All issues

Volume 32, Issue 8
Displaying 1-17 of 17 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Lori Shayne Alamo BUSA, Takeshi KOMATSU, Saeed MOHAMMADI, Masatoshi MA ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 815-818
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe report on the colorimetric oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) by hydrogen peroxide using horseradish peroxidase on photolithography-fabricated (P-PAD) and wax-printed (W-PAD) paper-based analytical devices. Fabricating PADs via photolithography exposes the hydrophilic areas to polymers (photoresists) and solvents, not only reducing the hydrophilicity, but also affecting the TMB–H2O2 assay system with an unavoidable incomplete elimination of photoresist during fabrication. Detection signals are then observed in the presence of photoresist residues on the P-PAD, even at a blank HRP concentration. View full abstractDownload PDF (750K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (750K)
Original Papers
-
Jingjing YAN, Xin HUANG, Shaopu LIU, Jidong YANG, Yusheng YUAN, Ruilin ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 819-824
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple, rapid and effective method for auramine O (AO) detection was proposed by fluorescence and UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy. In the BR buffer system (pH 7.0), AO had a strong quenching ability to the fluorescence of bovin serum albumin (BSA) by dynamic quenching. In terms of the thermodynamic parameters calculated as ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0, the resulting binding of BSA and AO was mainly attributed to the hydrophobic interaction forces. The linearity of this method was in the concentration range from 0.16 to 50 μmol L−1 with a detection limit of 0.05 μmol L−1. Based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), the distance r (1.36 nm) between donor (BSA) and acceptor (AO) was obtained. Furthermore, the effects of foreign substances and ionic strength were evaluated under the optimum reaction conditions. BSA as a selective probe could be applied to the analysis of AO in medicines with satisfactory results. View full abstractDownload PDF (2087K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2087K) -
Tadaharu UEDA, Takashi OKUMURA, Yukino TANAKA, Saki AKASE, Tomoko SHIM ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 825-830
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new method was developed to evaluate antioxidant activity based on the redox properties of polyoxometalates, which are partially reduced by antioxidants to generate a limiting potential. The polyoxometalates [PMo12O40]3−, [PVW11O40]4− and [SV2W10O40]4− formed in situ were used as electrochemical probes for the new evaluation method, and their formation conditions were optimized to evaluate the antioxidant activities of gallic acid, ellagic acid, catechin, quercetin, morin, trans-ferulic acid, sesamol, α-tocopherol, δ-tocopherol and L-ascorbic acid. The observed difference between initial potential and limiting potential (ΔE) were compared with spectrophotometrically evaluated antioxidant activities. In addition, the antioxidant capacities of five beverages (Japanese green tea, concentrated catechin-containing green tea, grapefruit juice, red wine and Japanese sake) were evaluated. View full abstractDownload PDF (650K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (650K) -
Erina KOHYAMA, Takao CHIKUMOTO, Hiroyuki TADA, Kiyoyuki KITAICHI, Tada ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 831-837
