All issues

Volume 30, Issue 2
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Special Reviews
-
Shu TAIRA, Kohei UEMATSU, Daisaku KANEKO, Hajime KATANOArticle type: Special Reviews
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 197-203
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTwo-dimensional mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of biological samples by means of what is called MS imaging (MSI) is now being used to analyze analyte distribution because it facilitates determination of the existence (what is it?) and localization (where is it?) of biomolecules. Reconstruction of mass image by target signal is given after two-dimensional MS measurements on a sample section. From only one section, we can understand the existence and localization of many molecules without the need of an antibody or fluorescent reagent. In this review, we introduce the analysis of localization of functional constituents and nutrients in herbal medicine products via MSI. The ginsenosides were mainly distributed in the periderm and the tip region of the root of Panax ginseng. The capsaicin was found to be more dominantly localized in the placenta than the pericarp and seed in Capsicum fruits. We expect MSI will be a useful technique for optical quality assurance. View full abstractDownload PDF (26302K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (26302K) -
Hiroyuki NISHI, Kumi NAGAMATSUArticle type: Special Reviews
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 205-211
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis article presents a mini-review of the recent results in the ultra high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) separation of pharmaceuticals by our group. High performance UHPLC separation employing core-shell particle C18 columns was demonstrated. High performance (high theoretical plate number of approximately 20000/10 cm, low theoretical plate height of 5 μm) was obtained without any specific devices in the conventional HPLC apparatus, only through changing detector sampling times and the inner diameter of the connecting tube. High theoretical plate numbers with low column back pressure obtained by the core-shell particle columns enabled fast separation of the analytes. Methanol, which gives high column pressure drops in the reversed-phase mode HPLC compared with acetonitrile, can be used without any trouble. One analysis of the purity testing of diltiazem hydrochloride was performed within 100 s. One analysis in the photostability testing of mecobalamin (vitamin B12 analogue) was successful within 180 s.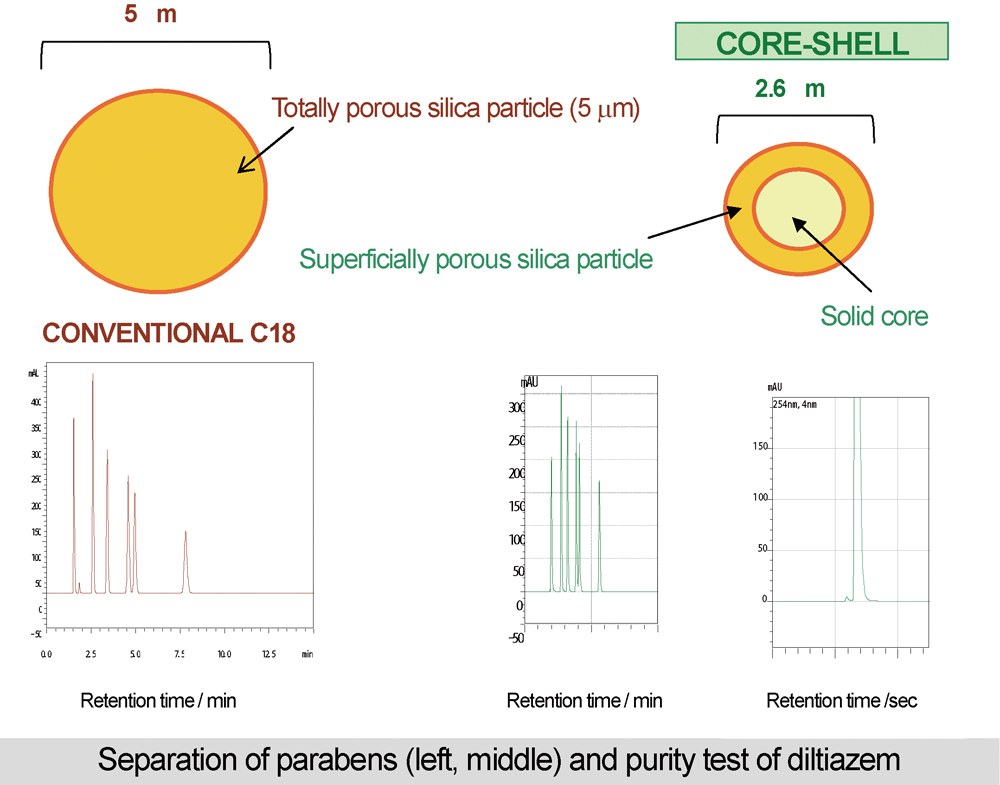 View full abstractDownload PDF (3210K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3210K) -
Soichi YABUKIArticle type: Special Reviews
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 213-217
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLong-term stability is a key property of enzyme membranes that can be used for biosensors, bioreactors, and bio-fuel cells. This review discusses factors that decrease the stability, and provides two examples of enzyme membranes, a polyion complex membrane and a cellulose membrane, with which stability loss can be avoided. By using these materials, long-term stability was improved. These supporting materials could be applied to construct biosensors, bioreactors, and bio-fuel cells. View full abstractDownload PDF (983K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (983K) -
Shin-ichi MIYASHITA, Alexander S. GROOMBRIDGE, Shin-ichiro FUJII, Akik ...Article type: Special Reviews
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 219-224
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTime-resolved inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) has attracted much attention for elemental and multiparametric analysis of single cells, instead of a classical bulk analysis of large amount of cells after a dissolution. In the time-resolved measurement, cells are directly introduced into the plasma via nebulizing or micro drop dispensing, and then ion plumes corresponding to single cells are individually detected with a high time resolution. The sensitivity and cell throughput in the measurement strongly depend on the time resolution. A high cell introduction efficiency into the plasma supports for a reduction of cell consumption. Biomolecules can also be measured through the attachment of elemental tags, and then the amount distribution of elements and biomolecules in single cells can be evaluated, while providing information concerning cell-to-cell variations. By applying ICP time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ICP-TOFMS), multiparametric analysis of elements and biomolecules can be achieved similar to that by a flow cytometer. This article highlights the technical aspects of the time-resolved ICP-MS measurement technique for elemental and multiparametric analysis of single cells. View full abstractDownload PDF (4030K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4030K)
