All issues

Volume 29, Issue 9
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Papers
-
Atsushi NAKATA, Tomonori NOMOTO, Taro TOYOTA, Masanori FUJINAMIArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 865-869
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) of supported phospholipid bilayers in an aqueous environment is discussed in this paper. Two bilayer membranes were examined: 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) and 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC). We fabricated alumina- and silver-coated tungsten tips that are very robust in water. There was a large time-dependence in the TERS spectra for the DOPC bilayers, whereas no such time-dependence was observed in the DPPC bilayer spectra under the probe tip. The spectral changes of DOPC bilayers are discussed in terms of the fluidity of the liquid crystalline phase. Time-resolved TERS thus has the potential to characterize inhomogeneity and diffusion in fluidic phospholipid bilayer membranes.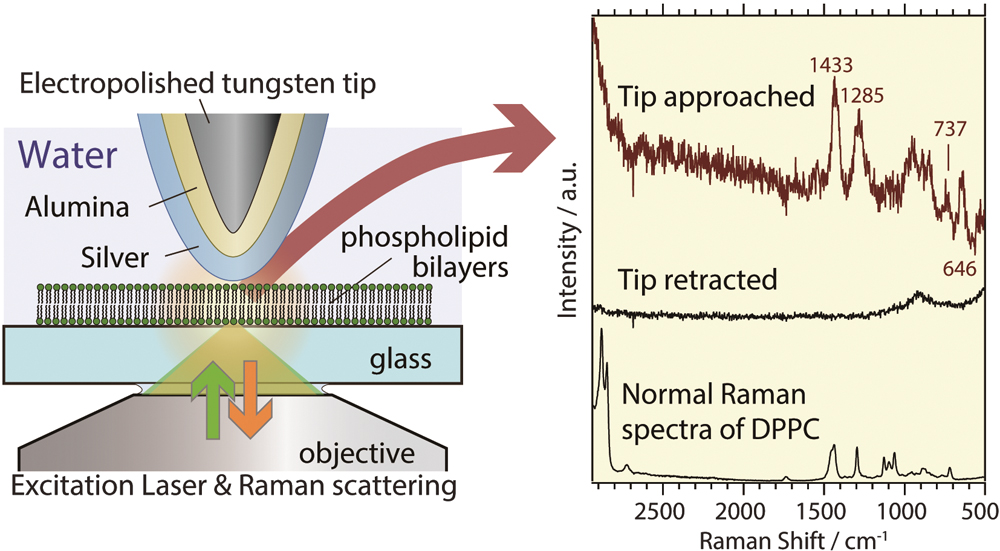 View full abstractDownload PDF (881K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (881K) -
Sharif HASAN, Jinhua DONG, Yuko HARA, Yoshihito MORIZANE, Futoshi SHIB ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 871-876
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialOpen sandwich (OS) immunoassay utilizes antigen-dependent stabilization of an antibody variable region to quantify various antigens, enabling noncompetitive detection of small molecules with a broad working range. For further improvement of its sensitivity, OS Immuno-PCR was attempted with recombinant fusion proteins. The maltose binding protein-fused heavy chain variable region (MBP-VH) of an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal fragment of human osteocalcin (bone Gla protein, BGP), a biomarker for bone-related diseases, was immobilized onto microplate wells, and the antigen together with streptavidin (SA)-fused light chain variable region of the same antibody (SA-VL) was added and incubated. The amount of immobilized SA-VL was quantified by tethered biotinylated DNA, which was used to estimate the amount of antigen by realtime PCR. When BGP C-terminal peptide was detected, the limit of detection was 100 fg/mL, which was superior than that of our previously reported phage-based OS Immuno-PCR. The developed OS Immuno-PCR system will be useful for the detection of small molecule biomarkers for disease prevention. View full abstractDownload PDF (5506K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5506K) -
Misato SAKAMOTO, Atsushi SHOJI, Masao SUGAWARAArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 877-883
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA highly sensitive and rapid method for the determination of substance P (SP) and streptolysin O (SLO) in human serum is described. The assay is based on enriching the analyte by agglutination/precipitation of immuno-liposomes and enhancing the fluorescence intensity by gramicidin A channels. A mixture of the immuno-liposomes encapsulating a pH-sensitive fluorescence dye BCECF, gramicidin A and a given concentration of SP (or SLO) is preincubated in a solution and captured on anti-SP (or anti-SLO)-modified cover slips, followed by measuring fluorescence images after removing excess liposomes. The method allowed quantifying SP and SLO in the range from sub-pg mL−1 to pg mL−1, with detection limits of 0.32 pg mL−1 and 8 fg mL−1, respectively. The present method could determine SP and SLO in 50 – 125 times diluted human serum without any extraction steps. The assay can be completed within 60 min. View full abstractDownload PDF (1126K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1126K) -
Wesley W. HSIAO, Hsien-Shun LIAO, Hsing-Hung LIN, Yueh-Lun LEE, Chia-K ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 885-892
