42 巻, 3 号
選択された号の論文の32件中1~32を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Current Topics - Drug Discovery: Recent Progress and the Future
-
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 303
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (154K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Current Topics: Reviews
-
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 304-311
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3367K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 312-318
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (924K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 319-326
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (5195K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 327-336
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (796K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 337-342
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1409K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 343-347
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (621K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Current Topics: Regular Article
-
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 348-353
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (492K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Communication to the Editor
-
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 354-356
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (912K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Regular Articles
-
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 357-364
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1752K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 365-372
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (6471K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 373-378
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2018/12/28PDF形式でダウンロード (438K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 379-388
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1230K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 389-393
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (771K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 394-400
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2018/12/27PDF形式でダウンロード (1614K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 401-410
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (3800K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 411-416
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1247K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 417-423
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/01/10PDF形式でダウンロード (839K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 424-431
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1082K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 432-441
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2137K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 442-447
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2296K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 448-452
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 448-452
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
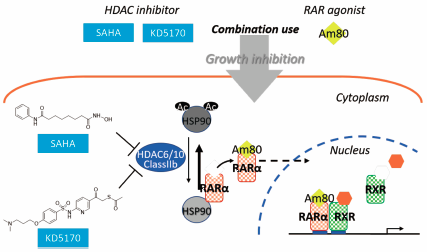
Editor's pickThe growth-inhibitory effects of Am80 (tamibarotene), a specific retinoic acid receptor (RAR) α/β agonist, in combination with a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) on androgen receptor positive or negative prostate cancer cell lines were investigated. Ishigami-Yuasa et al. found that the combination therapy of Am80 and SAHA showed an enhanced growth-inhibitory effect on LNCaP cells. Studies with various HDAC isotype-selective inhibitors indicated that the Class IIb HDACs, especially HDAC6, had significant roles in the enhanced effect of the combination. Thus, dual targeting of Class IIb HDAC and RARα would be useful therapeutic strategy for prostate cancer.
PDF形式でダウンロード (707K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 453-461
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/01/10PDF形式でダウンロード (3930K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 462-467
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2018/12/26PDF形式でダウンロード (760K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 468-474
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2057K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 475-480
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2018/12/28PDF形式でダウンロード (1238K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 481-488
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (825K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 489-495
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2019/01/10PDF形式でダウンロード (919K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Notes
-
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 496-500
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2973K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 501-506
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (499K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 507-511
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (482K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2019 年 42 巻 3 号 p. 512-515
発行日: 2019/03/01
公開日: 2019/03/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2018/12/20PDF形式でダウンロード (298K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|