巻号一覧

39 巻, 1 号
選択された号の論文の19件中1~19を表示しています
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Reviews
-
Shin-ya Morita2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 1-24
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLIncreased levels of apolipoprotein B (apoB)-containing lipoproteins, such as low density lipoproteins (LDL) and chylomicron remnants, are associated with the development of atherosclerosis. Chylomicrons containing apoB-48 are secreted from the intestine during the postprandial state, whereas very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) containing apoB-100 are constitutively formed in the liver. Chylomicron remnants and VLDL remnants are produced by the lipoprotein lipase-mediated lipolysis of triglycerides, which is activated by apolipoprotein C-II bound on the particle surfaces. The hepatic uptake of these remnants is facilitated by apolipoprotein E (apoE), but is inhibited by apolipoproteins C-I, C-II and C-III. In the plasma, VLDL remnants are further converted into LDL by the hydrolysis of triglycerides. ApoB-100 is responsible for the hepatic uptake of LDL. LDL receptor, LDL receptor-related protein and heparan sulfate proteoglycans are involved in the hepatic clearance of lipoproteins containing apoB-100 and/or apoE. The subendothelial retention and modification of apoB-containing lipoproteins are crucial events in the initiation of atherosclerosis. In the subendothelium, the uptake of modified lipoproteins by macrophages leads to the formation of foam cells storing excess amounts of cholesteryl esters and subsequently to apoptosis. This review describes the current knowledge about the metabolism and modification of apoB-containing lipoproteins involved in dyslipidemia and atherogenesis. In particular, I focus on the effects of apolipoproteins, lipid composition and particle size on lipoprotein metabolism and on the roles of cholesterol, sphingomyelinase and apoB denaturation in macrophage foam cell formation and apoptosis. A detailed understanding of these mechanisms will help to develop new therapeutic strategies. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5810K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5810K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shinta Saito, Noritaka Adachi2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 25-32
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLGene targeting via homologous recombination, albeit highly inefficient in human cells, is considered a powerful tool for analyzing gene functions. Despite recent progress in the application of artificial nucleases for genome editing, safety issues remain a concern, particularly when genetic modification is used for therapeutic purposes. Therefore, the development of gene-targeting vectors is necessary for safe and sophisticated genetic modification. In this paper, we describe the effect of vector structure on random integration, which is a major obstacle in efficient gene targeting. In addition, we focus on the features of exon-trapping-type gene-targeting vectors, and discuss a novel strategy for negative selection to enhance gene targeting in human cells.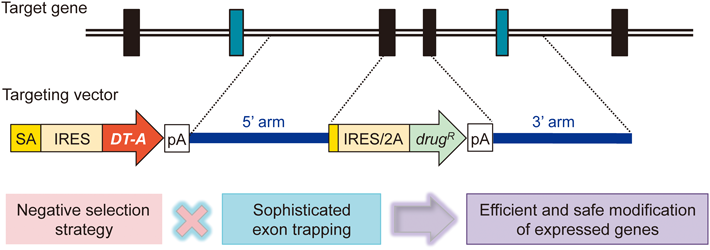 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (766K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (766K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Regular Articles
-
Hiroyasu Sakai, Ken Sato, Yuki Kai, Yoshihiko Chiba, Minoru Narita2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 33-41
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/11/14ジャーナル フリー HTMLRecently the global expression of taste 2 receptors (TAS2Rs) on smooth muscle cells in human airways was demonstrated. Here, the effects of agonists of taste receptor, type 2, denatonium and 6-n-propyl-2-thiouracil, on smooth-muscle contraction were examined in the rat and mouse. Contractions induced by carbachol (CCh), high K+, and sodium fluoride, but not calyculin-A, were inhibited significantly in the presence of a TAS2R agonist in the bronchial smooth muscle of mice. The contraction induced by CCh was inhibited by TAS2R agonists in ileal smooth muscle. Phenylephrine-induced contraction was also inhibited by TAS2R agonists in aortic smooth muscle. Gastrointestinal motility and blood pressure were attenuated by administration of TAS2R agonists in vivo. These findings suggest that TAS2R may be receptor for endogenous biologically active substances as well as for bitter tastes on the tongue. TAS2R signaling could be employed in the development of anti-asthmatic, anti-spasmodic, and anti-hypertensive drugs. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1817K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1817K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yanan Sun, Mengshu Wang, Bingxue Sun, Feng Li, Shubo Liu, Yong Zhang, ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 42-48