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSynthetic compounds structurally derived from the mild stimulant 2-amino-1-phenyl-1-propanone, known as cathinone derivatives, are one of the largest growing class of synthetic designer drugs. The characterization of these drugs is complicated by the structural diversity and similarity of compounds in the ever-growing cathinone family. This paper demonstrates the successful application of gas chromatography–electron ionization–tandem mass spectrometry (GC-EI-MS-MS) and liquid chromatography–photodiode array (LC-PDA) analysis to differentiate structurally similar derivatives including regioisomers of cathinones. Product ion spectrometry of iminium ions allows for an univocal differentiation of the studied cathinones with the same aminoalkyl moiety. Furthermore, the product ion spectrometry of acylium ions and ultraviolet spectra obtained by LC-PDA enabled differentiation of regioisomers resulting from different substitution patterns on the aromatic ring. The validity of the method was demonstrated by the analysis of N-alkylated ortho-, meta-, and para-alkylcathinones along with the scaffolds of buphedrones and pentiophenones. View full abstractDownload PDF (1031K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1031K) -
Akira TAKEDA, Hirofumi TSUKADA, Yuichi TAKAKU, Naoya SATTA, Mitsuhisa ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 839-845
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe developed a rapid, simple method for the iodine speciation analysis of water and applied it to natural water samples. Simultaneous determinations of I− and IO3− were achieved with an HPLC system with amperometric detection for I− and spectrophotometric detection after a postcolumn reaction for IO3−. We determined the I− and IO3− concentrations in 20-μL water samples within 10 min. Total I concentrations in water samples were determined after the decomposition of organics by off-line UV irradiation for 30 min, followed by reduction to I−. The analytical conditions were optimized by using test solutions rich in organic matter extracted from soils. We tested the new method with samples of groundwater, spring water, precipitation, soil percolate, stream water, and seawater as well as solutions extracted from soil. The method worked well, although the concentrations of some I species were below detection. This method is suitable for routine speciation analysis, which is important for studies of I behavior in the environment.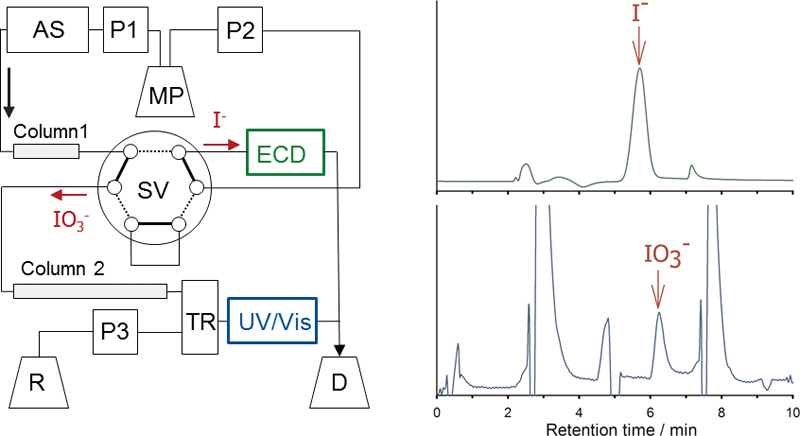 View full abstractDownload PDF (980K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (980K) -
Dalibor M. STANKOVIC, Eda MEHMETI, Kurt KALCHERArticle type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 847-851
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA boron doped diamond (BDD) electrode was investigated for use as an electrochemical sensor for α-lipoic acid (LA) using amperometric and differential pulse voltammetric detection. LA displays a well expressed oxidation peak at +0.9 V vs. Ag/AgCl in solutions with a pH value of 3. It was found that signals obtained are linearly related to the concentration range from 0.3 to 105 μM with detection limit of 0.088 μM. Interferences by common compounds such as ascorbic acid, uric acid and dopamine were tested and the method was successfully applied to the determination of LA in human body fluids where it gave recoveries in the range from 95 to 97%.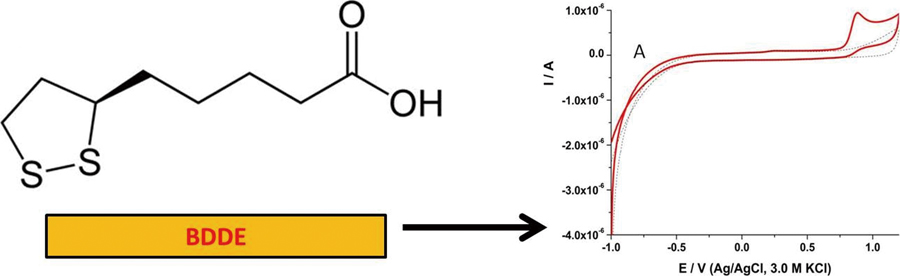 View full abstractDownload PDF (875K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (875K) -
Iku INABA, Hideki KURAMITZ, Kazuharu SUGAWARAArticle type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 853-859
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA reaction to casein, along with β-lactoglobulin, is a main cause of milk allergies, and also is a useful indicator of protein in allergic analyses. In the present study, a simple casein sensor was developed based on the interaction between a phosphate group of casein and electroactive [Ru(NH3)6]3+. We evaluated the voltammetric behavior of a casein-[Ru(NH3)6]3+ complex using a glassy carbon electrode. When the ruthenium(III) complex was combined with the phosphate groups of casein, the structure of the casein was changed. Since the hydrophobicity of casein was increased due to the binding, the casein was adsorbed onto the electrode. Furthermore, we modified an electrode with a ruthenium(III) ions/collagen film. When the sensor was applied to the detection of the casein contained in milk, the values coincided with those indicated by the manufacturer. Accordingly, this electrode could be a powerful sensor for the determination of casein in several foods. View full abstractDownload PDF (1390K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1390K) -
