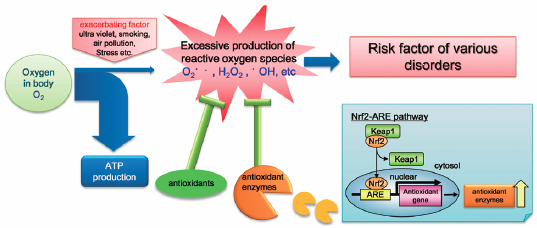
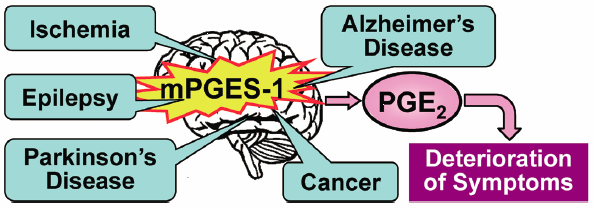
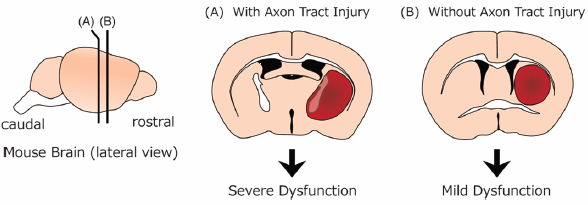
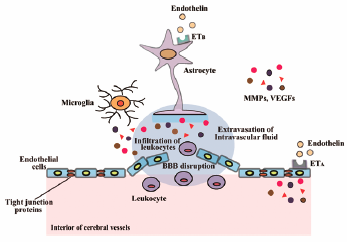
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 547
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (151K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 548-552
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (395K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 553-556
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (518K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 557-563
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (613K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 564-568
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (951K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 569-575
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1695K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 576-582
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/02/03PDF形式でダウンロード (2114K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 583-593
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/02/10PDF形式でダウンロード (3683K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 594-597
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 594-597
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
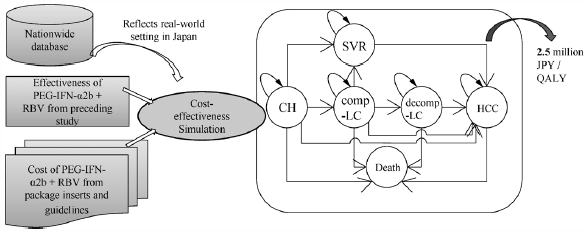
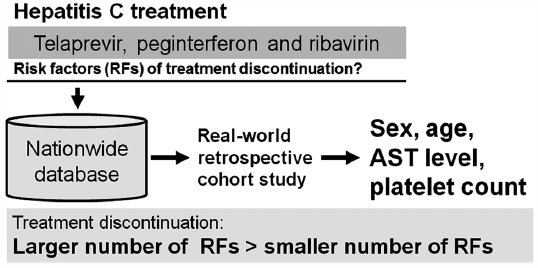
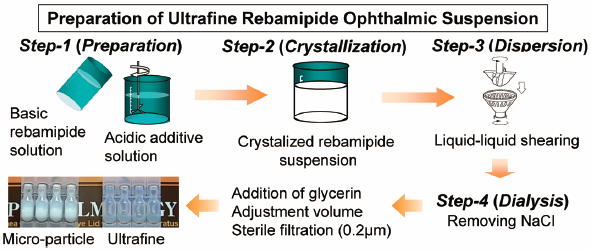
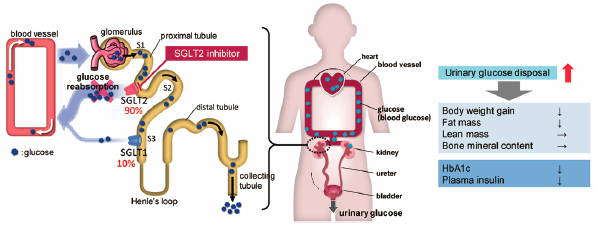
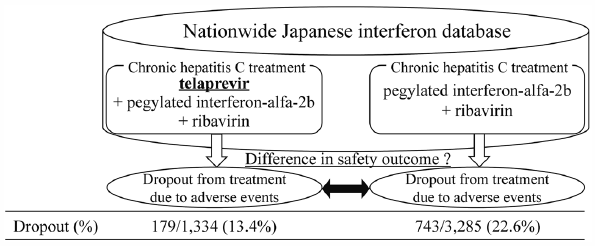
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/02/15Editor's pickEconomic evaluation has been recently carried out using real-world data instead of clinical trial data. Akutagawa et al. conducted a cost-outcome description based on a nationwide registry providing information on hepatitis treatment in Japan and estimated the utility of the analysis. Specifically, they evaluated the cost-outcome description of a 48-week peginterferon plus ribavirin treatment in patients infected by the hepatitis C virus. Simulations were based on a Markov model. After setting the cohorts using data from the registry, and assuming a societal perspective for the calculation of costs, they estimated 2.5 million JPY per quality-adjusted life years (QALY) for treatments over a 10-year period. They analyzed patients’ statistics at each disease stage using their registry data and calculated the costs. Their results reflect more closely a real-world clinical situation as compared to the widely used clinical trial method.
PDF形式でダウンロード (320K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 598-609
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3169K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 610-615
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (7136K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 616-620
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (335K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 621-629
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (737K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 630-637
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1619K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 638-644
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (5672K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 645-649
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/02/17PDF形式でダウンロード (336K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 650-657
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1276K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 658-664
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3752K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 665-674
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (6646K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 675-680
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (387K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 681-686
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (479K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 687-692
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/02/09PDF形式でダウンロード (336K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 693-697
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3853K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 698-702
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (440K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 703-710
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (658K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 711-715
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3733K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 716-721
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3468K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 722-725
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (467K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 726-728
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (279K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 729-732
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (621K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2017 年40 巻5 号 p. 733-737
発行日: 2017/05/01
公開日: 2017/05/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2017/02/23PDF形式でダウンロード (486K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|