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe purpose of this study was to investigate the gastrointestinal stability of exenatide to determine the key factor(s) contributing to peptide degradation during the oral delivery process. The effects of pH and various digestive enzymes on the degradation kinetics of exenatide were determined. Moreover, the degradation clearances of peptide were also examined using rat everted intestinal rings and intestinal homogenates from various intestinal locations. Exenatide was comparatively stable within a pH range of 1.2–8. However, obvious degradation was observed in the presence of digestive enzymes. The order of enzymes, in terms of ability to degradate exenatide, was chymotrypsin>aminopeptidase N>carboxypeptidase A>trypsin>pepsin. Chymotrypsin showed the greatest ability to degrade exenatide (half-life t1/2, 5.784×10−2 h), whereas aminopeptidase N and carboxylpeptidase A gave t1/2 values of 3.53 and 10.16 h, respectively. The degradation of exenatide was found to be peptide concentration- and intestinal site-dependent, with a lower clearance in the upper part of the duodenum and the lower part of the ileum. When using intestinal homogenates as enzyme sources, the order, in terms of peptide degradation ability, was ileum>jejunum>duodenum. However, no significant difference was observed in the remaining peptide concentrations throughout 2 h of incubation, which may be due to the involvement of cytosolic enzymes. These results revealed key factors contributing to peptide degradation, and suggest that the inhibition of chymotrypsin and site-specific delivery of exenatide might be advantageous in overcoming metabolic obstacles during its oral delivery. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (714K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (714K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hitoshi Shimomura, Rina Nogami, Ayako Shigeno, Shuji Shimada, Takao Ao ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 49-53
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLRifampicin (RFP; 30 mg/kg) was orally administered to fasted or fed rats using ultrapure water as the vehicle, and the influence of food on its pharmacokinetics was investigated. To examine the influence of intragastric pH and RFP solubility, similar experiments were performed using 0.1 M HCl (pH 1.0), 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), or 10% Tween 80 vehicles. Plasma RFP concentrations were measured by HPLC-UV for 24 h. The administration of RFP to fed rats in ultrapure water (10% dissolved) resulted in a significant 40% reduction in the maximum plasma drug concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration–time curve (AUC0–24), as compared with fasted rats (p<0.05). RFP administration in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (10% dissolved) produced approximately 25% lower Cmax and AUC0–24 values, as compared with those achieved by RFP in ultrapure water in fasted rats. The administration of RFP in 0.1 M HCl (100% dissolved) to fasted rats increased the AUC0–24 by approximately 1.8-fold, compared with ultrapure water, suggesting that increasing RFP solubility increased its absorption. The 10% Tween 80 vehicles (60% dissolved) enhanced the absorption of RFP to a similar level as observed when using 0.1 M HCl solution, suggesting that both the improvement in solubility and P-glycoprotein inhibition by Tween 80 increased the absorption. This study suggested that RFP solubility in gastrointestinal fluid may be an important determinant of absorption and that it would be beneficial to change the timing of RFP administration to patients with insufficient clinical outcomes by administration after a meal.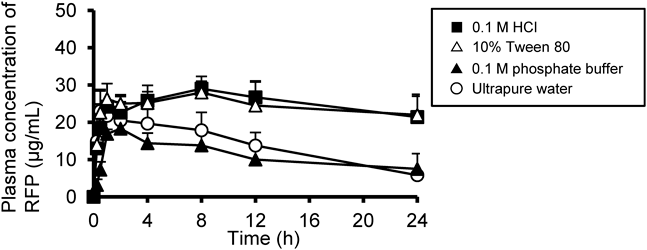 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (345K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (345K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Pichanan Intayoung, Pornngarm Limtrakul, Supachai Yodkeeree2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 54-61
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/10/23ジャーナル フリー HTMLCrebanine, an aporphine alkaloid, displays various biological activities such as anticancer and antimicrobial activities. In this study, we further investigated the suppressive effect of crebanine on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced expression of proinflammatory mediators and the molecular mechanisms underlying these activities in RAW264.7 macrophages. Crebanine inhibited the production of proinflammatory cytokines including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Moreover, crebanine suppressed LPS-induced inducible nitric oxide (iNO) and prostaglandin E2 and reduced the expression of iNO synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in RAW264.7 cells. Crebanine suppressed LPS-induced phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including extracellular signaling-regulated kinase 1/2, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling. In addition, the specific inhibitor of MAPKs and Akt reduced the expression of IL-6 and NO production in LPS-induced macrophages. Furthermore, crebanine inhibited LPS-induced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation by reducing the phosphorylation of p65 at Ser536 but not the p65 translocation to the nucleus and inhibitory factor kappa B alpha degradation. Crebanine also suppressed phosphorylation and nucleus translocation of activator protein-1 (AP-1). These observations suggest that the antiinflammatory properties of crebanine may stem from the inhibition of proinflammatory mediators via suppression of the NF-κB, AP-1, MAPKs, and Akt signaling pathways. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1357K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1357K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yoko Idota, Yumi Kogure, Takako Kato, Mana Ogawa, Shoko Kobayashi, Chi ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 62-67
