheral intravenous infusion of DTIC in clinical settings. Although light shielding during infusion decreases the photo-degradation of DTIC, its usefulness for the preparation of DTIC has not yet been fully clarified. The aim of this study was to investigate the light conditions during the preparation of DTIC solution in the compounding room from the viewpoint of the production amount of Diazo-IC. DTIC solution was prepared in the compounding room. Various light and temperature conditions and dissolving solutions during the preparation were investigated. The amounts of DTIC and Diazo-IC in solutions were determined using an HPLC coupled to UV detection. The photo-degradation of DTIC was estimated by the amount of Diazo-IC. Diazo-IC production in the dissolving solutions increased in a time-dependent manner at 4 and 25°C under light shielding. Light exposure during the dissolving process did not affect the DTIC and Diazo-IC concentrations. Light shielding during dissolution did not alter the Diazo-IC production until 4 h after dilution. In conclusion, short duration light exposure did not affect Diazo-IC production. These findings suggest that light shielding is not needed in the preparation of DTIC in the compounding room from the viewpoint of Diazo-IC production.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (411K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (411K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Setsuo Kinoshita, Tadahaya Mizuno, Megumi Hori, Michiaki Kohno, Hiroyu ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2069-2075
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Proteome profiling based on two-dimensional (2D)-DIGE might be a useful tool for investigating drug-like compounds and the mode of action of drugs. However, obtaining data for profiling requires high labor costs, and it is difficult to control the reproducibility of spot positions because 2D-DIGE usually requires large-size glass plates and spot alignments are greatly affected by the quality of DryStrips and polyacrylamide gels (PAGs). Therefore, we have developed a novel platform by employing small size DryStrips and PAGs, and an image analysis strategy based on dual correction of spot alignment and volume. Our system can automatically detect a large number of consistent spots through all images. Cytosol fractions of HeLa cells treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or bortezomib were analyzed, 1697 consistent spots were detected, and 775 of them were significantly changed with the treatment. Deviations between different days and lot sets of DryStrips and PAGs were investigated by calculating the correlation coefficients. The mean values of the correlation between days and lot sets were 0.96 and 0.94, respectively. Clustering analysis of all the treatment data clearly separated the DMSO or bortezomib treated groups beyond day deviations. Thus, we have succeeded in developing an easy-to-handle 2D-DIGE system that can be a novel proteome profiling platform.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2902K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2902K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Luciana N. Moreira, Grazielle C. Silva, Diógenes V. Câmara, Rodrigo M. ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2076-2082
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The cyclitol bornesitol is the main constituent of the leaves from the antihypertensive medicinal plant Hancornia speciosa. This study aimed to investigate the ability of bornesitol to reduce blood pressure and its mechanism of action. Normotensive Wistar rats were divided into control group and bornesitol groups treated intravenously with bornesitol (0.1, 1.0 and 3.0 mg/kg). Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were recorded in non-anesthetized awake animals. Nitric oxide (NO) and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) were measured in plasma by using colorimetric methods. Vascular reactivity study was performed in rat aorta rings and the involvement of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), calcium-calmodulin complex and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway in the vasodilator effect was investigated. Administration of bornesitol significantly reduced the SBP, increased the plasmatic level of nitrite, and decreased ACE activity in normotensive rats. In the rat aorta, bornesitol induced endothelium-dependent vasodilatation, which was abolished by NOS blockade. While calcium-calmodulin complex inhibition decreased the vasodilator effect of bornesitol, the inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway did not alter it. Bornesitol reduced the blood pressure by a mechanism involving an increased production or bioavailability of NO, inhibition of ACE, and by an endothelium- and NO-dependent vasodilator effect. The present results support the use of bornesitol as an active marker for the cardiovascular activity of Hancornia speciosa.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (824K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (824K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yue Chen, Rui Niu, Yufang Xiang, Ningsheng Wang, Junfeng Bai, Bianling ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2083-2088
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLPharmacovigilance is important to monitor the safety of drugs. There are, however, problems with the quality of adverse drug reaction reports in China. This study aimed to analyze the quality of adverse drug reaction reports in China, identify the factors affecting it, and propose measures to improve it. In our study, the western province of Shaanxi, the central province of Hubei and the eastern province of Jiangsu were chosen as typical, and adverse drug reaction reports from these three provinces from 2015 to 2017 were systematically sampled. The sampling reports were scored and graded to assess their quality. The results showed that only 10.18% were considered high quality in a total of 3429 reports. There were statistically significant differences in quality by year, province, report type, report source, and occupation of the reporter (p < 0.001). Reports from Shaanxi were slightly poorer quality, and “new” and “serious” reports and those from pharmacists were higher quality. Five indicators were particularly poor quality: patient information, adverse drug reaction, reporter information, drug information and vigilance. In conclusion, the quality of adverse drug reaction reports in China still needs improvement. Factors affecting quality included timing, location, report type, report source, and reporter’s occupation. It may be helpful to publicize the importance of monitoring adverse drug reactions and improve the knowledge of reporters.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (329K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (329K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Tomohiro Izumisawa, Tomoyoshi Kaneko, Masakazu Soma, Masahiko Imai, No ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2089-2094
