
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Fumihiko KITAGAWAArticle type: Highlights
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 899-900
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Krassimir STOEV, Kenji SAKURAIArticle type: Reviews
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 901-922
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 06, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the early 1960s, scientists achieved the breakthroughs in the fields of solid surfaces and artificial layered structures. The advancement of surface science has been supported by the advent of ultra-high vacuum technologies, newly discovered and established scanning probe microscopy with atomic resolution, as well as some other advanced surface-sensitive spectroscopy and microscopy. On the other hand, it has been well recognized that a number of functions are related to the structures of the interfaces, which are the thin planes connecting different materials, most likely by layering thin films. Despite the scientific significance, so far, research on such buried layers and interfaces has been limited, because the probing depth of almost all existing sophisticated analytical methods is limited to the top surface. The present article describes the recent progress in the nanometer scale analysis of buried layers and interfaces, particularly by using X-rays and neutrons. The methods are essentially promising to non-destructively probe such buried structures in thin films. The latest scientific research has been reviewed, and includes applications to bio-chemical, organic, electronic, magnetic, spintronic, self-organizing and complicated systems as well as buried liquid–liquid and solid–liquid interfaces. Some emerging analytical techniques and instruments, which provide new attractive features such as imaging and real time analysis, are also discussed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1431K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1431K) -
Hiroka SUGAI, Shunsuke TOMITA, Ryoji KURITAArticle type: Reviews
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 923-934
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 03, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo capture a broader scope of complex biological phenomena, alternatives to conventional sensing based on specificity for cell detection and characterization are needed. Pattern-recognition-based sensing is an analytical method designed to mimic mammalian sensory systems for analyte identification based on the pattern recognition of multivariate data, which are generated using an array of multiple probes that cross-reactively interact with analytes. This sensing approach is significantly different from conventional specific cell sensing based on highly specific probes, including antibodies against biomarkers. Encouraged by the advantages of this technique, such as the simplicity, rapidity, and tunability of the systems without requiring a priori knowledge of biomarkers, numerous sensor arrays have been developed over the past decade and used in a variety of cell sensing applications; these include disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and fundamental research. This review summarizes recent progress in pattern-recognition-based cell sensing, with a particular focus on guidelines for designing materials and arrays, techniques for analyzing response patterns, and applications of sensor systems that are focused primarily for the biomedical field.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1726K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1726K)
-
Nan LI, Siqingaowa HAN, Chen ZHANG, Shuang LIN, Xuan-yu SHA, Wuliji HA ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 935-940
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 31, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis paper described how a high-yield, monodisperse Au nanobipyramids (Au NBs) sol was prepared by a seed-mediated method, and gold nanoparticles were assembled on the surface of a silicon wafer by self-assembly technology to obtain a solid SERS substrate. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the average length of Au NBs was 34.31 nm, and the analysis enhancement factor (AEF) was approximately 7.3 × 105 with rhodamine 6G (R6G) used as a probe. SERS detection of chlortetracycline hydrochloride (CCH) in milk was performed utilizing the prepared Au NBs substrate, and the limit of detection was 0.01 mg/mL. In the range of 0.01 – 1 mg/mL, the mass concentration of CCH and the SERS signal intensity satisfied the linear relationship y = 258.467x + 150.501; the value of the correlation coefficient was 0.9785. In addition, the recovery of spiked samples fluctuated between 96.80 to 111.38%. These results proved that the method is simple and fast, and it is promising to be applied to the field detection of antibiotics in milk.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (390K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (390K) -