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLWe examined whether calcium alginate (Ca-Alg) reduces blood cholesterol levels in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. First, we examined taurocholate adsorption in vitro by various types of sodium alginate (Na-Alg). High molecular-weight, guluronic acid-rich Na-Alg showed the greatest adsorption of taurocholate, and therefore the corresponding Ca-Alg was chosen for the in vivo study. Rats were fed a high-cholesterol diet or a Ca-Alg-containing diet for 2 weeks. Body weight and diet intake were measured, and the general condition of the animals was monitored during this period. After 14 d, the plasma concentration of cholesterol, portal plasma concentration of bile acid, and bile acid in feces were measured. The plasma concentration of cholesterol was significantly reduced in rats fed a 2% Ca-Alg-containing diet. Furthermore, the portal concentration of bile acid was significantly lowered in the 2% Ca-Alg group. A tendency for a Ca-Alg concentration-dependent increase in fecal excretion of bile acid was also seen, although it was not statistically significant. While several changes in biochemical parameters and histopathological findings were observed, all the values remained within the physiological range. These results indicate that Ca-Alg is effective in reducing plasma cholesterol. A possible mechanism would be enhanced fecal excretion of bile acid due to reduced intestinal reabsorption, which in turn might stimulate bile acid synthesis from cholesterol in the liver, leading to a decrease in plasma cholesterol. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2816K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2816K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Nobuyasu Yamaguchi, Takashi Baba, Tomoaki Ichijo, Yuka Himezawa, Kanam ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 68-77
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLApproximately 180 t/km2 of Asian dust particles are estimated to fall annually on Beijing, China, and there is significant concern about the influence of microbes transported by Asian dust events on human health and downwind ecosystems. In this study, we collected Asian dust particles in Beijing, and analyzed the bacterial communities on these particles by culture-independent methods. Bacterial cells on Asian dust particles were visualized first by laser scanning microscopy, which demonstrated that Asian dust particles carry bacterial cells to Beijing. Bacterial abundance, as determined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR), was 108 to 109 cells/g, a value about 10 times higher than that in Asian dust source soils. Inter-seasonal variability of bacterial community structures among Asian dust samples, as compared by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP), was low during the Asian dust season. Several viable bacteria, including intestinal bacteria, were found in Asian dust samples by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). Clone library analysis targeting 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequences demonstrated that bacterial phylogenetic diversity was high in the dust samples, and most of these were environmental bacteria distributed in soil and air. The dominant species in the clone library was Segetibacter aerophilus (Bacteroidetes), which was first isolated from an Asian dust sample collected in Korea. Our results also indicate the possibility of a change in the bacterial community structure during transportation and increases in desiccation-tolerant bacteria such as Firmicutes.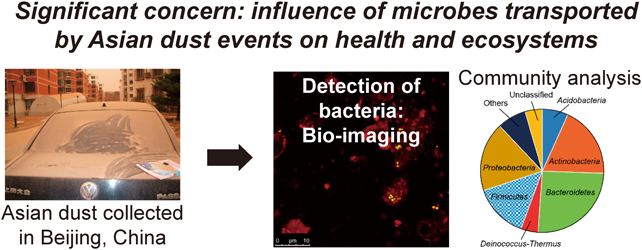 Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4866K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4866K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yukiko Sakakibara, Miki Katoh, Yuya Kondo, Masayuki Nadai2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 78-83
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLUridine 5′-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) catalyzes a major phase II reaction in a drug-metabolizing enzyme system. Although the UGT1A subfamily is expressed mainly in the liver, it is also expressed in the brain. The purpose of the present study was to elucidate the effect of β-naphthoflavone (BNF), one of the major inducers of drug-metabolizing enzymes, on Ugt1a6 and Ugt1a7 mRNA expression and their glucuronidation in the rat brain. Eight-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were treated intraperitoneally with BNF (80 mg/kg), once daily for 7 d. Ugt1a6 and Ugt1a7 mRNA expression increased in the cerebellum and hippocampus (Ugt1a6: 2.1- and 2.3-fold, respectively; Ugt1a7: 1.7- and 2.8-fold, respectively); acetaminophen glucuronidation also increased in the same regions by 4.1- and 2.7-fold, respectively. BNF induced Ugt1a6 and Ugt1a7 mRNA expression and their glucuronidation, and the degree of induction differed among 9 regions. BNF also upregulated CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP1B1 mRNAs in the rat brain. Since the aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway was activated by BNF, it is indicated that Ugt1a6 and Ugt1a7 were induced via AhR in the rat brain. This study clarified that Ugt1a6 and Ugt1a7 mRNA expression and their enzyme activities were altered by BNF, suggesting that these changes may lead to alteration in the pharmacokinetics of UGT substrate in rat brain. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (848K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (848K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Masaki Kumondai, Hiroki Hosono, Kazuhiko Orikasa, Yoichi Arai, Tomio A ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 84-89