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSToxocarosis is a zoonosis caused by the transmission of the Toxocara canis (T. canis) larvae to humans. Its infectious third-stage larvae can invade the brains of paratenic hosts. The resultant brain damage can result in cerebral toxocarosis (CT). Astrocytes have important neurotrophic and neuroprotective functions in the brain. Substantial studies have shown that astrocyte apoptosis may contribute to the pathogenesis of many acute and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. We propose an alternation detection method, a combination of the astigmatic detection microscopy (ADM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) techniques, to investigate the apoptosis of astrocytes triggered with T. canis larval excretory/secretory (Tc E/S) antigen. The variation in the pathology of a cell’s morphological changes was investigated with ADM and AFM analyses and then confirmed by western blotting. The results showed that the round cells increased as the concentration of Tc E/S antigen and incubated time increased. In addition, the mean height of apoptotic cells was approximately twice that of untreated normal cells, which meant there was correlation between the Tc E/S antigen treatment and cell height. For each cleaved caspase-3 in the cells cocultured with Tc E/S antigen and incubated for 9 h, the corresponding intensities increased about 34-fold (34.4 ± 1.8) compared with those of the control cells. This method can provide researchers with a perspective for understanding the limited information on the mechanism of astroglial injury and death during a T. canis larval invasion in a brain infection. View full abstractDownload PDF (3587K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3587K) -
Adriana M. PIMENTA, M. Renata S. SOUTO, Rita I. L. CATARINO, M. Fernan ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 893-898
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn automatic system was developed to determine ofloxacin in biological fluids and pharmaceutical formulations. Drug detection was carried out by a potentiometric membrane sensor based on [bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]borate as molecular-recognition material. The tubular shaped detector system was solidly attached to the manifold, creating a high-throughput stable setup (50 samples per hour) appropriate for routine antibiotic assessment. Under the optimized flow conditions, the sensor displayed a mean detection limit of 1 × 10−5 M, a linear response over the concentrations of 2 × 10−5 to 5 × 10−3 M (slope of 57.4 mV decade−1) and a wide working pH range (2.1 – 6.6). The procedure was successfully applied to ofloxacin analysis in pharmaceuticals (relative deviation lower than 6%) and biological fluids at levels usually found after drug administration of clinical doses (recoveries between 91 and 106%). No significant interference from common excipients found in commercial formulations and inorganic ions usually present in biological fluids was noticed. View full abstractDownload PDF (514K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (514K) -
Chun-Yan LI, Yu ZHOU, Yong-Fei LI, Chun-Xiang ZOU, Xue-Fei KONGArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 899-903
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this paper, we unveil a novel rhodamine compound-based fluorescent chemosensor (compound 1) for fluorescent detection of Hg2+ in an aqueous solution. The fluorescence enhancement of compound 1 was attributed to the formation of a complex between compound 1 and Hg2+ by 1:1 complex ration (K = 8.0 × 104), which has been utilized as the basis of fabrication of the Hg2+-sensitive chemosensor. A comparison of this method with some other fluorescence methods for the determination of Hg2+ indicated that this method has high selectivity and good water solubility. The analytical