Wei LIU, Lian-kui DAIArticle type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 861-866
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRaman spectroscopy is adopted to detect the low-content benzene concentrations in gasoline products. Due to the peak overlap of benzene and other species in the gasoline spectrum, the associated statistical regression methods cannot make stable predictions unless there are enough training samples. To extend their extrapolation to small-size training sets, we propose the method of partial least squares based on a spectral pretreatment of interference peak subtraction (IPS-PLS). During the analysis, after spectral interpolation and baseline removal, we extract the benzene peak by interference peak subtraction (IPS), and then partial least squares (PLS) is applied to make a prediction. The experimental results demonstrate that, IPS can extract benzene information effectively, and help to decrease principal components needed by PLS, thus IPS-PLS is superior to direct PLS with small-size training sets, and depends less on the training sample distribution. Meanwhile, IPS-PLS can reach the standard of ASTM 3606-10 with the least of 9 training samples, while keeping its max predictive error less than 0.1254% (v/v), which shows promising prospects in gasoline quality test. View full abstractDownload PDF (1006K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1006K) -
Onur YAYAYÜRÜK, Emür HENDENArticle type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 867-873
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA selective matrix separation/enrichment method, utilizing a simple batch procedure with nickel/nickel boride (Ni/NixB) nanoparticles was proposed for the determination of inorganic mercury(II), Hg2+ and methyl mercury(I), CH3Hg+ in waters prior to cold vapor-atomic fluorescence spectrometry (CV-AFS). The Ni/NixB nanoparticles, were synthesized by the chemical reduction of Ni(II) to Ni/NixB. The novel adsorbent was selective to Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ species between pH values of 4 – 10. Both of the mercury species were recovered from the adsorbent using 1.0 mol L−1 hot HNO3 with high efficiency. It was observed that the adsorbent selectively removed Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ from the bulk solution in the presence of several competitor ions (As3+, Sb3+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ and Fe3+) with ≥96% adsorption. The limit of detection (3σ above blank) was found to be 1.8 ng L−1 with a preconcentration factor of 20. The validation of the method was tested through spike recovery experiments with several water samples (tap and seawater) at μg L−1 concentration levels, and all recovery values were found to vary between 95 and 105%. View full abstractDownload PDF (922K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (922K) -
Yuki INOUE, Yo TSUTAMOTO, Daiki MUKO, Kazuaki NANAMURA, Tsuyoshi SAWAD ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 875-880
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSpherical gold nanoparticles with cationic surfaces were prepared in hexadecyltrimethylammonium (CTA+) chloride (CTAC) and CTA+ bromide (CTAB) solutions. In a CTAC solution, ascorbic acid reduction of gold ions (AuCl4−) induced spontaneous nucleation of gold clusters, which resulted in the formation of small gold nanoparticles (<5 nm). In a CTAB solution, the combination of ascorbic acid and AuBr4− induced low spontaneous nucleation, and therefore controllable crystal growth of seed particles was possible. To obtain uniform gold nanoparticles, seed particles (<5 nm) were first prepared in a CTAC solution using NaBH4 as a reducing agent. Subsequent growth reactions of the seeds in CTAB solutions were controllable to obtain gold nanoparticles with diameters ranging from 7 to 60 nm. View full abstractDownload PDF (1096K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1096K) -
