- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1498-1505
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1498-1505
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
Editor's pickAlthough most previous studies in this area used recombinant adiponectin, herein, the author used native high-molecular-weight (HMW) adiponectin purified from human plasma, which is considered the most active form of circulating adiponectin. The current results clearly demonstrate that native HMW adiponectin preferentially inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1β expression but not tumor necrosis factor-α expression by inhibiting the Akt-C/EBPβ inflammatory signaling pathway in macrophages. Furthermore, HMW adiponectin preconditioning is essential for achieving the anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin. Thus, these findings highlight the regulatory mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory function of adiponectin.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1856K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1506-1511
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (6871K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1512-1516
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (841K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1517-1526
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2436K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1527-1534
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/09/07PDF形式でダウンロード (4164K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1535-1547
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1535-1547
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
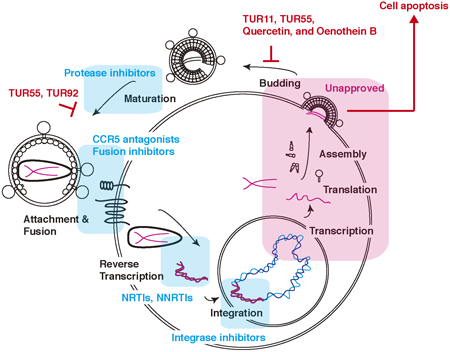
Editor's pickAuthors suggest that plant extracts, including quercetin and oenothein B, reduce the amount of virus in the cell supernatants and induce cytotoxicity in HIV-1-infected T cells but not HTLV-1-infected T cells. The large amount of oenothein B were detected in Onagraceae. Thus, the plant extracts might block the HIV-1 release and kill the HIV-1-infected cells. Consequently, the plant extracts from the plant library of Turkey might be suitable candidates to develop novel anti-retroviral drugs that target the late phase of the HIV-1 life cycle.
PDF形式でダウンロード (4755K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1548-1557
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (1948K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1558-1568
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (8998K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1569-1575
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (5797K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1576-1582
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (997K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1583-1591
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1583-1591
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
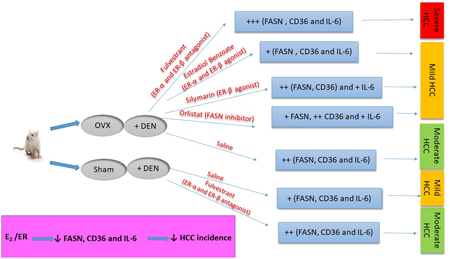
Editor's pickCitrus sudachi is a popular fruit in Tokushima Prefecture, Japan, and its peel contains high amounts of polymethoxyflavones with the most abundant being sudachitin (SDC) followed by demethoxysudachitin (DMSDC). The effects of SDC and DMSDC on the cardiovascular system have not been investigated. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of SDC and DMSDC on vascular tonus and to investigate mechanism of action of SDC using aorta preparations isolated from rats. The results demonstrated that SDC and DMSDC cause endothelial-independent relaxation, and that the mechanism of vasorelaxation by SDC is associated with the enhancement of cAMP- and cGMP-dependent pathways.
PDF形式でダウンロード (976K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1592-1600
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (4506K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1601-1608
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1601-1608
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
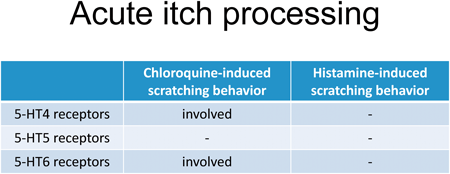
[早期公開] 公開日: 2023/09/16Editor's pickAntidepressants, such as milnacipran, a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, and mirtazapine, a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant attenuate the induction of scratching events by chloroquine (CQ) or histamine. However, it remains unclear whether serotonin or noradrenaline is involved in attenuating effects of these antidepressants. Miyahara and colleagues show that 5-HT4 and 5-HT6 receptors are involved in the amelioration of CQ-induced scratches, but not histamine-induced scratches, engendered by the antidepressants. These findings suggest that 5-HT4, 5-HT5, and 5-HT6 receptors play differential roles in acute pruriceptive processing after administration of CQ or histamine.
PDF形式でダウンロード (668K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1609-1618
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1609-1618
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
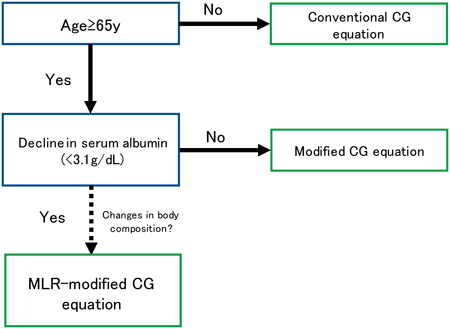
Editor's pickThe authors validated the modified Cockcroft-Gault equation, developed previously for aged-oriented cohort, in a newly obtained dataset and found that good renal function estimates were obtained for patients exceeding 65 years of age. Using statistical analysis, estimates for a subset of patients in this cohort were identified to be inadequate and this deviation from estimates was attributed to a decreased albumin level. A multivariate linear regression estimating equation was developed for this region by incorporating body composition parameters. A flow diagram was proposed to select an appropriate renal function estimating equation particularly for older patients.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1007K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1619-1624
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (6167K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1625-1629
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (865K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1630-1634
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (318K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1635-1638
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (2334K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1639-1642
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (376K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1643-1646
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (567K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
2023 年 46 巻 11 号 p. 1647
発行日: 2023/11/01
公開日: 2023/11/01
PDF形式でダウンロード (149K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|