performance characteristics of the proposed Hg2+-sensitive chemosensor were investigated. The chemosensor can be applied to the quantification of Hg2+ with a linear range from 6.6 × 10−7 to 2.4 × 10−4 M and a detection limit of 1.3 × 10−7 M. The experiment results show that the response behavior of compound 1 towards Hg2+ is pH independent in neutral conditions (pH 5.0 – 9.0). Most importantly, the fluorescence changes of the chemosensor are remarkably specific for Hg2+ in the presence of other metal ions, which meet the selective requirements for practical application. Moreover, the response of the chemosensor toward Hg2+ is fast (response time less than 1 min). In addition, the chemosensor has been used for the determination of Hg2+ in river water samples with satisfactory results. View full abstractDownload PDF (918K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (918K) -
Tetsuo KUWABARA, Kosuke SUGIYAMAArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 905-909
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA modified β-cyclodextrin (1) tethered with a phenylaminoazobenzen moiety has been synthesized for the purpose of developing a new guest-responsive color-change chemosensor. When the solution became acidic, 1 changed color from yellow to purple due to a structural change of the dye moiety from the azo form to the azonium one by protonation on the azo group. However, the pH titration curve of 1 was affected by the presence of the guest, as shown by the fact that the curve in the acidic region shifted to the neutral side by the presence of 1-adamantanol. This suggests that 1 has a potential to show a guest-induced absorption variation under the acidic condition. Upon guest addition at pH 0.61 at the concentration of 1 with 1 × 10−5 M, 1 showed a colorless-to-color change. Such hyperchromisity in the absorption spectrum of 1 is associated with a guest-induced conformational change of the dye moiety from inside to outside of the CD cavity, and is used for molecular sensing. Among various guests, 1 was found to be highly sensitive to a steroidal guest having a C12 hydroxyl group in the framework, such as ursodeoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid in an acidic aqueous solution.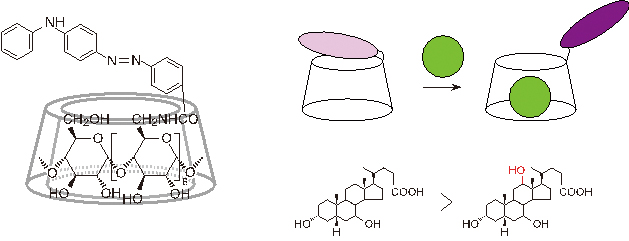 View full abstractDownload PDF (464K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (464K) -
Taro TOYOTA, Koyo UCHIYAMA, Takahiro KIMURA, Tomonori NOMOTO, Masanori ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 911-917
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe used a time-resolved interfacial tension measurement method with quasi-elastic laser scattering to investigate the effects of electrolytes and various surfactants on the nonlinear dynamics of the chemical oscillation that occurred at a water/nitrobenzene interface when a surfactant was added to the interface through a capillary. For both cationic and anionic surfactants, an electrolyte in the water phase was required for slow desorption of the surfactant from the interface. In the absence of an electrolyte, repulsion between the polar head groups of the ionic surfactants hindered adsorption of the surfactant molecules at the interface, resulting in their rapid desorption. In contrast, the presence of an electrolyte induced adsorption of the surfactant ions by screening their charged polar heads. Zwitterionic and nonionic surfactants were also examined and we deduced that the salting out effect of the surfactant produced by the presence of an electrolyte results in strongly attractive interactions between the surfactant molecules and the water/nitrobenzene interface. View full abstractDownload PDF (576K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (576K)
Notes
-
Tatsuo YOSHIDA, Asami ITOU, Rise YAMAMOTO, Toshiaki TOBINO, Hiroshi MU ...Article type: Notes
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 919-922