Levent ÖZCAN, Muhammet ALTUNTAS, Aysel BÜYÜKSAGIS, Hayr ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 881-886
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialPencil graphite electrodes modified with Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Fe(II) metallophthalocyaninetetrasulfonates (MePcTSs) were investigated for an electrochemical determination of bisphenol A (BPA). The electrochemical performances of the modified electrodes for different pH values in phosphate and the Britton–Robinson buffers were determined by cyclic voltammetry; the electrode performances were better in the Britton–Robinson buffer. NiPcTS and CoPcTS modifications of the electrodes had remarkable enhancements on their performances. The differential pulse voltammetry parameters for the electrodes were optimized, and we found that the electrochemical response versus the concentration of BPA is linear from 5.0 × 10−7 to 1.0 × 10−5 M for the NiPcTS and CoPcTS modified electrodes. The detection limits of these modified electrodes are 2.9 × 10−7 and 4.3 × 10−7 M, respectively, and the effects of interfering species are less than 5%. The results show that NiPcTS and CoPcTS modified pencil graphite electrodes could be used for electrochemical determinations of BPA for analytical purposes. View full abstractDownload PDF (821K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (821K) -
Bei Hua KANG, Na LI, Shi Gang LIU, Nian Bing LI, Hong Qun LUOArticle type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 887-892
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHerein is reported a simple and label-free fluorescent detection method for hemin based on using protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) as a fluorescent signal reporter. PPIX emits weak fluorescence in an aqueous solution. When PPIX binds to G-quadruplexes, the fluorescence intensity of PPIX is greatly increased. While in the presence of target hemin, hemin competes with PPIX toward G-quadruplexes because its affinity to G-quadruplexes is higher than that of PPIX. With the formation of the hemin-G-quadruplex complex, PPIX is released to the solution from the G-quadruplex accompanied by quenching of the fluorescence of the system. This fluorescence change of the system can be used to monitor hemin with a low detection limit of 36 nM. In addition, the possible binding sites for PPIX binding to the G-quadruplex are discussed based on competition between hemin and PPIX. What is more, this method might pave the way for applying G-quadruplexes and PPIX to more sensing systems.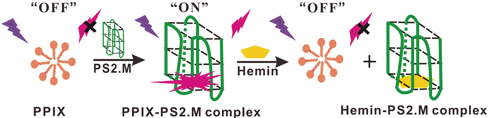 View full abstractDownload PDF (1178K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1178K) -
Ryoko TOMITA, Kenichiro TODOROKI, Hiroshi MARUOKA, Hideyuki YOSHIDA, T ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 893-900
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe performed a comprehensive quantification of 20 amino acids in RPMI 1640 medium-cultured human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells to evaluate the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil treatment under hypoxic and hypoglycemic conditions, which mimic the tumor microenvironment. In this study, we developed a simple and comprehensive analytical method by using LC-MS/MS connected to the Intrada amino acid column, which eluted amino acids within 9 min. The present method covered a linearity range of 3.6 – 1818 μM, except for Gly (227 – 1818 μM), Ala, Asp, His (7.1 – 1818 μM each), and Trp (3.6 – 909 μM). The limits of detection were in the range of 0.02 – 38.0 pmol per injection in a standard solution. Amino acid concentration data were analyzed using principal-component analysis to represent samples on two-dimensional graphs. Linear discriminant analysis was used to classify samples on the score plots. Using this approach, the effect of 5-fluorouracil treatment could be successfully discriminated at high discrimination rates. Moreover, several amino acids were extracted from corresponding loading plots as candidate markers for distinguishing the effects of the 5-fluorouracil treatment or tumor microenvironmental conditions. These results suggest that our proposed method might be a useful tool for evaluating the efficacy of anticancer drugs in the tumor microenvironment. View full abstractDownload PDF (1022K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1022K) -