Toshio TAKAYANAGI, Sota IWASAKI, Yuta BECCHAKU, Shun YABE, Kotaro MORI ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 941-946
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 31, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWater-soluble carbon nanodots (CND) were synthesized under microwave irradiation from glutamic acid or glutamic acid–boric acid mixture. The CNDs were collected in an aqueous solution through size fractionation by centrifugal filtration. The CNDs thus prepared were subjected to characterization by capillary electrophoresis (CE). A peak signal of anionic substance was detected in the electropherogram, and it was found to be a major component of the CNDs. The effective electrophoretic mobility of the major component was almost identical over the pH range between 6.7 and 11.6, suggesting that the functional group of amine or boric acid moiety was not included in the CNDs. The effective electrophoretic mobility decreased at an acidic pH of less than 5, and it was suggested that carboxylate moiety was included in the CNDs. A signal of less-charged CNDs was also detected in the electropherogram, and the CNDs were characterized by a CE format of micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Two or four peaks were detected just after the electroosmotic flow; the less-charged CNDs were thus hydrophilic. The affinity interaction was also examined between the major anionic CNDs and a hydrophobic pairing cation. The peak signal of the major anionic CNDs broadened, and its theoretical number of plates decreased in the presence of tetrabutylammonium ion in the separation buffer. A small portion of the anionic CNDs were a little hydrophobic at different degrees, and their effective electrophoretic mobility decreased by the hydrophobic interaction, resulting in peak broadening of the anionic CNDs.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (290K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (290K) -
Shihua YU, Zhigang LIU, Na XU, Jie CHEN, Yan GAOArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 947-951
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 07, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFull width at half maximum (FWHM) of diffraction peaks of native cellulose is larger than 1°. The diffraction peaks of the crystalline phase largely coincide with those of the amorphous phase of cellulose, leading to the low resolution. Therefore, when calculating the crystallinity of natural cellulose by fitting the peaks, only relying on the single evaluation factor of Rwp (R-weighted Pattern) may lead to great randomicity of calculation results. Due to the special crystal structure of natural cellulose and the characteristics of crystallinity determination by peak separation method, the XRD Rietveld fitting method is adopted to determine the crystallinity of native cellulose. Through limiting the convergence conditions of fitting functions, we firstly discuss the effects of peak shape functions, scanning range, and the positions of amorphous peaks on crystallinity determination, which helps to reduce the randomness of XRD in solving crystallinity of cellulose and improve the precision of calculation. Then, three evaluation indexes (Rwp, FWHM, and RSD) are used to evaluate the rationality of crystallinity calculation results. Moreover, the reproducibility and precision of the crystallinity of three kinds of natural cellulose are tested under the optimized conditions. At the same time, the optimized fitting method is adopted to calculate the content of cellulose I and II, which can be used to guide the selection of alkali concentration and alkali treatment time in the spinning process of native cellulose.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1181K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1181K) -
Shumei TIAN, Wenli ZHANG, Jinwei SHI, Zixian GUO, Ming LIArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 953-957
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 07, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNanochannel plastic membranes are excellent materials for electroosmotic pump (EOP) elements owing to their surface charge properties, flexibility and cost-effectiveness. However, the surface charge properties of plastics are inferior to those of silicate-based materials. This paper reports a performance-enhanced EOP equipped with a glassified track-etch polycarbonate membrane (PC), which has a nanochannel surface covered by allylhydridopolycarbosilane (AHPCS). The effects of applied voltage, pH and membrane pore size on the electroosmotic flow velocity, along with a comparative study of the EOP with coated and pure membranes were investigated. It was found that when low DC voltage (10 – 40 V) was applied to both ends of the pump, the magnitude of the electroosmotic flow was linearly proportional to the voltage when the pore size of the membrane was less than 600 nm. A higher flow rate was obtained with larger pore size membranes. Compared with the uncoated film, the coated one showed faster electroosmosis velocity, with higher stability under the same conditions. For pH 10.0 buffer solution, a flow rate of 89.13 μL/min was obtained in the modified membrane-based EOP with excellent repeatability and durability, while the flow rate was only 37.89 μL/min in the bare PC membrane under 20 V. In order to demonstrate the performance of the developed EOP, the EOP was used for microcomplexometric titration to determine actual tap water hardness. The measured results were highly consistent with the results of a conventional complexometric titration methed. The EOP with an AHPCS-coated plastic membrane expanded the application range to harsh condition solutions, such as high-concentration acids or bases.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (859K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (859K) -
