All issues

Volume 30, Issue 8
Displaying 1-12 of 12 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Motoya SAKATO, Naoki HIRAYAMAArticle type: Rapid Communications
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 783-785
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the chelate extraction of zinc(II) into an ionic liquid (IL), 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (C4mimTf2N), with 8-(p-toluenesulfonamido)quinoline (Htsq), the co-existence of a certain amount of chloride anion in the aqueous phase resulted in an enhancement of the extractability. This enhancement did not occur at all in that into chloroform, a conventional organic extraction solvent. The specific synergistic effect was based on the dominant extraction of a neutral ternary complex, Zn(tsq)Cl, which is unstable in molecular organic solvents. View full abstractDownload PDF (600K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (600K)
Original Papers
-
Wanna WIMOLWATTANAPUN, Supamatthree BUNPRAPOB, Mang Dung HO, SUTISNA, ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 787-792
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSInstrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA) was applied for the accurate and precise determination of minor and trace elements in small-sized aliquants (1 to 2 mg) of two certified reference materials (CRM), NIES No. 8 and NIST 1632c. Four laboratories used either comparative- or k0-INAA, or both, and repeated the analysis more than ten times for each CRM. Based on z-scores and zeta scores of analytical data, QA/QC in analyzing such small scale of the two reference samples was assessed, revealing that there was a clear difference in the analytical ability among participating laboratories. It was concluded that the two CRM samples on the mg scale can be used as reference samples in INAA of a similarly small-scaled sample, at least for the 16 – 18 elements examined.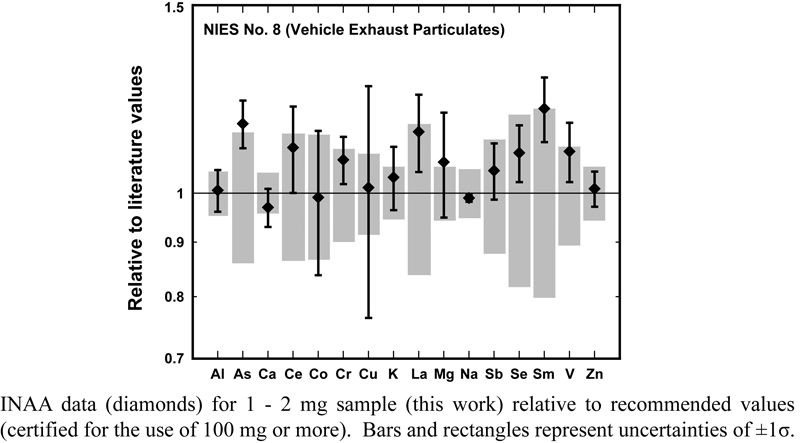 View full abstractDownload PDF (371K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (371K) -
Andrzej BURAKOWSKI, Jacek GLINSKIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 793-798
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSClassical acoustic acid-base titration was monitored using sound speed and density measurements. Plots of these parameters, as well as of the adiabatic compressibility coefficient calculated from them, exhibit changes with the volume of added titrant. Compressibility changes can be explained and quantitatively predicted theoretically in terms of Pasynski theory of non-compressible hydrates combined with that of the additivity of the hydration numbers with the amount and type of ions and molecules present in solution. It also seems that this development could be applied in chemical engineering for monitoring the course of chemical processes, since the applied experimental methods can be carried out almost independently on the medium under test (harmful, aggressive, etc.).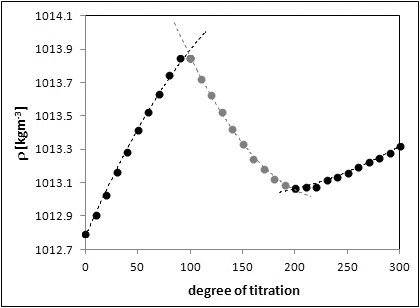 View full abstractDownload PDF (893K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (893K) -
Takeshi TAJIRI, Shuzo MATSUMOTO, Toshihiko IMATO, Toshihiro OKAMOTO, M ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 799-804
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe immobilized an antibody (anti-β-Galactosidase) on a polystyrene microsphere by using a covalent bond, and observed the resonance peaks in the scattered light intensity spectra related to the whispering gallery mode (WGM) excitation of the microsphere. The amount and the optical parameters, i.e., thickness and refractive index, of anti-β-Galactosidase on the sphere surface were evaluated based on an absorbance measurement and a resonance peak shift measurement, respectively. Moreover, we measured the variation of the WGM spectra depending on the concentration of the enzyme solution (β-Galactosidase), which allowed us to optically evaluate the thickness and the refractive index of the antigen–antibody layer from the shift of the WGM spectra peak. View full abstractDownload PDF (7519K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (7519K) -