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLSeveral of the procarcinogens inhaled in tobacco smoke, the primary risk factor for bladder cancer, are activated by CYP2A6. The association between the whole-gene deletion of CYP2A6 (CYP2A6*4) and a reduced risk of bladder cancer was suggested in Chinese Han smokers. However, there is no evidence for association between the risk of bladder cancer and CYP2A6 genotypes in the Japanese population. Using genomic DNA from smokers of the Japanese population (163 bladder cancer patients and 116 controls), we conducted a case-control study to assess the association between CYP2A6 polymorphisms and the risk of bladder cancer. Determination of CYP2A6 genotypes was carried out by amplifying each exon of CYP2A6 using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Sanger sequencing. The CYP2A6*4 allele was identified by an allele-specific PCR assay. Bladder cancer risk was evaluated using the activity score (AS) system based on CYP2A6 genotypes. The odds ratios (95% confidence interval) for the AS 0, AS 0.5, AS 1.0, and AS 1.5 groups were 0.46 (0.12–1.83), 0.43 (0.15–1.25), 0.86 (0.40–1.86), and 1.36 (0.60–3.06), respectively. In conclusion, although decreased CYP2A6 AS tended to reduce the risk of bladder cancer in Japanese smokers, no significant association was recognized in this population. However, given the relatively small size of the sample, further study is required to conclude the lack of a statistically significant association between CYP2A6 genotypes and the risk of bladder cancer. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (312K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (312K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Myoung-schook Yoou, Mu Hyun Jin, So Young Lee, Sang Hwa Lee, Byunghyun ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 90-96
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLCordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) is one of the active components isolated from Cordyceps militaris, and has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-aging, and anti-cancer effects. Mast cell-derived thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of allergic inflammatory reactions. Here, we investigated the regulatory effect and mechanisms of cordycepin on the expression of TSLP in the human mast cell line, HMC-1 cells, and in the human keratinocyte cell line, HaCaT cells. Cordycepin significantly decreased the production and mRNA expression of TSLP through the inhibition of caspase-1 and nuclear factor-κB activation. Cordycepin also significantly reduced the phosphorylation of receptor-interacting protein 2 and inhibitory kappa B (IκB) kinase β. Cordycepin significantly decreased the production and mRNA expression of interleukin (IL)-8, IL-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in activated HMC-1 cells. Moreover, cordycepin significantly decreased the levels of TSLP in activated HaCaT cells. Our studies suggest that cordycepin can be applied to the treatment of allergic inflammatory diseases exacerbated by TSLP. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (989K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (989K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Gong Fang, Guocheng Li, Chaohai Pang, Wenxi Li, Dingyong Wang, Chunxia ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 97-103
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/10/15ジャーナル フリー HTMLThis paper describes the ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) of pristimerin from Celastrus orbiculatus. Methanol was the most effective for pristimerin extraction, followed by ethanol, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, and water. To optimize the conditions, the Box–Behnken design, a widely used form of response surface methodology, was used to investigate the effects of parameters on UAE. Several variables, such as extraction time, ultrasonic power, extraction temperature, and solvent-to-solid (S/S) ratio were investigated. The highest extraction yield of 1.843 mg/g was obtained using methanol under optimal conditions with an extraction time of 40 min, ultrasonic power of 105 W, an S/S ratio of 40 mL/g, and an extraction temperature of 52°C. The experimental values under optimal conditions agreed well with the predicted values, suggesting that UAE has good potential as an extraction method for pristimerin from C. orbiculatus. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1234K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1234K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yasushi Ishida, Kosuke Ebihara, Masahiro Tabuchi, Sachiko Imamura, Kyo ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 104-113
