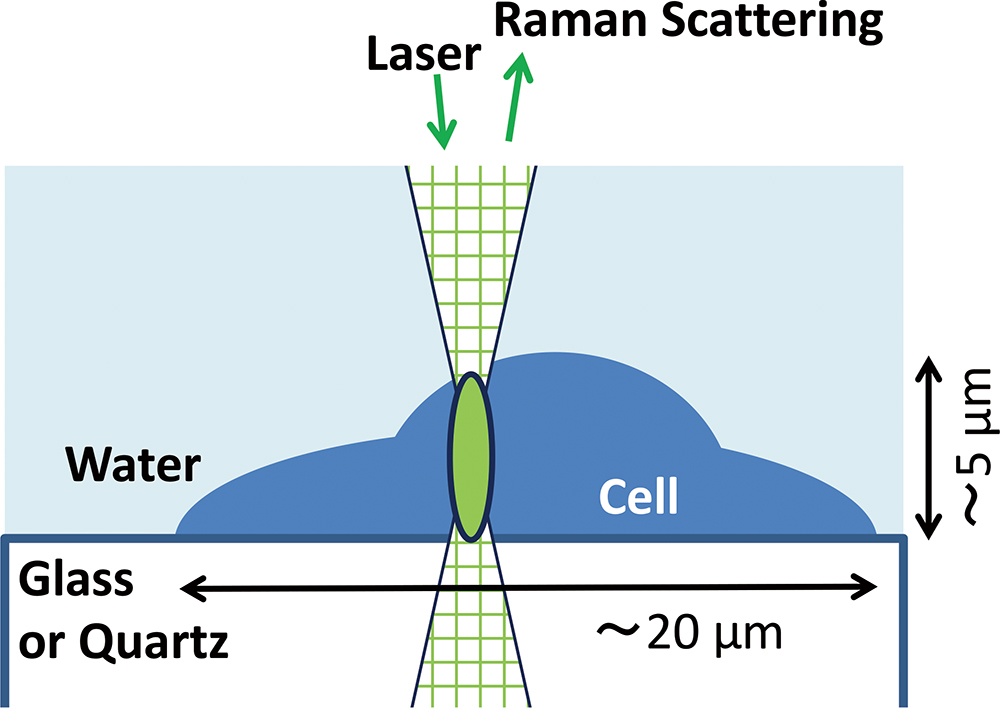
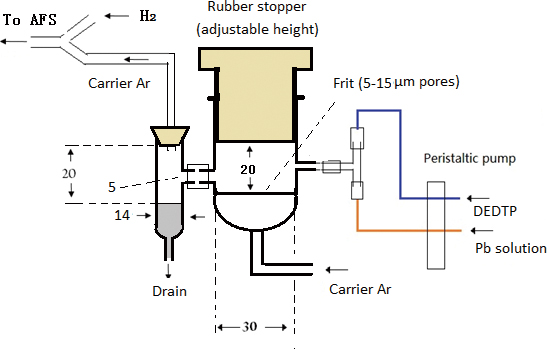
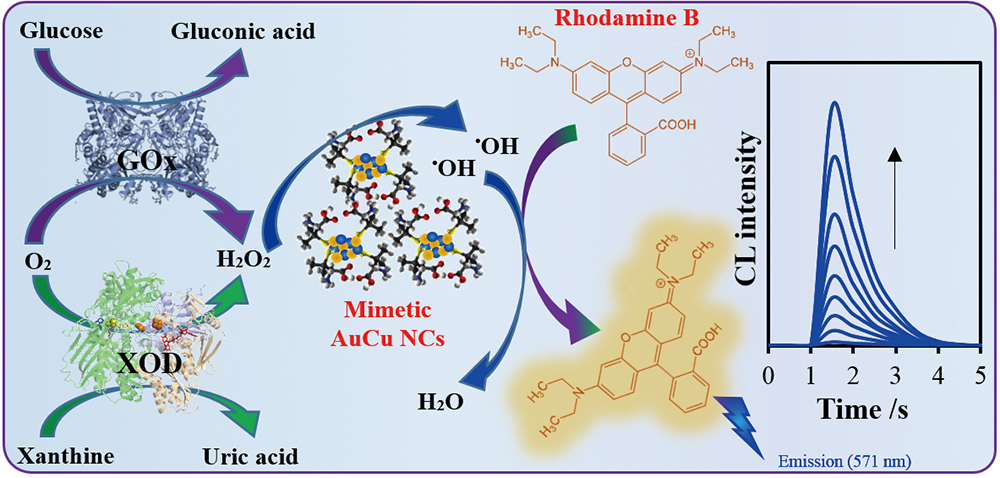
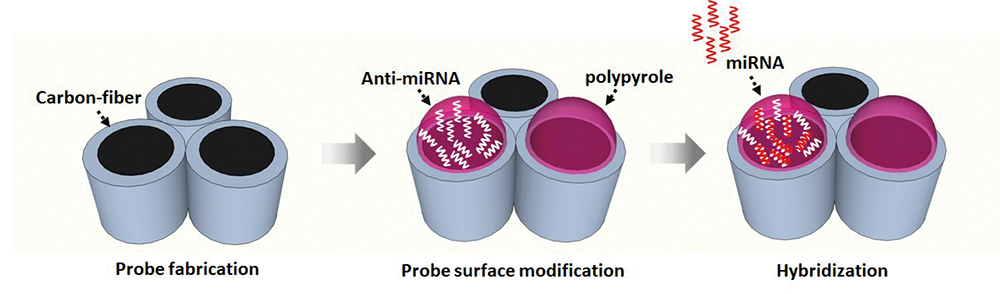
Volume 35, Issue 5
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 477
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Download PDF (78K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 479-491
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 25, 2019Download PDF (529K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 493-498
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 05, 2018Download PDF (1514K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 499-504
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 28, 2018Download PDF (164K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 505-509
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 28, 2018Download PDF (958K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 511-515
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 28, 2018Download PDF (160K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 517-520
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 28, 2018Download PDF (273K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 521-527
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 04, 2019Download PDF (1211K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 529-534
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 04, 2019Download PDF (1701K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 535-541
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 11, 2019Download PDF (797K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 543-550
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 18, 2019Download PDF (9553K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 551-556
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 18, 2019Download PDF (279K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 557-563
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 18, 2019Download PDF (304K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 565-569
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 25, 2019Download PDF (881K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 571-576
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 25, 2019Download PDF (1224K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 577-583
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 25, 2019Download PDF (520K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 585-588
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Download PDF (164K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 589-593
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 18, 2019Download PDF (921K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 595-598
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 18, 2019Download PDF (218K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2019Volume 35Issue 5 Pages 599
Published: May 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2019
Download PDF (1149K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|