Naoki UNO, Katsunori YANAGIHARAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 805-810
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) is a widely used technique for detecting genomic structural variants. The technique is based on hybridization and ligation, followed by amplification of the ligation products. Therefore, ligation is considered a fundamental process that determines the feasibility and fidelity of MLPA. However, despite the widespread use of this technique, its reaction mechanism has not been fully analyzed. Herein, we describe a ligation-independent pathway for MLPA and introduce a ligation-independent probe amplification system that can be used to obtain amplified products without the hybridization and ligation processes. Fragment analysis revealed that the ligation-independent pathway is functional and that the capacity to discriminate single nucleotides with MLPA does not depend on ligation. These findings indicate that the feasibility and fidelity of MLPA do not rely on ligation. View full abstractDownload PDF (1188K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1188K) -
Mei-Lan HONG, Li-Juan LI, Hui-Xia HAN, Xia CHUArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 811-815
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA label-free fluorescent assay for the detection of trypsin by using oligonucleotide-templated silver nanoclusters (Ag NCs) and cytochrome c (Cyt c) has been demonstrated. When negatively charged Ag NCs and positively charged Cyt c are mixed, they tend to form a hybrid complex, and then lead the fluorescence of Ag NCs to be quenched significantly due to electron transfer between Ag NCs and the heme cofactor of Cyt c. In the presence of trypsin, it catalyzes the hydrolytic cleavage of Cyt c to small peptide fragments, and releases the heme moiety from the Ag NCs/Cyt c complex; the quenched fluorescence restores therewith. By virtue of this specific response, the fluorescent biosensor has a linear range of from 0.7 to 4 μg mL−1 and from 9 to 120 μg mL−1 with a detection limit of 58.7 ng mL−1. Aside from the easy manufacture aspect, our method also possesses a high signal-to-background ratio (∼11), excellent selectivity and good biocompatibility, which makes it a promising bioanalysis for a trypsin activity assay. View full abstractDownload PDF (1397K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1397K) -
Xueling CAO, Lili LIAN, Hongwei LI, Yuqing WU, Dawei LOUArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 817-822
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the present study, biomolecule-stabilized Au nanoclusters were demonstrated as a novel fluorescence probe for sensitive and selective detection of pazufloxacin mesilate (PZFX) for the first time. The linear decrease in the fluorescence intensity of Au nanoclusters induced by PZFX allowed for the quantitative detection of PZFX in the range of 0.15 μg/mL to 1 mg/mL, and the detection limit for PZFX was 0.2 μg/mL. Circular dichroism spectroscopy and fluorescence decay studies were then performed to discuss the quenching mechanism. In addition, practical application of the present approach was also demonstrated for real samples, which suggested its great potential for accurate analysis of similar drugs. View full abstractDownload PDF (2441K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2441K) -
Salwa A. AHMED, Ezzat M. SOLIMANArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 823-831
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThree solid phase extractors based on silica coated magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4–SiO2) functionalized aliphatic diamines were synthesized. The magnetic core of Fe3O4 was synthesized first by the sol-gel method, then protected by a layer of silica using tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) followed by functionalization using three aliphatic diamines: 1,2-ethanediamine (1,2-EDA), 1,5-pentanediamine (1,5-PDA) and 1,8-octanediamine (1,8-ODA). These steps for producing the targeted three adsorbents Fe3O4–SiO2–1,2-EDA, Fe3O4–SiO2–1,5-PDA and Fe3O4–SiO2–1,8-ODA with different amines spacer arm were followed up using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectra and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The effect of the spacer arm length of the diamines on selective binding and metal capacity values of Cu(II) ions was studied as a function of the time needed to attain equilibrium under optimized conditions of pH, mass of adsorbent and initial concentration of Cu(II) ions. The order of increasing metal capacity for copper ions using magnetic nano-adsorbents was Fe3O4–SiO2–1,2-EDA < Fe3O4–SiO2–1,5-PDA < Fe3O4–SiO2–1,8-ODA at 5 s equilibrium time. View full abstractDownload PDF (895K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (895K) -
