All issues

Volume 29, Issue 7
Displaying 1-15 of 15 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Yuiko TASAKI-HANDA, Kenta OOI, Mikiya TANAKA, Akihiro WAKISAKAArticle type: Rapid Communications
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 685-687
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe exchange of lanthanide(III) ions (Ln3+) between a solution and a coordination polymer (CP) formed by cerium(III) or samarium(III) ion and an organophosphorous ligand has been studied. The CPs exhibit distinctive Ln3+ affinity that varies with a small change in its framework, depending on the central Ln3+. View full abstractDownload PDF (428K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (428K)
Original Papers
-
Manami HOMMATSU, Hisamitsu OKAHASHI, Keisuke OHTA, Yusuke TAMAI, Kazuh ...Article type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 689-695
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA polymerase chain reaction (PCR)/ligase detection reaction (LDR)/flow-through hybridization assay using chemiluminescence (CL) detection was developed for analyzing point mutations in gene fragments with high diagnostic value for colorectal cancers. A flow-through hybridization format using a capillary tube, in which probe DNA-immobilized magnetic beads were packed, provided accelerated hybridization kinetics of target DNA (i.e. LDR product) to the probe DNA. Simple fluid manipulations enabled both allele-specific hybridization and the removal of non-specifically bound DNA in the wash step. Furthermore, the use of CL detection greatly simplified the detection scheme, since CL does not require a light source for excitation of the fluorescent dye tags on the LDR products. Preliminary results demonstrated that this analytical system could detect both homozygous and heterozygous mutations, without the expensive instrumentation and cumbersome procedures required by conventional DNA microarray-based methods.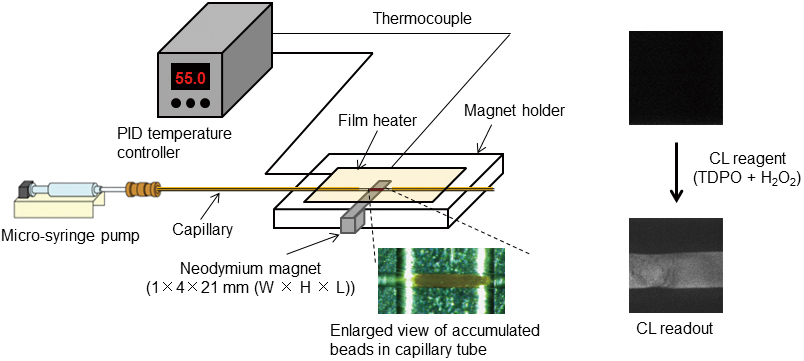 View full abstractDownload PDF (2884K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2884K) -
Masako OKA, Hiroshi KAMIMORIArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 697-702
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the present study, we developed an assay of interactions of amphotericin B (AmB) deoxycholate, Fungizone, with two model lipid membranes that mimicked mammal cell membranes and fungal membranes. We also analyzed the binding kinetics of the mammal cell membranes and fungal membranes using surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Fungizone showed a higher affinity for the model fungal membrane than that of the model mammal cell membrane, and the binding selectivity of Fungizone in the temperature dependence could be represented by this SPR system. This method also showed reproducible immobilization of model liposome membranes on the sensor chip under two temperature conditions (25 and 37°C). The binding characteristics of the medicinal additive of Fungizone, sodium deoxycholate, were clarified on the assay of interactions of the drug product to the lipid membrane, and it was confirmed that the sodium deoxycholate did not affect the estimation of membrane selectivity of Fungizone. Furthermore, the affinities of AmB and Fungizone were discussed by comparing these affinity constants. The results demonstrate that this newly established SPR method could be applied to estimate the lipid-membrane interaction of Fungizone as a drug product of AmB. View full abstractDownload PDF (465K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (465K) -
Yeong Hee AHN, Ji Seok KIM, Sung Ho KIMArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 703-708
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe polymerization reaction of toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and hydroxyl compounds has been widely used for the production of polyurea resins. Since the composition and molecular-weight distribution of polymer adducts greatly influence the final properties of the resuting polymer, the development of analytical tools capable of monitoring the polyaddition reactions is important to control them as well as the properties of the resuting polymer. Here we report that matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI TOF MS) is useful to precisely monitor time-dependent dynamic events occurring in the polymerization reaction of TDI with water. For this purpose, the polymerization reactions were conducted in two different reaction systems, continuously supplying sufficient water and depleting water after an initial exposure of water to provide an anhydrous storage