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIsotianil (3,4-dichloro-2′-cyano-1,2-thiazole-5-carboxanilide) is a new plant-activating pesticide. Usage of the pesticide was approved for rice fields in 2010 and its production increased 400 times (2 × 104 kg) in the next year. In this work, a method for determining isotianil in brown rice and rice field soil was investigated for the first time. Isotianil was extracted by supercritical fluid extraction and measured by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Isotianil was successfully analyzed with good recoveries (95.1 – 99.3%) even from soil samples with strong adsorption of pesticides. View full abstractDownload PDF (377K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (377K) -
Toshiro MATSUNAGA, Mihoko MORIIZUMI, Tsunenori KAMEDAArticle type: Notes
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 923-926
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo characterize organic nitrogen present in cattle manure compost, a hot-water extract of the compost along with an acid-insoluble (humic acid-like) fraction either treated with alkali or laccase or untreated were separated by size-exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography (SE-HPLC). Nitrogen was then detected by chemiluminescent nitrogen detection (CLND), and humic acid-like substances were detected by measuring the absorbance at 420 nm. The acid-insoluble fraction comprised the higher molecular-weight region in the chromatogram of the whole extract, and its chromatogram pattern of CLND was similar to that of the absorbance at 420 nm. Changes in the molecular-weight distribution of the acid-insoluble fraction detected by CLND due to alkaline degradation and laccase polymerization were in agreement with those observed by measuring the absorbance at 420 nm. These results, together with other data, demonstrate that protein and humic acid-like moieties are present in the same molecule in compost organic matter.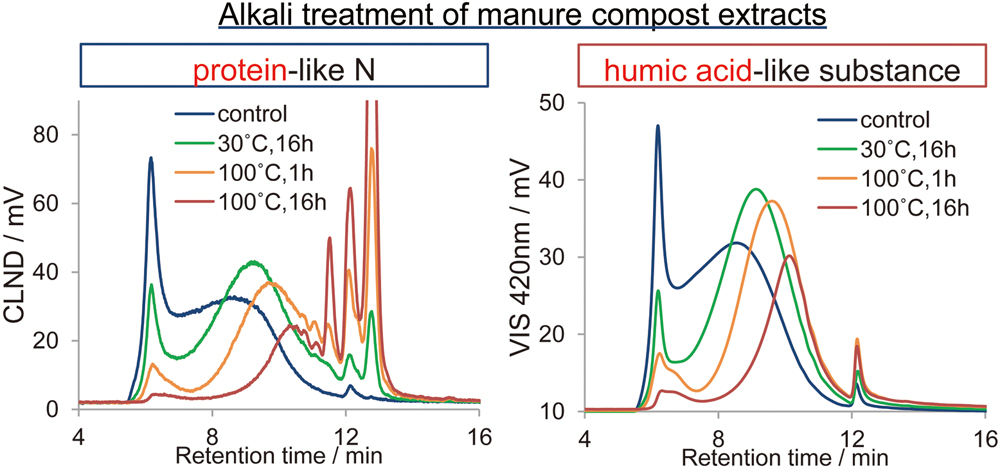 View full abstractDownload PDF (1532K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1532K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Irmina DIALA, Shinobu SATO, Michihiko USUI, Keisuke NAKASHIMA, Tatsuji ...Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 927-930
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is implicated in periodontal disease, and there was an attempt to quantitate it by a membrane-based microwave-mediated electrochemical enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (MMeELISA) using p-aminophenyl phosphate (pAPP) with an over-all time of 1.5 h. A differential pulse voltammetric signal increased linearly with an increase in the amount of TNF-α with a detection limit of 0.48 pg mL−1. This bio-sensing platform revealed a significant difference in the TNF-α level between GCF samples from periodontal patients and healthy volunteers. View full abstractDownload PDF (606K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (606K)
Retraction
-
Lifeng ZHANGArticle type: Retraction
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 931
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis article published in Anal. Sci., 2010, 26(3), 325 was withdrawn by the Editor on June 7, 2013, because it was concluded that the author has copied significant parts of an earlier paper (Y. Jiang and Z. Xie, Determination of Ibandronate and its Degradation Products by Ion-Pair RP LC with Evaporative Light-Scattering Detection, Chromatographia, 2005, 62, 257, doi: 10.1365/s10337-005-0618-4). We regret that this was not detected during the reviewing process.View full abstractDownload PDF (40K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2013 Volume 29 Issue 9 Pages 933
Published: September 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1608K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|