
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
小林 直弘, 小山 元道, 小林 憲司, 北條 智彦, 秋山 英二原稿種別: 論文
2021 年 85 巻 2 号 p. 49-58
発行日: 2021/02/01
公開日: 2021/01/25
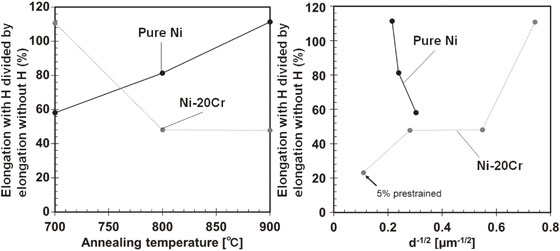
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/12/25ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe grain size effects on the hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of pure Ni and Ni-20Cr alloy were investigated. The hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility was evaluated by tensile testing under electrochemical hydrogen charging. Relative elongation, defined as the elongation under hydrogen charging divided by elongation in air, increased with increasing grain size in pure Ni (the grain size was in the range of 11-22 µm). In contrast, the relative elongation of Ni-20Cr alloy increased with decreasing grain size from 13 to 1.8 µm. Correspondingly, intergranular fracture was suppressed by grain coarsening in pure Ni and grain refinement in the Ni-20Cr alloy. In addition, the intergranular fracture surface in pure Ni showed curved slip lines, and in the Ni-20Cr alloy showed straight line marks. These fractographic features imply that the mechanisms of the hydrogen-assisted intergranular crack growth were different in pure Ni and Ni-20Cr alloy and this can be attributed to the difference in stacking fault energy.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (8147K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (8147K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
福元 健太, 大上 悟, 丹羽 司, 菊池 義治, 赤松 慎也, 中野 博昭原稿種別: 論文
2021 年 85 巻 2 号 p. 59-66
発行日: 2021/02/01
公開日: 2021/01/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/12/18ジャーナル フリー HTMLElectrodeposition of Zn was performed on an Fe electrode at a current density of 50-5000 A·m−2 and a charge of 4 × 104 C·m−2 in an unagitated zincate solution at 313 K containing 0.62 mol·dm−3 of ZnO, 4.0 mol·dm−3 of KOH or NaOH, and organic additives. The effects of KOH and NaOH on the deposition behavior of Zn in solution containing organic additives and the microstructure of the deposits were investigated. In solution containing a quaternary ammonium cation (PQ) and a quaternary ammonium salt with a benzene ring (QA), the current efficiency for Zn deposition at high current density region of 1000 to 5000 A·m−2 to produce the glossy films was higher with KOH than that with NaOH. At high current densities above 1000 A·m−2, Zn deposition approaches the diffusion limitation of ZnO22− ions. With additions of PQ and QA, the diffusion of ZnO22− ions was significantly suppressed, and the degree of suppression was smaller with KOH than that with NaOH. The polarization resistance at 200 A·m−2 investigated by AC impedance revealed that the adsorption ability of PQ and QA onto the cathode was smaller with KOH than that with NaOH. Since the suppression effect of additives on the Zn deposition is smaller with KOH than that with NaOH, the current efficiency for Zn deposition at high current density region is larger with KOH. The upper limit of current density to produce the glossy films was smaller with KOH than that with NaOH, and the spongy thin films were partially observed on the platelets crystals obtained at high current density in KOH solution. The content of C resulting from the additives in deposited Zn was smaller with KOH. These phenomena are attributed to the adsorption ability of PQ and QA onto the cathode being smaller with KOH.
 Fig. 6 Current efficiency for Zn deposition from the KOH and NaOH solutions with and without additives. [● KOH without additive, ▲ KOH with PQ and QA, ○ NaOH without additive, △ NaOH with PQ and QA] Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3299K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Fig. 6 Current efficiency for Zn deposition from the KOH and NaOH solutions with and without additives. [● KOH without additive, ▲ KOH with PQ and QA, ○ NaOH without additive, △ NaOH with PQ and QA] Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3299K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 佐藤 宏和, 足立 望, 戸髙 義一原稿種別: 論文
佐藤 宏和, 足立 望, 戸髙 義一原稿種別: 論文
2021 年 85 巻 2 号 p. 67-74
発行日: 2021/02/01
公開日: 2021/01/25
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe effect of one-pass strain, |±Δε|, on grain refinement was systematically investigated by cyclic - HPT straining with a repetitive deformation process in which positive and negative shear strain are introduced. The steady-state grain size, dss, depended on |±Δε| rather than the given total strain, Σ |±Δε|. The unstable dislocation cell walls formed by positive strain, +Δε, was discomposed by negative strain, −Δε. The stability of dislocation cell wall increased as the number of dislocations introduced by applying |±Δε| in a grain, n, increased. The decrease in n was caused by decreasing +Δε and grain size. It was found that n affected the stability of dislocation cell walls and was an important factor in determining dss.