condition of prepolymer adducts. Samples prepared in a time course from the two different reaction systems were analyzed by a MALDI TOF mass spectrometer. The polymerization adducts of TDI and water were monitored and showed to consist of three structural types of polymer adduct series, including diisocyanate, monoamino, and diamino series. These MALDI mass data efficiently reflected changes in the reaction conditions of each TDI polymerization reaction, thereby providing precise information at the molecular level for time-dependent events occurring during the polymerization reaction. These events included changes between the polymer adduct series and in the molecular-weight distribution of each polymer adduct series. The results obtained in this study suggest that high-throughput MALDI MS-based dynamic monitoring of polymerization can be used to precisely control the polymerization reaction as well as to rapidly monitor the state of prepolymers in storage.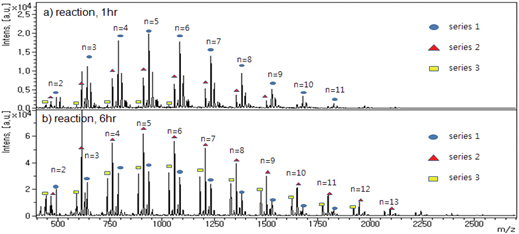 View full abstractDownload PDF (1764K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1764K) -
Xi LUO, Ningfang CAI, Zeneng CHENGArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 709-713
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method for the determination of uric acid in human plasma was developed and validated. Separation was achieved on a C18 column by the mobile phase of 30% water (containing 0.5% formic acid) and 70% methanol. Quantification was done using a multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode to monitor the precursor-to-product ion transitions of m/z 169.1 → m/z 141.1 for uric acid and m/z 171 → m/z 143 for 1,3-15N uric acid (IS) at a positive ionization mode. The calibration curve was established over the range of 0.4096 – 100 mg/L, and the correlation coefficient was better than 0.99. The intra-day and inter-day relative standard deviations were less than 5.1%. The accuracy determined at three concentrations ranged between 92.7 and 102.3%. This method was successfully applied to an efficacy study of intravenous recombinant urate oxidase produced by Escherichia coli in a clinical phase I study.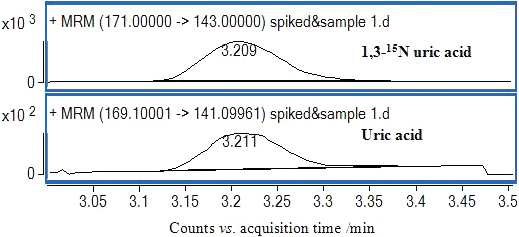 View full abstractDownload PDF (594K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (594K) -
Kazunori SAITOH, Naoki SOETA, Hiroaki MINAMISAWA, Masami SHIBUKAWAArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 715-721
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialOn-line redox derivatization HPLC was applied for the analysis of Fe(II) and Fe(III) cyanide complexes. The HPLC system used consisted of two C18 silica columns treated with trimethylstearylammonium chloride and a small column packed with porous graphitic carbon (PGC) placed between them. The PGC column treated with sodium sulfite completely reduced the Fe(III) cyanide complex to the Fe(II) complex, while the Fe(II) cyanide complex was converted to the Fe(III) complex by the PGC column treated with hydrogen peroxide. On the other hand, the oxidation states of the other metal cyanide complexes were not affected by PGC. Selective separations of the Fe(II) and Fe(III) cyanide complexes from the other metal complexes were demonstrated by on-line redox derivatization HPLC using the oxidized and reduced PGC column as the redox derivatization unit, respectively. The method was successfully applied for the analysis of Fe(II) cyanide complex in food grade salt. View full abstractDownload PDF (799K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (799K) -
Hisanori IWAI, Masami FUKUSHIMA, Mitsuo YAMAMOTOArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 723-728
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA fertilizer, comprised of a mixture of steel slag and compost, was used to restore seaweed beds in barren coastal areas. Complex Fe(II) species, supplied by steel slag, play a significant role in supplying Fe(II) to coastal areas and stimulating seaweed growth. Seawater extractable organic matter (SWEOM) from compost is generally assumed to serve as a chelator of Fe(II) in the fertilizer. It is considered that the bioavailability of Fe(II)-SWEOM complexes is higher in the dissociable (labile) species. In the present study, a method for determining labile species of Fe(II)-SWEOM complexes in seawater (pH 8.0, I = 0.7) was developed. The method is based on a ligand-exchange reaction between SWEOM and ferrozine (FZ). Because Fe(II) is readily oxidized to Fe(III) under normal seawater conditions, ascorbic acid was added as an antioxidant. The coloring for the Fe-FZ complex in the presence of SWEOM was retarded. This retarding can be attributed to a ligand-exchange reaction between FZ and labile Fe(II)-SWEOM complexes. Conditional binding constants for the labile Fe(II)-SWEOM complexes and binding capacities of labile sites in SWEOM to Fe(II) were evaluated for a variety of total Fe(II) concentrations.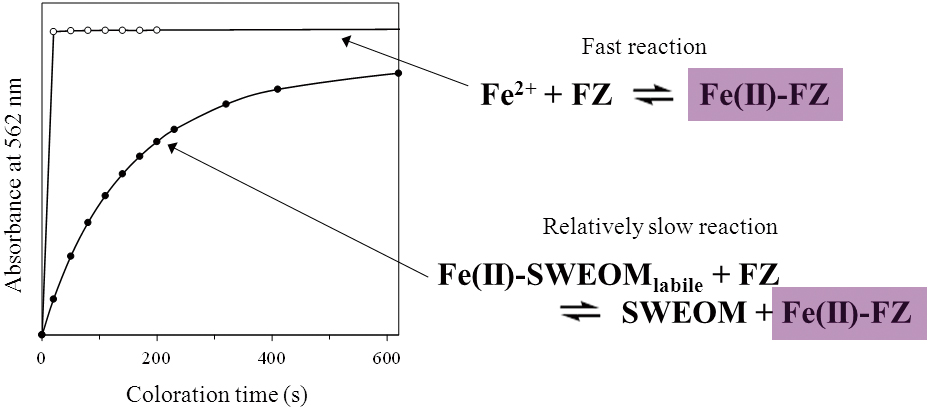 View full abstractDownload PDF (668K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (668K) -