Yusuke KITAMURA, Kotaro MISHIO, Pelin ARSLAN, Boui IKEDA, Chiharu IMOT ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 959-964
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 14, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFerrocene (Fc) and β-cyclodextrin (βCyD) were modified at each end of stem-loop structured DNA as an electrochemical signal generator and its quencher, respectively, to give an electrochemical molecular beacon (eMB). A relatively high efficiency of signal quenching was achieved by an inclusion complex (βCyD ⊃ Fc) formation that was induced on the stem structure of the closed form (= stem-loop structure) of eMB. With the addition of target DNA, the structure of eMB opened to form a linear duplex, where the Fc dissociated from the βCyD to restore its intrinsic electrochemical signal. The signal contrast of the electric current for this off/on-type sensor was high, ca. 95. This technique did not require any modification of the electrode surface, and it realized the detection of the target nucleic acids in a homogeneous solution with a high sensitivity using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipped with electrochemical detector.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (858K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (858K) -
Dandan WANG, Fenghua GENG, Yongxiang WANG, Yu MA, Guixin LI, Peng QU, ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 965-970
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 14, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA novel fluorescent aptasensor based on the G-quadruplex induced fluorescent quenching of psoralen and the competitive interactions between 4′-aminomethyl-4,5′,8-trimethylpsoralen (AMT), adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and G-rich DNA functionalized split ATP aptamer was proposed. The binding of ATP to the G-rich DNA functionalized split aptamer induced a significant enhancement in fluorescence emission intensity while undergoing excitation at 340 nm. Under the optimal conditions, the developed aptasensor showed high selectivity and good accuracy for detecting ATP. The practicality of the proposed aptasensor has been confirmed by successfully analyzing ATP in spiked human blood serum samples with satisfactory results. As far as we know, this is the first time that the intrinsic quenching ability of G-quadruplex was applied to simply construct a fluorescence turn-on and label-free aptasensor. On account of the superiority of the simplicity of the design strategy, more work is expected in the future to develop a variety of novel sensors for other important analytes using the quenching capability of G-quadruplex through reasonable designs.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (838K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (838K) -
Albert D. DUKES IIIArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 971-975
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 21, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe Henry’s law constant defines the solubility of a gas in a liquid solution. In this study, a new method for measuring the Henry’s law constant is described. This new colorimetric method is suited for gases which react with water to form acidic or basic solutions when they dissolve, and makes use of measuring the concentration of two forms of a colorimetric pH indicator. By measuring the concentration of the protonated and deprotonated forms of the indicator with UV-visible absorption spectroscopy, the concentration of the hydronium in solution was determined. After determining the hydronium concentration, the equilibrium expression for the dissolved gas reacting with water was solved to determine the concentration of the dissolved gas. The concentration of the dissolved gas and the measured partial pressure of the dissolved gas at equilibrium were then used to calculate the Henry’s law constant for the gas. The efficacy of the method is demonstrated by measuring the Henry’s law constant for carbon dioxide in water over a range of pressures (0.680 – 5.10 atm). The results obtained with this method are comparable to the value for the Henry’s law constant that have been previously reported via more traditional methods, and yielded values for the Henry’s law constant for carbon dioxide that ranged from 3.45 × 10−2 to 3.99 × 10−2 M atm−1.