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/09/18ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe pharmacokinetics of vancomycin (VAN) was retrospectively examined based on trough concentrations at large scale to identify pharmacokinetic differences between Japanese hematologic malignancy and non-malignancy patients. Data from 261 hematologic malignancy patients and 261 non-malignancy patients, including the patient’s background, VAN dose, and pharmacokinetics of VAN estimated by an empirical Bayesian method, were collected and analyzed. Our results showed significantly higher values for VAN clearance and shorter elimination half-lives in patients with hematologic malignancies than non-malignancy patients. In addition, multiple regression analysis under adjusting for confounding factors by propensity score, showed that VAN clearance significantly increased in relation to hematologic malignancies. In conclusion, since in hematologic cancer patients VAN clearance is increased, the blood concentration of VAN becomes lower than expected and this may contribute to the survival of resistant bacteria when VAN is administered at low doses. These results suggest that early monitoring of VAN levels in hematologic cancer patients might be recommended to maintain desired effects without side-effects.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (363K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (363K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hiroki Ishikawa, Satoshi Ino, Takuji Nakashima, Hirotaka Matsuo, Yōko ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2095-2101
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
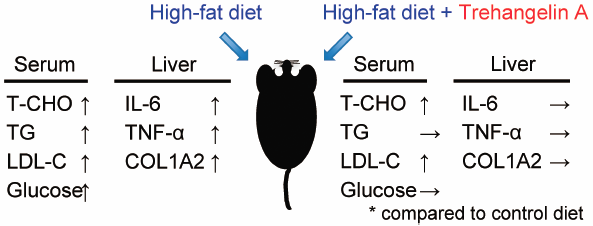
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe purpose of this study is to determine whether or not trehangelin A (THG-A) is effective in treating the metabolic clinical condition caused by a high-fat diet. The body weight, epididymal adipose volume, alanine transaminase (ALT), total-cholesterol (T-CHO), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and glucose concentrations in serum increased in mice fed a high-fat diet compared to mice fed a control diet. On the other hand, adiponectin level in serum of mice fed a high-fat diet decreased compared to that of control mice. When mice fed a high-fat diet were intraperitoneally administered THG-A of 20 mg/kg three times per week, the levels of TG and glucose in serum were significantly reduced compared to those fed high-fat without THG-A. Interestingly, the levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in serum were increased by THG-A administration in both mice fed a control diet and those fed high-fat diet. The decreased level of adiponectin by a high-fat diet was also recovered by THG-A treatment. The liver expression of mRNA from pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, were significantly increased in mice fed a high-fat diet compared to those fed a control diet. However, the increased IL-6 levels in mice fed a high-fat diet were significantly suppressed by THG-A treatment. Furthermore, the increased expression of TNF-α mRNA or COL1A2 mRNA by a high-fat diets tended to be decreased in mice treated with THG-A. These results show that THG-A treatment attenuates the progression of metabolic clinical conditions, suggesting its potential efficacy against obesity-related metabolic disorders.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3406K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3406K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yoshihisa Yamamoto, Rie Yamauchi, Shuji Ohno, Kazunori Asai, Toshiro F ...2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2102-2108
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
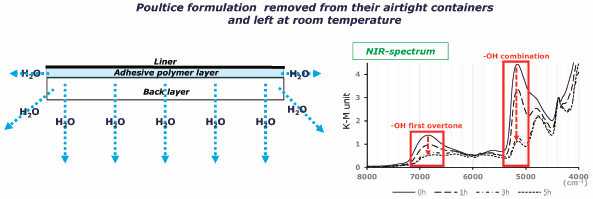
電子付録The poultice formulation is a patch containing a large amount of water. It is known that the water contained in the adhesive polymer layer (ADPL) of poultice affects the cooling sensation and skin permeability of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). In this study, we evaluated the relationship between the water content in a ketoprofen poultice formulation and the amount of time the poultice was left out at room temperature after removal from the airtight container, as well as the influence of the decreasing water content on the skin permeability of the API. After removing the poultice from the container for 1 h, the mass of the ADPL decreased by approximately 40%. When the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum of the ADPL of poultice was measured, the peaks reflecting the hydroxyl group were attenuated depending on the time left out at room temperature. It is suggested that the changes in the mass and NIR spectrum of the ADPL are caused by the change in the water content. Moreover, when the permeability of API was evaluated on hairless mouse skin, the cumulative skin permeation amount and flux decreased, while the lag time was prolonged as the time left out increased. These results suggest that the skin permeability of the API is impaired by water evaporation and that maintaining the water in the ADPL in poultice is very important from not only the viewpoint of cooling sensation, tackiness and moisturizing but also the skin permeability of the API.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (709K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (709K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Yuki Ishiura, Hanako Ishimaru, Tadashi Watanabe, Masahiro Fujimuro2019 年 42 巻 12 号 p. 2109-2112
発行日: 2019/12/01
公開日: 2019/12/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLPrimary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is a rare subtype of non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma and is caused by Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) in immunosuppressed patients. PEL is an aggressive lymphoma and is frequently resistant to conventional chemotherapies. Sulforaphane (SFN), a natural compound found in cruciferous vegetables and broccoli sprouts, modulates signaling pathways and epigenetic gene expression. However, the anti-proliferative effects of SFN on PEL cells and the underlying mechanisms have not been identified. Here, we found that SFN decreased the viability of KSHV-infected PEL cells compared to KSHV-uninfected B-lymphoma cells. The anti-proliferative effects of SFN on PEL cells were mediated by apoptosis with activating caspases. In addition, SFN inhibited the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) and AKT in PEL cells. We also showed that p38MAPK and AKT inhibitors reduced PEL cell growth. The constitutive and/or transient activation of p38MAPK and AKT signaling are necessary for the survival and proliferation of PEL cells. Our data and previous literature indicate that SFN represses the phosphorylation of p38MAPK and AKT, which results in PEL cell apoptosis. Moreover, we investigated whether MG132 or sangivamycin (Sangi) in combination with SFN potentiated the cytotoxic effects of SFN on PEL cells. Compared to treatment with SFN alone, the addition of MG132 or Sangi enhanced the cytotoxic activity of SFN in a synergistic manner. In conclusion, the anti-proliferative effects of SFN indicate its potential as a new substance for the treatment of PEL.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1162K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1162K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|