Orhan HAZER, Dilara DEMIRArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 729-734
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPoly(1,3-thiazol-2-yl methacrylamide-co-4-vinyl pyridine-co-divinylbenzene) was prepared and used as a sorbent for the solid-phase extraction of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solution. Two forms of chromium showed different exchange capacities at different pH values; Cr(VI) was selectively retained especially at pH 2. The total chromium was determined after the oxidization of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) by potassium permanganate as an oxidizing agent. Then, Cr(III) was calculated by subtracting the Cr(VI) concentration from the total chromium concentration. The optimum conditions were found for species of Cr(VI) (pH 2; eluent, 4 mol L−1 NH3; sample flow rates, 2 mL min−1 and eluent flow rates, 1 mL min−1 etc.). The adsorption capacity and binding equilibrium constant were calculated to be 80.0 mg g−1 and 0.018 L mg−1, respectively. A preconcentration factor of 30 and a three-sigma detection limit of 2.4 μg L−1 (n = 20) were achieved for Cr(VI) ions. The developed method was applied to stream water and waste water samples. At the same time, the polymer was applied to a certified reference material (CRM) (TMDA-52.3) sample. View full abstractDownload PDF (446K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (446K) -
Guodong FENG, Yuanyuan DING, Zhiyong GONG, Yanna DAI, Qiang FEIArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 735-740
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, a quinoline–thiourea conjugate (1-phenyl-3-(quinoline-8-yl) thiourea, PQT) was synthesized and used as a fluorescence sensor to detect mercury ion. The observation is coincident with the well-documented phenomenon that a thiocarbonyl-containing group on a fluorochrome quenches the fluorescence due to the heavy atom effect of the S atom. The large fluorescence enhancement of PQT in the buffered MeCN–water mixture (1/1 v/v; HEPES 100 mM; pH 8.0) was caused by the Hg2+ induced transformation of the thiourea function into a urea group. As such, protic solvents can be ascribed to hydrogen bond formation on the carbonyl oxygen to reduce the internal conversion rate. The fluorescence intensity of PQT was enhanced quantitatively with an increase in the concentration of mercury ion. The limit of detection of Hg2+ was 7.5 nM. The coexistence of other metal ions with mercury had no obvious influence on the detection of mercury. A quinolone–thiourea conjugate was used as a fluorescent probe to detect Hg2+ in aquatic plants and the experimental results were satisfactory. View full abstractDownload PDF (1003K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1003K) -
Nil OZBEK, Suleyman AKMANArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 741-746
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, the molecule formation mechanisms of strontium mono fluoride used for the determination of fluorine in a high-resolution continuum source atomic absorption spectrophotometer was investigated. To distinguish between the gas-phase and the condensed-phase mechanisms, the analyte (F) and the molecule forming element (Sr) were injected on the solid sampling platform manually, as mixed or separately, and the absorbances/peak shapes were compared. There was no significant difference between the absorbances. In addition, the peak shapes and the appearance times were almost the same for the two cases. It was proposed that the main pathway for SrF formation is a gas-phase combination reaction between Sr and F. When Sr and F were mixed on the platform, it was expected that at first SrF2 would be formed in the condensed phase, and then at elevated temperatures it was partly decomposed while either losing one F atom to form SrF, or completely decomposed to its atoms in the gas phase. View full abstractDownload PDF (1222K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1222K) -
Tomohiro NARUKAWA, Koichi CHIBAArticle type: Original Papers
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 747-752