Original Papers
-
Hirosuke HATAYAMA, Taro TOYOTA, Hideki HAYASHI, Tomonori NOMOTO, Masa ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 225-230
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, we describe the development of a novel tissue marker that can be injected from within the digestive tract by using an endoscopic instrument, and visualized using near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging. The marker was prepared in three steps, (i) mixing NIR-fluorescent indocyanine green (ICG) with giant vesicles (GVs) of lecithin, (ii) suspending the ICG-containing giant vesicles (ICG-GV) in an oil phase dissolving polyglycerol-polyricinoleate (PGPR), and (iii) centrifugation of the suspension layered on a buffered solution to obtain a giant polymer vesicle (polymerasome) containing ICG-GV. We injected the tissue marker into the inner gastric surface of an anesthetized pig using an endoscopic syringe, and observed the injection site using a fluorescence laparoscopic camera. The diameter of the spot blur was approximately 2 cm over a 5-h period, demonstrating the utility of this procedure as a tissue marker for tumor marking, and suggesting its potential for assisting navigation during surgical procedures. View full abstractDownload PDF (1262K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1262K) -
Hidekazu MIYAHARA, Takahiro IWAI, Yuki KABURAKI, Tomokazu KOZUMA, Kaor ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 231-235
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new inductively coupled plasma (ICP) torch with an air-cooling system has been designed and developed for both argon and helium plasma. The same torch and impedance-matching network could be used to generate stable Ar- and He-ICP. The torch consists of three concentric quartz tubes. The carrier gas, plasma gas, and cooling gas flow through the intervals between each tube. In an experiment, it was found that Ar-ICP could form a stable plasma under the following conditions: RF power of 1 kW, plasma gas flow rate of 11 L min−1, and cooling gas flow rate of 20 L min−1. For He-ICP, an input RF power of 2 kW, which is two-times higher than that of a conventional He-ICP, could be constantly applied to the plasma with plasma gas and cooling gas flow rates of 15 and 20 L min−1, respectively. Using this torch, it is possible to realize lower plasma gas consumption for Ar- and He-ICP and a high-power drive for He-ICP. It has been found that the air-cooling gas stabilizes the shape of the plasma due to the pressure difference between the cooling gas and the plasma gas. View full abstractDownload PDF (974K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (974K) -
Shigeo SATO, Yuuki ARAI, Kazuaki WAGATSUMAArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 237-243
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWhen a nitrogen microwave-induced plasma produced with an Okamoto-cavity was employed as a source for the nitridation of steel samples, the characteristics of the plasma were investigated by analyzing a spatially-resolved emission image of nitrogen excited species obtained with a two-dimensionally imaging spectrograph. Our previous study had reported on an excellent performance of the Okamoto-cavity microwave-induced plasma (MIP), enabling a nitrided layer having a several-micrometer-thickness to form on an iron substrate, even if the treatment is completed within 1 min, which is superior to a conventional plasma nitriding using low-pressure glow discharges requiring a prolonged treatment time. In this paper, the reason for this is discussed based on a spectrometric investigation. The emission images of band heads of nitrogen molecule and nitrogen molecule ion extended toward the axial/radial directions of the plasma at larger microwave powers supplied to the MIP, thus elevating the number density of the excited species of nitrogen, which would activate any chemical reaction on the iron substrate. However, a drastic increase in the growth rate of the nitrided layer when increasing the microwave power from 600 to 700 W, which had been observed in our previous study, could not be explained only from such a variation in the excited species of nitrogen. This result is probably because the growth process is dominantly controlled by thermal diffusion of nitrogen atom after it enters into the iron substrate, where the substrate temperature is the most important parameter concerning the mobility in the iron lattice. Therefore, the Okamoto-cavity MIP could contribute to a thermal source through radiative heating as well as a source of nitrogen excited species, especially in the growth process of the nitrided layer. View full abstractDownload PDF (4202K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4202K) -
