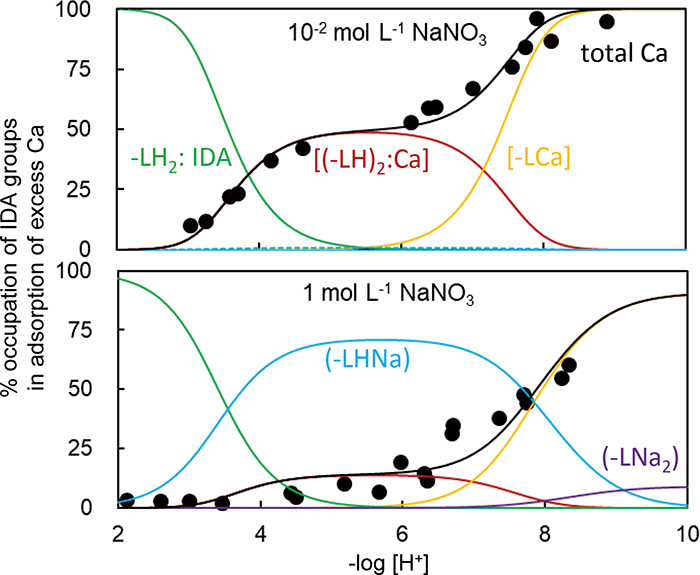
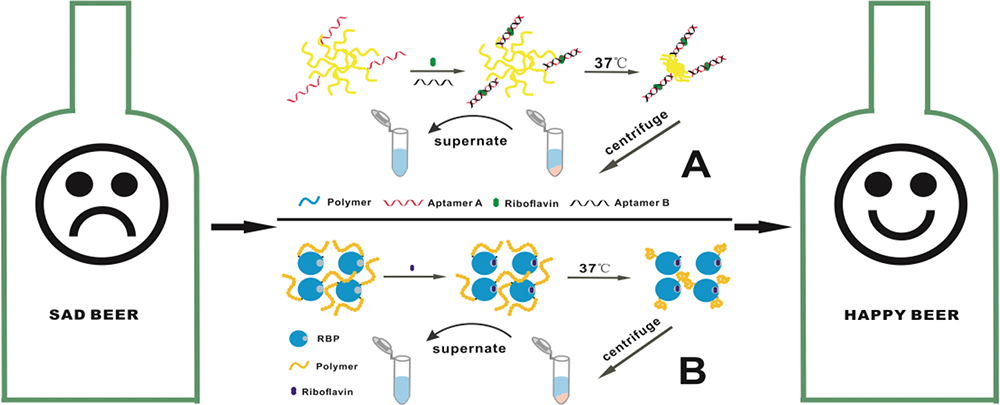
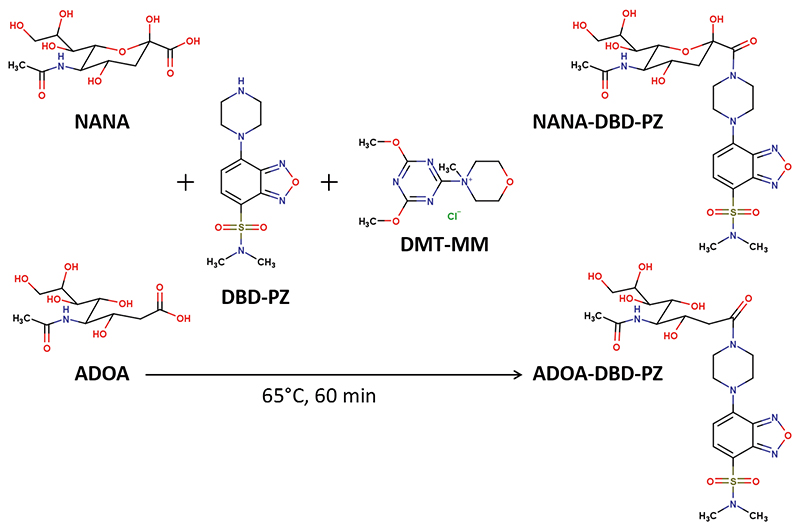
Volume 34, Issue 7
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 753-754
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (133K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 755-764
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (3444K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 765-770
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (445K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 771-776
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (2132K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 777-782
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (284K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 783-787
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (2180K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 789-794
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (903K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 795-800
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (1246K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 801-805
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (1405K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 807-813
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (1934K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 815-821
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (824K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 823-829
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (1177K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 831-836
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (590K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 837-840
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (716K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 841-844
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (174K) -
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 845-847
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (128K) -
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 849-851
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (111K) -
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 853-857
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (141K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 859
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (1678K)
Errata
-
Article type: Errata
2018Volume 34Issue 7 Pages 863
Published: July 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2018
Download PDF (27K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|