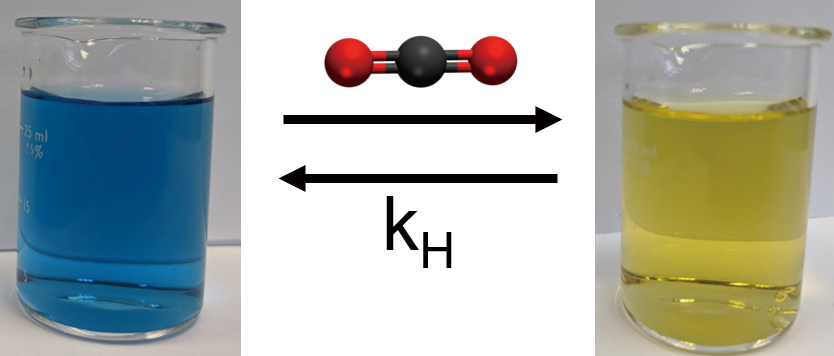 View full abstractDownload PDF (186K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (186K) -
Yuuki OTSUKA, Tomoko SHIMAMURA, Michio SAKAJI, Hikaru ARITA, Takehiro ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 977-980
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 28, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe cyclic dipeptides, 2,5-diketopiperazines (DKPs), draw attention as bioactive and taste compounds. DKPs, especially those containing Proline (Pro), are contained in heated and fermented foods. Herein, we developed a method for a simultaneous quantitative analysis of Pro-containing DKPs using LC-MS/MS. After optimizing the LC-MS/MS conditions, the developed method was applied to quantify Pro-containing DKPs in Goishi tea, which is a post-fermented tea produced by a two-step aerobic-anaerobic fermentation process. Consequently, 17 kinds of Pro-containing DKPs could be quantified, and the total amount of Pro-containing DKPs was 3.40 mg/L. The recovery in a spiked test was 93 – 117%, which is satisfactory. We believe that the developed method can be used to elucidate the role of Pro-containing DKPs in food.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (261K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (261K) -
Pawitrabhorn SAMUTRTAI, Sucheewin KROBTHONG, Sittiruk ROYTRAKULArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 981-987
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 28, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLC-MS/MS-based proteomics coupled with an online bioinformatics platform was under evaluation for applicability to toxicological pathways evaluation at low cytotoxic concentration (LC10) of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) and ionic silver in human carcinoma cells after 48 h of exposure. Significantly, differentially-expressed proteins (One-way ANOVA, p < 0.05) with more than 4-fold compared to the control were subjected to functional pathway analysis by STITCH. SOTA clustering indicated a similarity of the protein expression between AgNP and the control group. We established a resemblance of proteins in the cell cycle pathway affected by both Ag substances. The differences in the toxicological pathways from AgNO3 were involved in the cellular organization and metabolic process of macromolecules, while the nucleic acid metabolic process was altered by AgNP. The present study supported the practicability of LC-MS/MS-based proteomics coupled with STITCH for the identification of toxicological pathways in both silvers. We appraised this platform technology to be promising and powerful for a toxicological screening of other new substances.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (754K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (754K) -
Masanori ANDO, Kosuke INAGAKI, Hideya KAWASAKI, Vasudevanpillai BIJU, ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 989-995
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 13, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe report photoluminescence-based ozone sensing using composite films composed of gold or platinum and red-emitting CdSe/ZnS core-shell quantum dots. The sensing efficiency of quantum dots is enhanced by the addition of noble metals. The composite films undergo reversible changes in photoluminescence intensity (measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 365/652 – 659 nm) in the presence of ppm levels of ozone in air at 25°C and at atmospheric pressure. The sensitivity of the composite films does not saturate with ozone in the 0.5 – 200 ppm concentration range. When compared with a quantum dot-only film, the composite films show higher sensitivities to 0.5 ppm ozone of 27% (gold) and 43% (platinum). When compared with a quantum dot-only film, the photoluminescence of the gold- or platinum-palladium alloy-based film recovers faster after the removal of ozone in the surrounding atmosphere. Thus, platinum- or gold-conjugated quantum-dot films form sensor modules for the reversible and highly sensitive detection of ozone under the tested ambient conditions.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1202K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1202K) -
Takumi HIGASHIJIMA, Naoya KISHIKAWA, Naotaka KURODAArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 997-1001