 Fig. 7 Relationship between the number of dislocations introduced by one-pass strain |±Δε| in one grain n and grain size d. The n at the steady-state grain size dss in c-HPT (|±Δε| < 3) were plotted. Each |±Δε| is indicated by a color in the color bar. Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
Fig. 7 Relationship between the number of dislocations introduced by one-pass strain |±Δε| in one grain n and grain size d. The n at the steady-state grain size dss in c-HPT (|±Δε| < 3) were plotted. Each |±Δε| is indicated by a color in the color bar. Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示Editor's pick2022年新進論文賞
PDF形式でダウンロード (3695K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
北原 学, 松岡 秀明, 浅田 崇史原稿種別: 論文
2021 年 85 巻 2 号 p. 75-83
発行日: 2021/02/01
公開日: 2021/01/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2020/12/25ジャーナル フリー HTMLAutomobile manufacturers are accelerating adoption of spot welding of Advanced High-Strength-Steels (AHSS) sheets to reduce weight of automobile bodies. Rapid evaluation of the hydrogen embrittlement (HE) resistance for the spot-welds of AHSS sheets is required, since it is worried that the HE resistance of the nugget will deteriorate compared to the base metal due to the difference in microstructure caused by rapid cooling and solidification during spot welding. However, evaluation of the HE resistance for the spot-welds have not been established. In this study, we prepared spot-welded specimens using AHSS sheets and performed tensile shear tests with varying tensile rates under hydrogen charging to evaluate the relationship between diffusible hydrogen content and tensile shear strength. As a result, the tensile shear strength of spot welds decreased as the amount of diffusible hydrogen increased. The quasi-cleavage fractured surface and intergranular fractured surface were observed at the nugget and inside the crack generated at the nugget-heat affected zone interface. Furthermore, as the results of crack growth behavior and hydrogen thermal desorption spectroscopy analysis, hydrogen embrittlement in spot welds can be attributed to the stress-induced diffusion of hydrogen and the hydrogen trapped in dislocation and vacancy clusters at the crack tip.
 Illustration of the method used to evaluate hydrogen embrittlement resistance and the relationship between diffusible hydrogen content, tensile shear strength and fracture surfaces. Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4759K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Illustration of the method used to evaluate hydrogen embrittlement resistance and the relationship between diffusible hydrogen content, tensile shear strength and fracture surfaces. Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4759K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
半谷 禎彦, 安藤 瑞季, 鈴木 良祐, 松原 雅昭, 宇都宮 登雄, 吉川 暢宏原稿種別: 速報論文
2021 年 85 巻 2 号 p. 84-87
発行日: 2021/02/01
公開日: 2021/01/25
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/01/08ジャーナル フリー HTMLIn this study, three-layered porous aluminum consisting of AC4CH (porosity: 70%) / pure aluminum (80%) / A6061 (75%) / and AC4CH (70%) / pure aluminum (70%) / A6061 (70%) were fabricated by a sintering and dissolution process. When plateau stress of each layer was significantly different, such as three-layered porous aluminum with varying porosities, exhibited clear multiple plateau regions corresponding to the deformation of each layer. In contrast, when plateau stress of each layer had a close value, such as three-layered porous aluminum with homogeneous porosities, exhibited no clear multiple plateau regions.
 Fig. 4 (a) Deformation behavior and (b) stress-strain curves of three-layered porous aluminum (Sample A) and corresponding uniform porous aluminum. Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1611K) HTML形式で全画面表示
Fig. 4 (a) Deformation behavior and (b) stress-strain curves of three-layered porous aluminum (Sample A) and corresponding uniform porous aluminum. Fullsize Image抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1611K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|