Tomohiro NARUKAWA, Eri MATSUMOTO, Tsutomu NISHIMURA, Akiharu HIOKIArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 245-250
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe concentrations of 16 elements in 10 rice flour samples and the distribution of the elements in the rice grains from which the flour were made were determined by ICP-MS and ICP-OES after microwave-assisted digestion of the samples. Arsenic speciation analysis was carried out by HPLC-ICP-MS following heat-assisted extraction of the sample. The concentrations of inorganic As (As(III) and As(V)), monomethylarsonic acid (MMAA) and dimethylarsinic acid (DMAA) and their distribution in the rice grains were determined. Portions of the brown rice were polished/milled to different degrees to yield milled off samples and polished rice samples. All samples were powdered and analyzed for 16 elements and for As species. The recoveries and mass balances for all elements in all samples showed good agreements with the starting materials. As(III), As(V), MMAA and DMAA were detected, and the sums of the concentrations of all species in the extract were 86 – 105% of the total As concentration in each case. View full abstractDownload PDF (614K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (614K) -
Padmarajaiah NAGARAJA, Narayanan ARADHANA, Aandamurthy SUMA, Ananthara ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 251-256
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialChlorpromazine hydrochloride (CPH) (3-(2-chloro-phenothiazine-10-yl)-propyl] dimethylamine hydrochloride) has been the subject of a large number of studies employing a broad spectrum of oxidants, and chosen to examine the course of electron transfer reactions. We report on a method to determine the antioxidant activity of some food and medicinal plants using the oxidation of CPH by chromium(VI) to form a stable CPH radical in the 1:1 orthophosphoric acid–ethyl alcohol (OPA-EtOH) medium. The pink color of the control solution was measured at λmax of 530 nm. Nine standard antioxidants have been studied by this method, along with the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) method. The EC50, TEC50, antioxidant efficacy and the stoichiometric values for antioxidants have been evaluated. The radical scavenging activity expressed as EC50 ranged from 9.2 μg/mL in Camellia sinensis to 448.18 μg/mL in Cuminum cyminum. The application of a simple and versatile antioxidant capacity assay for dietary polyphenols and medicinal plant extracts, which are commonly used in Ayurveda opens its relevance in the field of antioxidant analysis. View full abstractDownload PDF (724K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (724K) -
Yong-Fei LI, Yuan-Feng WEI, Ying TAN, Xue-Fei KONG, Kai ZHOU, Zhi-Min ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 257-262
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn inorganic–organic silica material (SBA-15-1), prepared by immobilization of the naphthalimide derivative within the channels of the mesoporous silica material SBA-15, is characterized by several spectroscopic methods. SBA-15-1 can be used as a chemical sensor for detecting and removing Hg2+ in a heterogeneous system. The fluorescence enhancement of SBA-15-1 was attributed to the formation of a complex between SBA-15-1 and Hg2+ by a 1:1 complex ratio with the photo-induced electron transfer (PET) being forbidden. The sensor can be applied to the quantification of Hg2+ with a linear range covering from 1.0 × 10−7 to 1.0 × 10−5 M under the neutral condition. Most importantly, the fluorescence changes of the sensor are remarkably specific for Hg2+ in the presence of other metal ions. Moreover, the response of the sensor toward Hg2+ is fast and chemically reversible. In addition, the sensor has been used for the determination of Hg2+ in environmental samples with satisfactory results.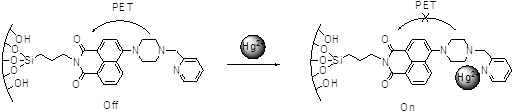 View full abstractDownload PDF (1306K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1306K) -