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 13, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe long-wavelength fluorogenic derivatization method for aryl halides was developed based on stilbene formation by the Heck coupling reaction between aryl halides and vinylbenzenes in the presence of palladium(II) acetate as a catalyst. Fluorescent maximum wavelengths of the derivative obtained by the proposed reaction were 365 – 450 nm, which were 50 – 100 nm longer than those of the biphenyl derivatives formed with our previously developed fluorogenic derivatization method. Also, by the investigation using vinylbenzenes containing electron-donating or -withdrawing functional groups, it was found that an internal charge transfer system could contribute to extend the emission wavelength of the derivative. Furthermore, the proposed reaction was applied to develop a pre-column derivatization HPLC with fluorescence detection method for aryl bromides using 4-vinylanisole. p-Substituted aryl bromide derivatives (i.e., p-bromobenzonitrile, p-bromoanisole, bromobenzene, p-bromobenzoic acid ethyl ester, p-bromotoluene) were successfully detected within 40 min with the detection limit of 0.007 – 0.264 μM. Despite the short reaction time of 10 min, the reaction yields for p-bromoanisole and bromobenzene were good at 101 and 87%, respectively.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (336K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (336K) -
Akira KOTANI, Maki KANEKO, Koichi MACHIDA, Kazuhiro YAMAMOTO, Hideki H ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 1003-1008
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 13, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA simple electrochemical procedure has been developed for determining the titratable acidity in Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus (SCF) and Schisandrae Sphenantherae Fructus (SSF) by means of reduction of quinone in the presence of acid compounds. To measure a voltammogram, a test solution was prepared by mixing a water extract from SCF or SSF and an electrolyte cocktail containing 3,5-di-tert-butyl-1,2-benzoquinone and NaCl. The quantitative results of titratable acidity in the SCF and SSF samples by the present voltammetry were in good agreement with those by neutralization titration using 0.1 M NaOH (r2 = 0.980): y = 1.003x + 0.010, where the y- and x-axes were the titratable acidity obtained by the present voltammetry and the neutralization titration, respectively. Further, the titratable acidities in the SSF samples were significantly lower than those in the SCF samples (p < 0.01). From these findings, we show that the titratable acidity is useful as an indicator to discriminate between SCF and SSF. Moreover, a prototype of electrochemical portable sensor for on-site analysis has been provided to perform this procedure.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (127K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (127K) -
Nobuyasu ITOH, Nobuyasu HANARIArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 1009-1013
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 20, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSConfocal Raman microscopes are widely used in various applications because they provide physical and chemical information at a submicron scale. A high lateral resolution in the confocal Raman microscope is essential for obtaining high-quality images. We used an array of tungsten dots at a 600 nm pitch on a Si substrate of the certified reference material (NMIJ CRM 5207-a) to reliably evaluate the lateral resolution of a confocal Raman microscope at various pinhole sizes. The precision of the mapping scale in the x- and y-pitches was confirmed from Si signal profiles, and the lateral resolution was evaluated by a straight-edge method using scale indicators in the reference material. Because these procedures are applicable to other confocal Raman microscopes with popular specifications (532 nm laser, 100× objective lens, numerical aperture 0.9, step size 0.1 μm), they are suitable for both a reliable evaluation of the lateral resolution of a confocal Raman microscope and for daily checks on the precision of its mapping scale.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2937K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2937K)
-
Tadahiro YAMASHITA, Takuya NISHINA, Ichiro MATSUSHITA, Ryo SUDOArticle type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 1015-1019
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 20, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe report on a novel microdevice to tune the curvature of a cell-adhering surface by controlling the air-pressure and micro-slit. Human aortic smooth muscle cells were cultured on demi-cylindrical concaves formed on a microdevice. Their shape-adapting behavior could be tracked when the groove direction was changed to the orthogonal direction. This microdevice demonstrated live observation of cells responding to dynamic changes of the anisotropic curvature of the adhering surface and could serve as a new platform to pursue mechanobiology on curved surfaces.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (6550K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (6550K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2020 Volume 36 Issue 8 Pages 1021
Published: August 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (92K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
