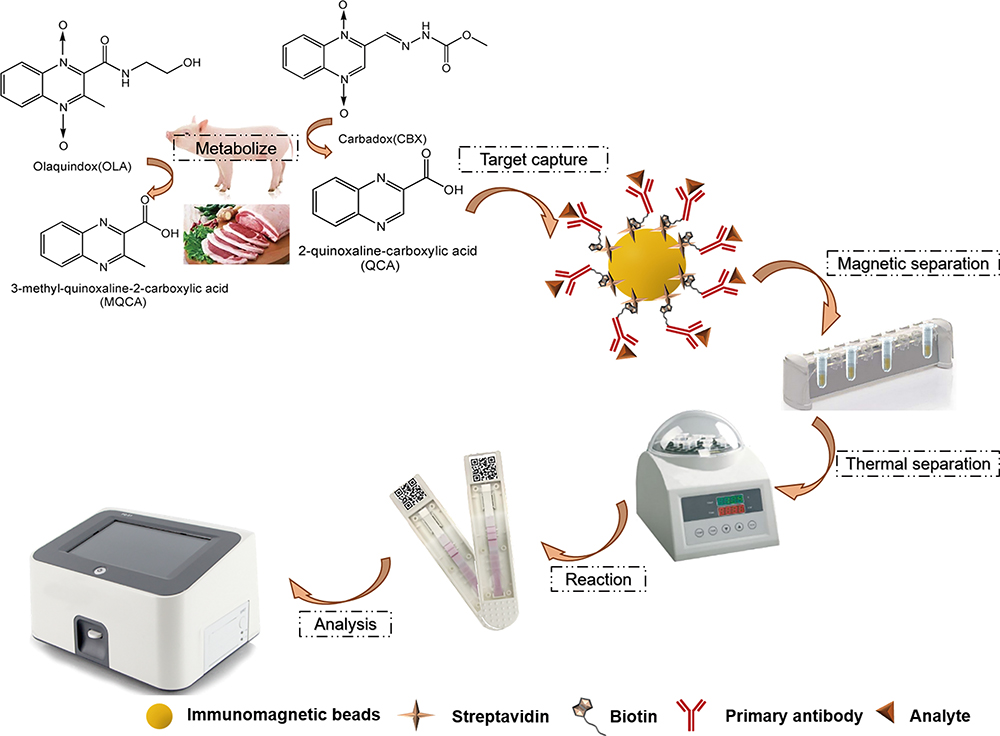
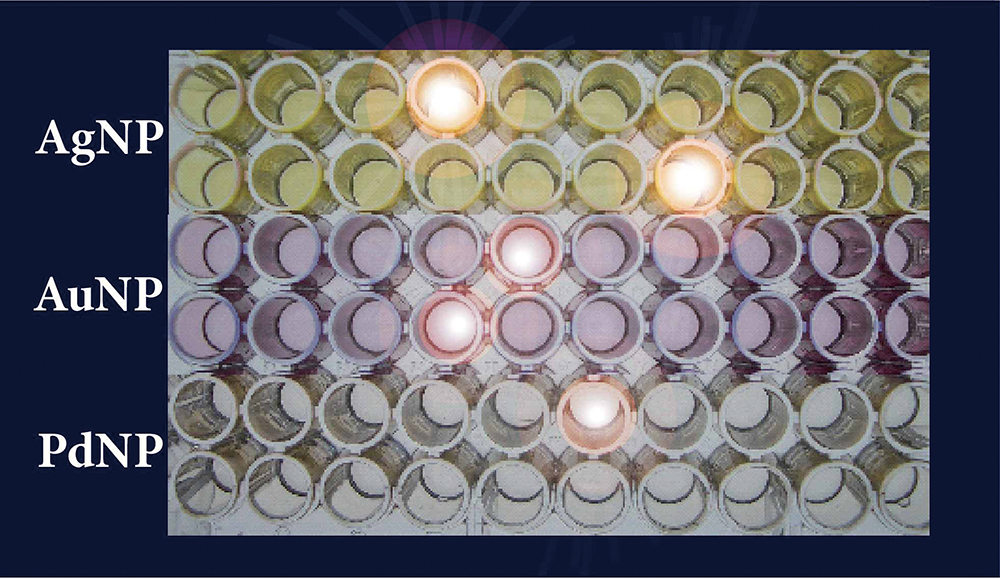
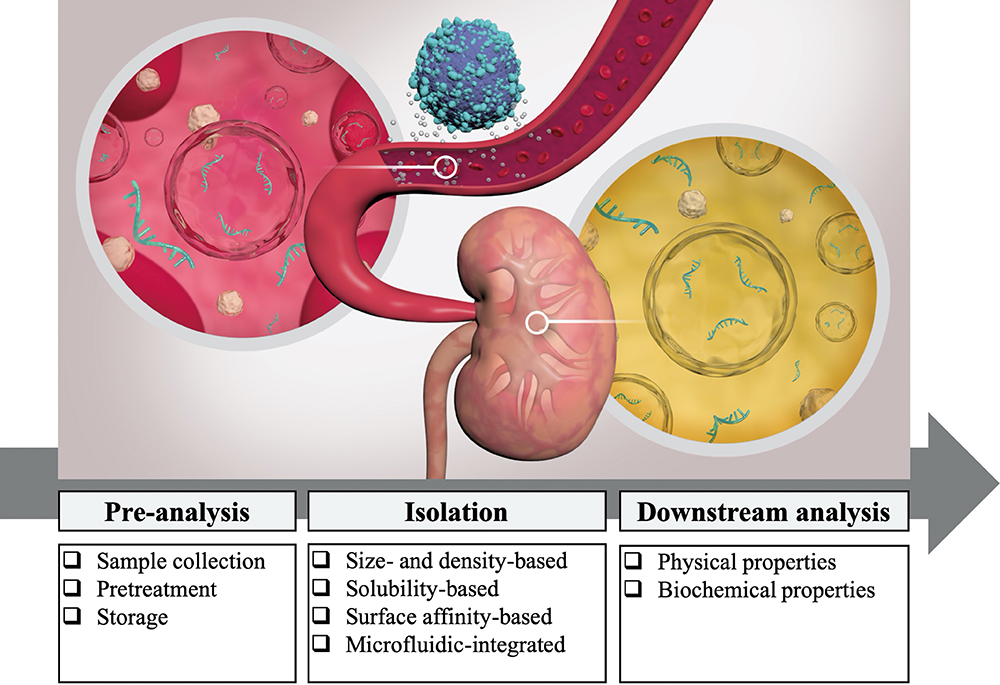
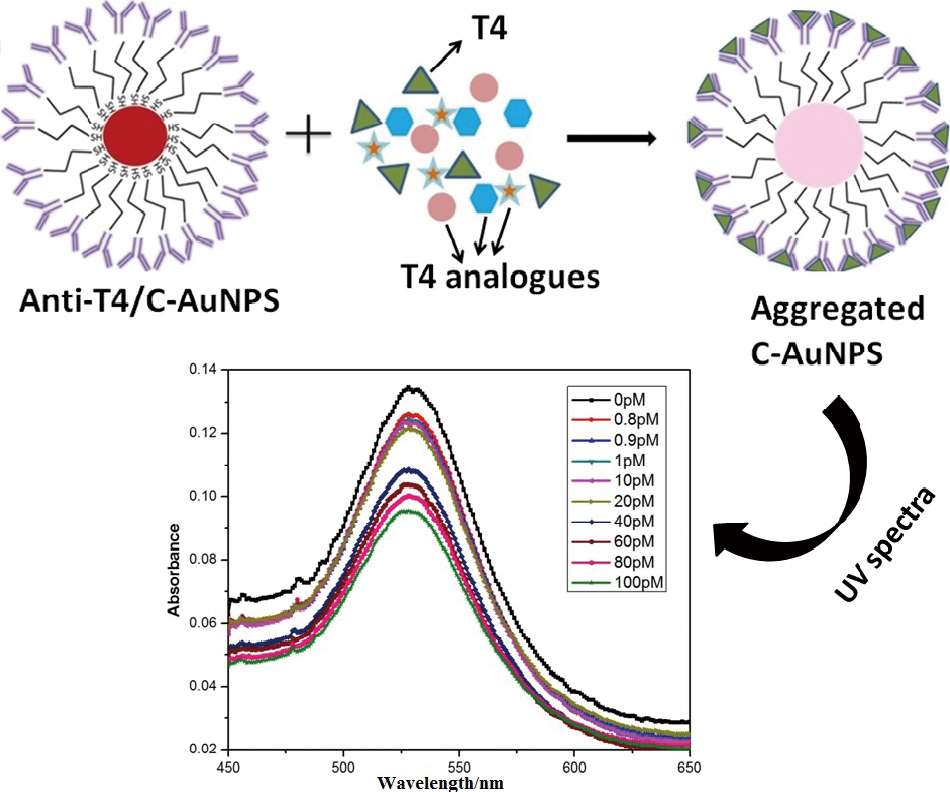
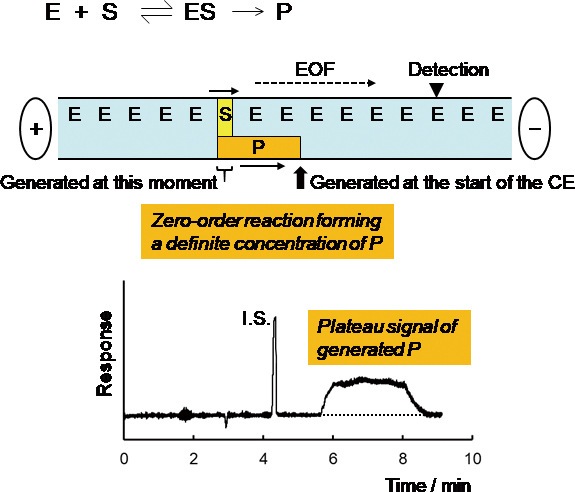
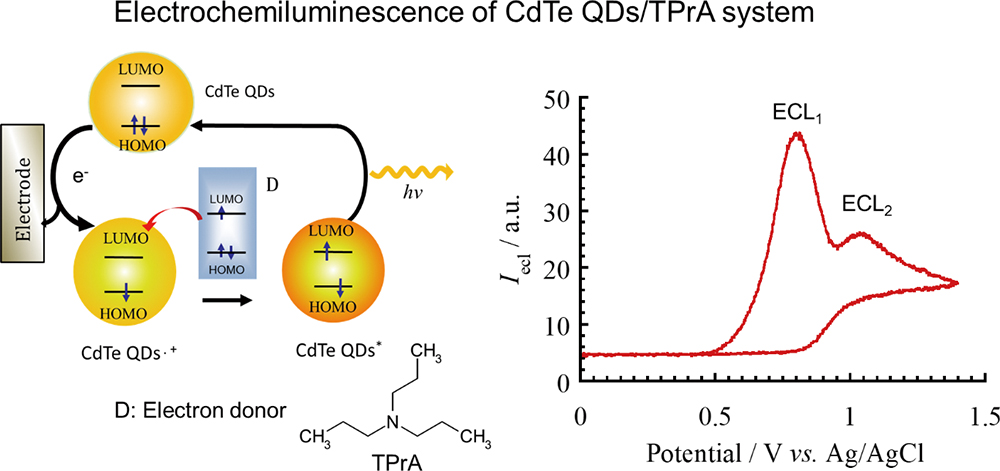
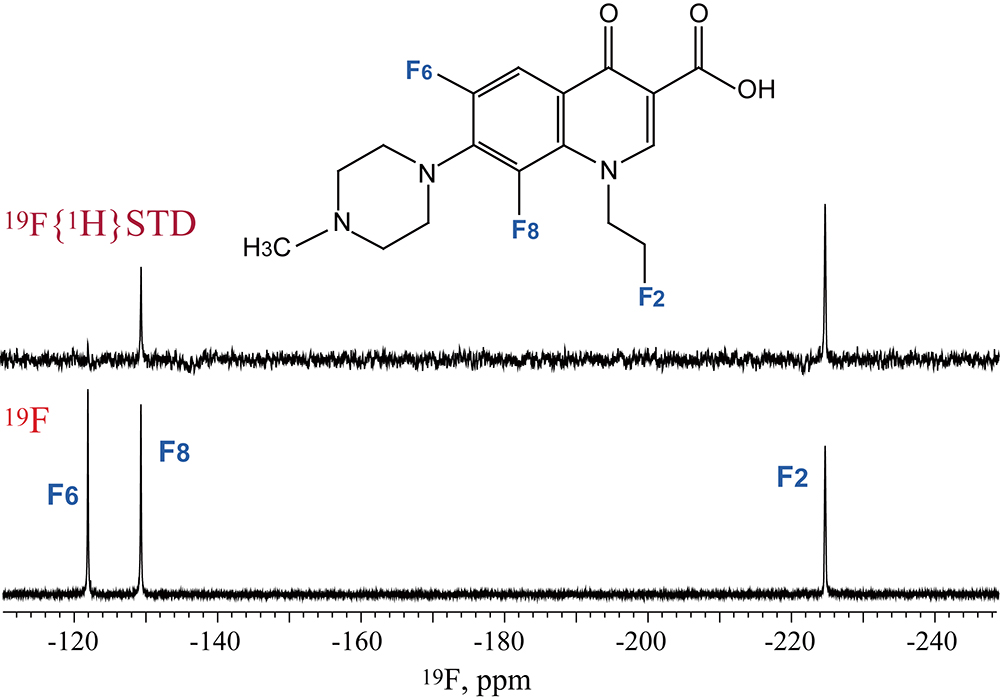
Volume 36, Issue 7
Displaying 1-22 of 22 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 781-782
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Download PDF (148K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 783-785
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 19, 2020Download PDF (398K) -
Article type: Rapid Communications
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 787-789
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 26, 2020Download PDF (311K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 791-798
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 13, 2020Download PDF (782K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 799-806
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 22, 2020Download PDF (2186K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 807-811
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 03, 2020Download PDF (276K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 813-819
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 10, 2020Download PDF (530K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 821-828
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 17, 2020Download PDF (2068K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 829-834
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 17, 2020Download PDF (508K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 835-840
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 24, 2020Download PDF (2220K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 841-846
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 24, 2020Download PDF (874K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 847-851
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 24, 2020Download PDF (855K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 853-858
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 24, 2020Download PDF (2442K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 859-863
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 31, 2020Download PDF (858K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 865-869
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 07, 2020Download PDF (811K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 871-875
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 24, 2020Download PDF (412K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 877-880
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 24, 2020Download PDF (238K) -
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 881-883
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 07, 2020Download PDF (162K) -
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 885-887
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 28, 2020Download PDF (327K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 889-892
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 31, 2020Download PDF (194K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 893
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Download PDF (184K)
Errata
-
Article type: Errata
2020Volume 36Issue 7 Pages 897
Published: July 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2020
Download PDF (28K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|