Kojiro SHIMOJO, Noboru AOYAGI, Takumi SAITO, Hiroyuki OKAMURA, Fukiko ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 263-269
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialLiquid–liquid extraction of lanthanide ions (Ln3+) using N,N-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) was comprehensively investigated, together with fluorescence spectroscopic characterization of the resulting extracted complexes in the organic phase. DODGAA enables the quantitative partitioning of all Ln3+ ions from moderately acidic solutions, while showing selectivity for heavier lanthanides, and provides remarkably high extraction separation performance for Ln3+ compared with typical carboxylic acid extractants. Furthermore, the mutual separation abilities of DODGAA for light lanthanides are higher than those of organophosphorus extractants. Slope analysis, loading tests, and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry measurements demonstrated that the transfer of Ln3+ with DODGAA proceeded through a proton-exchange reaction, forming a 1:3 complex, Ln(DODGAA)3. The stripping of Ln3+ from the extracting phase was successfully achieved under acidic conditions. Time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy revealed that the extracted Eu3+ ions were completely dehydrated by complexation with DODGAA. View full abstractDownload PDF (1009K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1009K) -
Yasuhiro SAKAMOTO, Yuki JINNO, Ikumi SHINODZUKA, Yusuke IWASAKI, Rie I ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 271-275
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA cleanup method employing quick and simple solid-phase dispersive extraction (SPDE) was investigated for its potential use in the determination of vancomycin (VCM) in serum by liquid chromatography/mass-spectrometry (LC/MS). SPDE was observed to be more rapid than conventional cartridge-type solid-phase extraction (SPE). In addition, in the analysis of viscous samples such as serum containing many proteins, SPDE could satisfactorily remove proteins even if deproteinization was not performed beforehand. The limit of detection (S/N = 3) and the limit of quantification (S/N > 10) of VCM by LC/MS were 0.05 and 0.2 ng/mL, respectively. The average recoveries of VCM from pooled serum spiked at 2, 10, and 100 ng/mL were 90.0, 90.8, and 98.6%, respectively. The repeatabilities were 7.5, 6.8, and 2.8%, and the intermediate precision values were 8.5, 6.8, and 7.0%, respectively. This suggests that the developed analytical method combing SPDE is useful for the determination of VCM in serum. View full abstractDownload PDF (648K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (648K) -
Kanji MIYABE, Yuhi MURATAArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 277-283
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe van Deemter equation and moment equations were used for analyzing the flow rate dependence of HETP experimentally measured in order to clarify chromatographic behavior from the kinetic points of view in columns packed with C18-silica monolith and C18-core-shell particles under RPLC conditions. They provided some information about molecular diffusion, eddy diffusion, and mass transfer kinetics in the columns. Additionally, the value of intra-stationary phase diffusivity was determined in the range of 10−7 – 10−6 cm2 s−1 by the moment analysis. Information about the contribution of the mass transfer resistance in the external liquid film around the stationary phase to HETP was also obtained. Its contribution increases with an increase in the flow velocity of the mobile phase. It was concluded that the moment equations can provide more detailed information about the kinetic behavior in the columns than the van Deemter equation.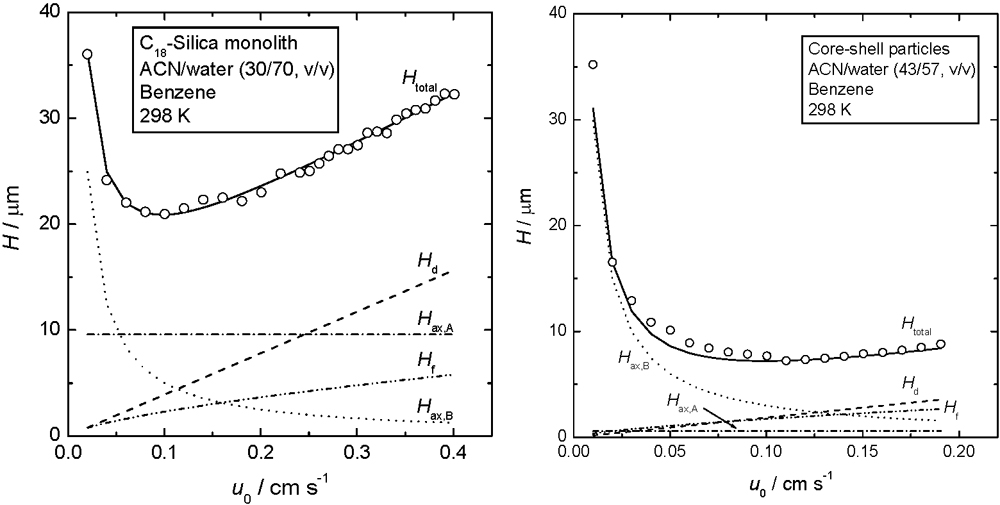 View full abstractDownload PDF (880K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (880K) -
New Support for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Based on Silica Coated with Alumina ParticlesJosé Leandro R. SILVEIRA, Samia R. DIB, Anizio M. FARIAArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 285-291