Ana C. F. VIDA, Elias A. G. ZAGATTOArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 833-838
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn flow-based analytical procedures requiring heating, liberation of air bubbles is avoided by trapping a sample selected portion into a heated hermetic environment. The flow-through cuvette is maintained into a temperature-controlled aluminium block, thus acting as the trapping element and allowing real-time monitoring. The feasibility of the innovation was demonstrated in the spectrophotometric catalytic determination of vanadium in mineral waters. Air bubbles were not released even for temperatures as high as 95°C. The proposed system handles about 25 samples per hour, requires only 3 mg p-anisidine per determination and yields precise results (r.s.d. = 2.1%), in agreement with ICP-MS. Detection limit was evaluated (3.3 σ criterion) as 0.1 μg L−1 V. View full abstractDownload PDF (528K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (528K) -
Isao NADAOKA, Emi HATAKEYAMA, Chihiro TANADA, Tasuku SAKAMOTO, Shinich ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 839-844
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe developed a rapid and useful routine screening assay for total L-carnitine content in various infant formulas and materials by liquid chromatography coupled with a tandem mass spectrometric method (LC-MS/MS) and alkaline hydrolysis. For separation of L-carnitine, a multi-mode octadecylsilane (ODS) column was used that contained ODS ligands, anion ligands, and cation ligands to avoid using ion-pairing agents. The stable isotope L-carnitine-d3 (m/z 165 → 103/85) was used in electrospray MS/MS in the multiple reaction monitoring mode with the ion transitions of m/z 162 → 103/85 for detection and quantitation of L-carnitine. Alkaline hydrolysis of short/medium chain (C2 – C15) acyl-L-carnitines in infant formula was analyzed by LC with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QTOF-MS). The majority of short/medium chain acyl-L-carnitines were hydrolyzed to free L-carnitine. The overall standard deviations for L-carnitine in infant formula, follow-up formula and raw materials ranged from 2.1 to 4.0. The overall mean recoveries ranged from 90.2 to 94.2%.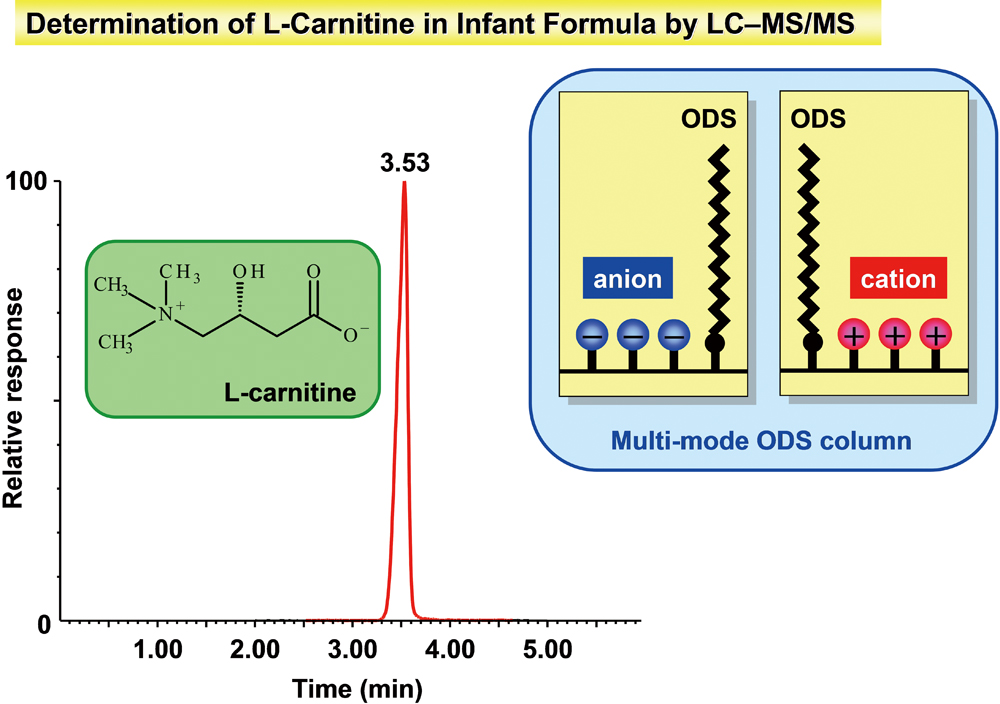 View full abstractDownload PDF (531K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (531K)
Notes
-
Koki HARIGAYA, Hiroyuki YAMADA, Shingo HORIMOTO, Hiroyuki NISHI, Jun H ...Article type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 845-850
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPhenylhydrazine is a genotoxic impurity commonly used as a raw material in active pharmaceutical ingredients. In this study, a novel method, using inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry combined with two-dimensional liquid chromatography (LC-ICP-MS), was employed for the quantitation of residual phenylhydrazine in antipyrine. The compound 2,3,5-triiodobenzoyl chloride, which contains three iodine atoms, was investigated as a derivatization reagent. The DL 0.06 ppm was obtained, and the method was applied to the quantitation of residual phenylhydrazine in antipyrine. No residual phenylhydrazine was detected in five lots of antipyrine obtained from the commercial source. View full abstractDownload PDF (684K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (684K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014 Volume 30 Issue 8 Pages 851
Published: August 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2581K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|