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of the traditional Japanese medicine yokukansan (YKS) on the function of dopamine (DA) in the rat nigrostriatal system. Unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions were produced in the rat nigrostriatal system. Despite a marked loss in the striatal immunoreactivity of tyrosine hydroxylase on the lesion side, striatal serotonin (5-HT) immunoreactivity was not affected. Treatment using L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) in conjunction with benserazide for 15 d induced abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) such as locomotive (rotational response), axial, forelimb, and orolingual movements in the lesioned rats. The L-DOPA-induced locomotive and axial, but not forelimb and orolingual, AIMs were significantly increased and prolonged by the pre-administration of YKS. We next investigated the effects of YKS on the production of DA from L-DOPA in 5-HT synthetic RIN 14B cells. RIN 14B cells produced DA and its metabolite, 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT), following L-DOPA treatment. YKS significantly augmented DA production and inhibited its metabolism to 3-MT in a manner similar to the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor entacapone. YKS and some alkaloids (corynoxeine: CX, geissoschizine methyl ether: GM) in Uncaria hook, a constituent herb of YKS, also inhibited COMT activity, indicating that the augmenting effect of YKS on L-DOPA-induced DA production in 5-HT synthetic cells was due to the inhibition of COMT by CX and GM. Our results suggest that YKS facilitates the DA supplemental effect of L-DOPA, and that COMT inhibition by CX and GM contributes, at least in part, to the effects of YKS. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5161K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5161K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Eizo Takahashi, Chiaki Fujinami, Teruo Kuroda, Yasuo Takeuchi, Shin-ic ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 114-120
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録In an attempt to discover inhibitory compounds against pore-forming toxins, some of the major toxins produced by bacteria, we herein examined the effects of four kinds of indolo[3,2-b]quinoline derivatives on hemolysis induced by the aerolysin-like hemolysin (ALH) of Aeromonas sobria and also by the alpha-hemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. The results showed that hemolysis induced by ALH was significantly reduced by every derivative, while that induced by alpha-hemolysis was significantly reduced by three out of the four derivatives. However, the degrees of reduction induced by these derivatives were not uniform. Each derivative exhibited its own activity to inhibit the respective hemolysin. Compounds 1 and 2, which possessed the amino group bonding the naphthalene moiety at the C-11 position of indolo[3,2-b]quinoline, had strong inhibitory effects on the activity of ALH. Compound 4 which consisted of benzofuran and quinoline had strong inhibitory effects on the activity of alpha-hemolysin. These results indicated that the amino group bonding the naphthalene moiety of compounds 1 and 2 assisted in their ability to inhibit ALH activity, while the oxygen atom at the 10 position of compound 4 strengthened its interaction with alpha-hemolysin. These compounds also suppressed the hemolytic activity of the supernatant of A. sobria or A. hydrophila, suggesting that these compounds were effective at the site of infection of these bacteria. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (534K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (534K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kota Naito, Chizuru Tanaka, Manami Mitsuhashi, Hajime Moteki, Mitsutos ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 121-129
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2015/11/14ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe involvement of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) and the 5-HT2 receptor subtypes in the induction of DNA synthesis and proliferation was investigated in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes to elucidate the intracellular signal transduction mechanisms. Hepatocyte parenchymal cells maintained in a serum-free, defined medium, synthesized DNA and proliferated in the presence of 5-HT or a selective 5-HT2B receptor agonist, BW723C86, but not in the presence of 5-HT2A, or 5-HT2C receptor agonists (TCB-2 and CP809101, respectively), in a time- and dose-dependent manner. A selective 5-HT2B receptor antagonist, LY272015 (10−7 M), and a specific phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor, U-73122 (10−6 M), as well as specific inhibitors of growth-related signal transducers—including AG1478, LY294002, PD98059, and rapamycin—completely inhibited 5-HT (10−6 M)- or BW723C86 (10−6 M)-induced hepatocyte DNA synthesis and proliferation. Both 5-HT and BW723C86 were shown to significantly stimulate the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor (EGF)/transforming growth factor (TGF)-α receptor tyrosine kinase (p175 kDa) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 2 on Western blot analysis. These results suggest that the proliferative mechanism of activating 5-HT is mediated mainly through 5-HT2B receptor-stimulated Gq/PLC and EGF/TGF-α-receptor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/ERK2/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways in primary cultured hepatocytes. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2286K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (2286K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Notes
-
Ryo Masuda, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Takaki Koide2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 130-134