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA dynamic reaction cell (DRC) is one of the most effective tools for eliminating spectral interferences caused by polyatomic molecules in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Oxygen gas (O2), by producing oxygenated ions, is very effective in reducing some specific spectral interferences. In this study, the oxygenation of elemental ions (M+) in the DRC was investigated experimentally, and a new explanation for oxygenation based on the enthalpy changes in the oxygenating reactions is proposed. The enthalpy changes of each M+ were calculated and the possibility of each reaction occurring was evaluated. The calculations were in good agreement with experimental observations. Theoretical and experimental results supported the hypothesis that the enthalpy changes (ΔH) of M++ O2 → MO+ + O and M+ + O → MO+ and the thermodynamic stability of M+–O are key factors controlling oxygenation of M+ in the DRC.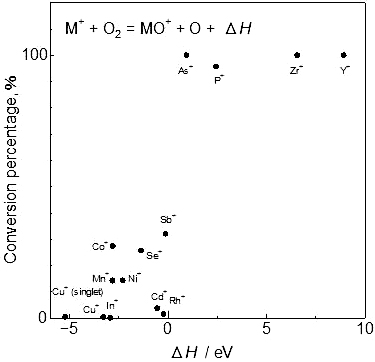 View full abstractDownload PDF (411K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (411K)
Notes
-
Jun KATO, Takuma KOSEKI, Yukie AOKI, Ayako YAMADA, Tatsuhiko TANAKAArticle type: Notes
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 753-755
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA definitive method is described for the indirect assay of several tens of milligrams of urea by coulometric titration. Urea was decomposed in concentrated sulfuric acid using a Kjeldahl flask. Subsequently, the formed ammonium ion was titrated with electrogenerated hypobromite ion in a sodium bromide-sodium tetraborate medium of pH 8.6, with amperometric end-point detection. Parameters affecting the pretreatment procedure were evaluated. The optimized conditions included the heating of 2 g of urea at around 300°C for 2 h with 10 cm3 of sulfuric acid. Under the proposed conditions, the assay value with expanded uncertainty (k = 2), 99.870 ± 0.026%, agreed well with the certified value of NIST SRM 912a urea, 99.9 ± 0.1%. View full abstractDownload PDF (393K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (393K) -
Qing-Wei ZHOU, Di WU, Qin MENG, Hai-Bo TANG, Zheng-Ren WEI, Ye KUANG, ...Article type: Notes
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 757-760
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA capillary electrophoresis method coupled with electrochemiluminescence detection for the analysis of vinorelbine (VNB) in the urine of tumor patients was established in this research. Complete determination of VNB was achieved in 8 min using a background electrolyte of 50 mmol/L phosphate buffer (pH 9.0) and a separation voltage of 15 kV. The calibration curves showed a linear range from 2.8 × 10−10 to 1.6 × 10−8 mol/L. The relative standard derivation for VNB was below 3.4%. The linear relationships were good and the correlation factor of VNB exceeded 0.985. The detection limits were 1.0 × 10−11 mol/L under the optimal conditions. The developed method was applied to the sensitive determination of VNB in the urine of tumor patients.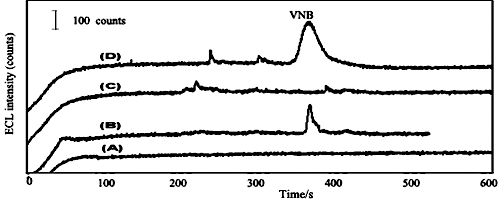 View full abstractDownload PDF (361K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (361K) -
Toru ORITA, Lee R. MOORE, Powrnima JOSHI, Masahiro TOMITA, Takashi HOR ...Article type: Notes
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 761-764
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialQuadrupole Magnetic Field-Flow Fractionation (QMgFFF) is a technique for characterization of sub-micrometer magnetic particles based on their retention in the magnetic field from flowing suspensions. Different magnetic field strengths and volumetric flow rates were tested using on-off field application and two commercial nanoparticle preparations that significantly differed in their retention parameter, λ (by nearly 8-fold). The fractograms showed a regular pattern of higher retention (98.6% v. 53.3%) for the larger particle (200 nm v. 90 nm) at the higher flow rate (0.05 mL/min v. 0.01 mL/min) at the highest magnetic field (0.52 T), as expected because of its lower retention parameter. The significance of this approach is a demonstration of a system that is simpler in operation than a programmed field QMgFFF in applications to particle mixtures consisting of two distinct particle fractions. This approach could be useful for detection of unwanted particulate contaminants, especially important in industrial and biomedical applications. View full abstractDownload PDF (458K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (458K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2013Volume 29Issue 7 Pages 765
Published: July 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1563K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|