Marco ROCCHICCIOLI, Roberta MOSCHINI, Laura CAPPIELLO, Francesco BALES ...Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 901-906
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA colorimetric coupled enzyme assay for the determination of cystathionine β-synthase activity is described. The method exploits cystathionine γ-lyase as an ancillary enzyme capable of transforming cystathionine, produced by cystathionine β-synthase, into cysteine. The cysteine is then spectrophotometrically detected at 560 nm, after its specific complexation with ninhydrin. This method was used to detect cystathionine β-synthase in crude extracts, and for the kinetic characterization of the enzyme partially purified from bovine kidney. A rapid two-step protocol is described for the partial purification of cystathionine γ-lyase from bovine kidney, aimed at a suitable and stable ancillary enzyme preparation.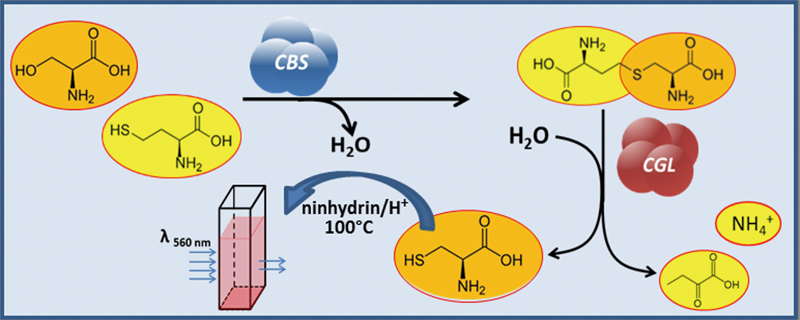 View full abstractDownload PDF (663K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (663K)
Notes
-
Hiroko KASAI, Masamichi NAKAKOSHI, Tomomi SUGITA, Mayu MATSUOKA, Yuzo ...Article type: Notes
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 907-910
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn order to discover new matrices suitable for the analyses of low molecular-weight compounds using positive-ion mode matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MS), 5-(3-trifluoromethylbenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione (3-CF3-BTD) was synthesized, and its effectiveness was compared with that when commercially available α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid was used. 3-CF3-BTD was sufficiently sensitive to analyze neurotransmitters, i.e., dopamine, serotonin, histamine, and epinephrine, in amounts of several picomoles. Similar to vacuum MALDI experiments, atmospheric-pressure MALDI-MS measurements using 3-CF3-BTD as a matrix also detected dopamine. View full abstractDownload PDF (1438K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1438K) -
Amanda TEROL, Monika MARCINKOWSKA, Francisco ARDINI, Marco GROTTIArticle type: Notes
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 911-915
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new method for the speciation analysis of arsenic in food using narrow-bore high-performance liquid-chromatography inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS) has been developed. Fast separation of arsenite, arsenate, monomethylarsonic acid and dimethylarsinic acid was carried out in 7 min using an anion-exchange narrow-bore Nucleosil 100 SB column and 12 mM ammonium dihydrogen phosphate of pH 5.2 as the mobile phase, at a flow rate of 0.3 mL min−1. A PFA-ST micronebulizer jointed to a cyclonic spray chamber was used for HPLC-ICP-MS coupling. Compared with standard-bore HPLC-ICP-MS, the new method has provided higher sensitivity, reduced mobile-phase consumption, a lower matrix plasma load and a shorter analysis time. The achieved instrumental limits of detection were in the 0.3 – 0.4 ng As mL−1 range, and the precision was better than 3%. The arsenic compounds were efficiently (>80%) extracted from various food samples using a 1:5 methanol/water solution, with additional ultrasonic treatment for rice products. The applicability of this method was demonstrated by the analysis of several samples, such as seafood (fish, mussels, shrimps, edible algae) and rice-based products (Jasmine and Arborio rice, spaghetti, flour, crackers), including three certified reference materials. View full abstractDownload PDF (663K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (663K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2016Volume 32Issue 8 Pages 917
Published: August 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2899K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|