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLCell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are attractive tools for delivering macromolecules that have poor membrane permeability, such as antibodies, into cells. However, the major drawback of conventional CPPs is their instability in bodily fluids. We previously reported a novel CPP employing a collagen-like triple-helical structure that exhibited remarkable resistance against serum proteases. Herein, we report the delivery of full-length immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody into cells using a triple-helical CPP. The CPP was conjugated to IgG via a one-pot reaction using 2-iminothiolane as a crosslinking reagent. The triple-helical CPP was less prone to being aggregated and neutralized by serum than was octaarginine, a conventional CPP. However, most of the conjugates were found to be entrapped in endosomes. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (7397K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (7397K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Takaki Koide, Naoyuki Yamamoto, Kazuma B. Taira, Hiroyuki Yasui2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 135-137
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLOrally ingested peptides are generally digested in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and absorbed in the form of oligopeptides. We previously reported that intravenously administered collagen-like triple-helical peptides circulated in the bloodstream and were excreted in their intact forms in urine nearly quantitatively. In the present study, we investigated the fates of orally administered collagen-like peptides in rats. (Pro-Hyp-Gly)10 (Hyp: 4-hydroxyproline), which formed a stable triple-helical structure, was stable in the GI tract, and 72.3±13.0% of the peptide was excreted in the feces. Its recovery ratio was similar to that of all-D-(Pro-Pro-Gly)10 (75.1±15.7%), the indigestible control. In contrast, (Pro-Hyp-Gly)5 and (Pro-Pro-Gly)10, the random coil conformations of which were dominant at body temperature, were not detected in fecal samples, indicating that they were digested by proteases. The high stability of the triple-helical conformation in mammalian bodies suggests the potential use of collagen-like peptides as novel scaffolds of peptide drugs. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (390K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (390K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Noriaki Nagai, Fumihiko Ogata, Naohito Kawasaki, Yoshimasa Ito2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 138-142
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLPrevious studies showed an increased prevalence of cataracts in postmenopausal women. In this study, we investigated changes in the levels of calcium ion (Ca2+) and interleukin (IL)-18, which are factors in cataract development, in the lenses of ovariectomized (OVX) rats, a model of postmenopausal woman. Although the Ca2+ content in the blood of OVX rats increased 1 month after ovariectomy and subsequently decreased, the Ca2+ content in the lenses was unchanged in OVX rats 1–3 months after ovariectomy. The Ca2+-ATPase activity in the lenses of OVX rats peaked 1 month after ovariectomy, and the behavior of Ca2+-ATPase activity in lenses of OVX rats was similar to that of the Ca2+ concentration in the blood. It is possible that hypercalcemia increases the Ca2+ inflow into the lens; however, the enhanced Ca2+-ATPase activity prevents the Ca2+ level from rising. On the other hand, we found that the levels of both IL-18 and interferon (IFN)-γ in the lenses of OVX rats were significantly increased as compared with the lenses of sham (control) rats during the period 1–3 months after surgery. These results suggest that the expression of IFN-γ via IL-18 in the lenses of OVX rats is induced by ovariectomy, and that excessive IL-18 and IFN-γ production in the lenses may be related to cataract development in postmenopausal women. These findings support those of previous studies that assessed lens opacification in postmenopausal women. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (408K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (408K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Kyoko Kobayashi, Wakana Matsuyama, Yuhei Arai, Saho Koizumi, Tatsuya S ...2016 年39 巻1 号 p. 143-147
発行日: 2016/01/01
公開日: 2016/01/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe promotion of fatty acid metabolism, to which peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor (PPAR) α contributes, has been suggested to participate in maintaining the function of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTECs). The loading of fatty acids to PTECs could result in cell inflammation and cell death. A “Kampo” medicine, Boiogito (BO), is used to treat overweight women exhibiting chronic fatigue and edema in the lower extremities or knees. BO improves renal function by reducing the portion of fatty acids, thereby preventing damage to PTECs. In this study, BO and Astragalus Root (AsR), a constituent crude drug of BO, were administered orally to intravenously bovine serum albumin (BSA)-administered mice to evaluate the PPARα–cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) binding protein (CBP) complex binding activity and/or mRNA expression of PPARα, as quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and/or polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Increases in PPARα–CBP complex binding activity and the expression of PPARα mRNA were observed not only in BO-administered mice but also in AsR-administered mice, accompanied by a decrease in the amount of renal fatty acid. Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (533K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Graphical Abstract Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (533K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|