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new material based on silica coated with alumina nanoparticles was proposed for use as a chromatographic support for reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Alumina nanoparticles were synthesized by a sol-gel process in reversed micelles composed of sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl)sulfosuccinate, and the support material was formed by the self-assembly of alumina layers on silica spheres. Spectroscopic and 29Si nuclear magnetic resonance results showed evidence of chemical bonds between the alumina nanoparticles and the silica spheres, while morphological characterizations showed that the aluminized silica maintained the morphological properties of silica desired for chromatographic purposes after alumina incorporation. Stability studies indicated that bare silica showed high dissolution (∼83%), while the aluminized silica remained practically unchanged (99%) after passing one liter of the alkaline mobile phase, indicating high stability under alkaline conditions. The C18 bonded aluminized silica phase showed great potential for use in high-performance liquid chromatography to separate basic molecules in the reversed-phase mode. View full abstractDownload PDF (730K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (730K) -
Hyun Jin JUNG, Mi-Ri GWON, Jeonghyeon PARK, Jeong Ju SEO, Sook Jin SEO ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 293-298
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCyclosporine is an immunosuppressant drug used in organ transplants or for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. We developed and validated a simple, sensitive, and specific method using UPLC-MS/MS to determine cyclosporine levels in human whole blood. MS/MS detection was performed in the positive electrospray ionization mode with multiple reaction monitoring. Cyclosporine was extracted from whole-blood samples using ascomycin as an internal standard. The mass transitions m/z 1203.49 → 1185.53 and m/z 814.71 → 796.67 were used to assay the analyte and IS. This method was validated with respect to linearity, specificity, accuracy, precision, recovery, and stability. The method exhibited a linear response from 10 to 1000 ng mL−1 with correlation coefficient values >0.99. The precision and the accuracy values were within 15%, except at the lower limit of quatification (LLOQ). Cyclosporine was stable in whole blood with no evidence of degradation. This method was successfully applied to a pharmacokinetic study of cyclosporine in healthy volunteers following oral administration. View full abstractDownload PDF (1196K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1196K) -
Kohei UEMATSU, Yuto MINAMI, Shu TAIRA, Hajime KATANOArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 299-308
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe effects of the cationic polymer ε-poly-L-lysine (εPL) on the enzymatic reaction rate of glucose oxidase (GOD) with ferrocene derivatives having different ionic charges have been investigated by measuring the ferrocene derivative-mediated catalytic current of oxidation by GOD. When negatively charged ferrocenes were used, the bioelectrocatalytic current, which is related to the enzymatic reaction rate, was increased by the addition of εPL. On the other hand, the reaction rates with positively charged ferrocenes were decreased by εPL. These promotion and suppression effects of εPL were remarkable at a certain pH range, where εPL and GOD were charged positively and negatively, respectively. Within this range, the polycationic εPL would be adsorbed onto the GOD surface to enhance the electrostatic interactions of the enzyme with negatively charged substrates, and repulsion with positively charged ones. These findings should be important for practical applications of enzymes. View full abstractDownload PDF (766K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (766K)
Notes
-
Yusuke KANNO, Takehito GOTO, Kosuke INO, Kumi Y. INOUE, Yasufumi TAKAH ...Article type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 305-309
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA flexible sensor based on SU-8 photoresist was fabricated and its electrochemical performance was investigated using cyclic voltammetry. The device consisted of interdigitated array (IDA) electrodes on an SU-8 layer. It exhibited a clear electrochemical response during redox cycling of ferrocenemethanol at the IDA electrodes. Since the device was flexible, it could be inserted into a narrow bent space to monitor electrochemical responses. The observed electrochemical behavior was found to be consistent with that predicted by simulations based on redox compound diffusion. View full abstractDownload PDF (4182K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4182K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014Volume 30Issue 2 Pages 311
Published: February 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2401K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|