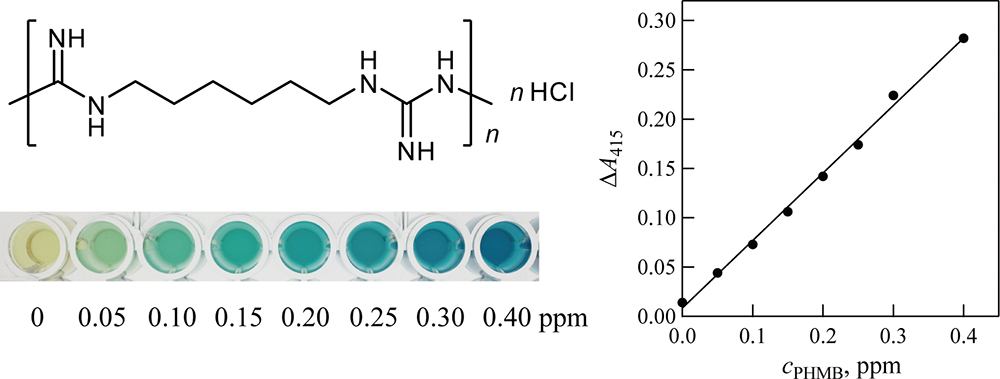
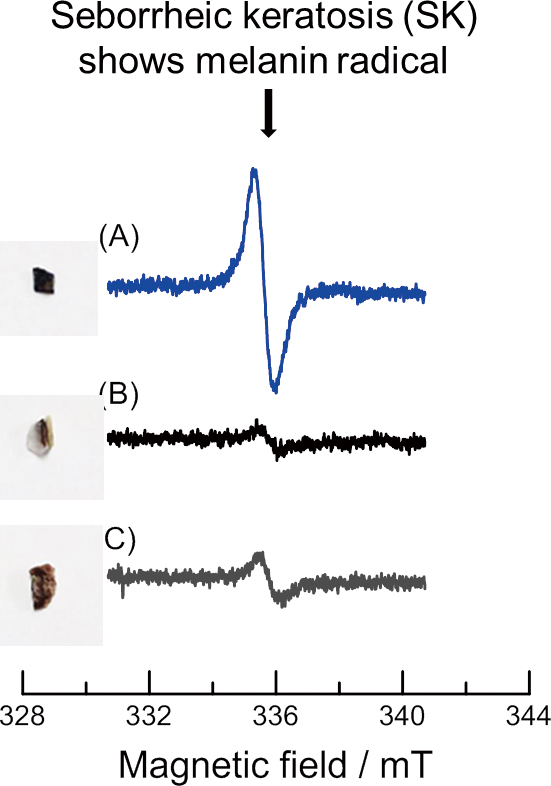
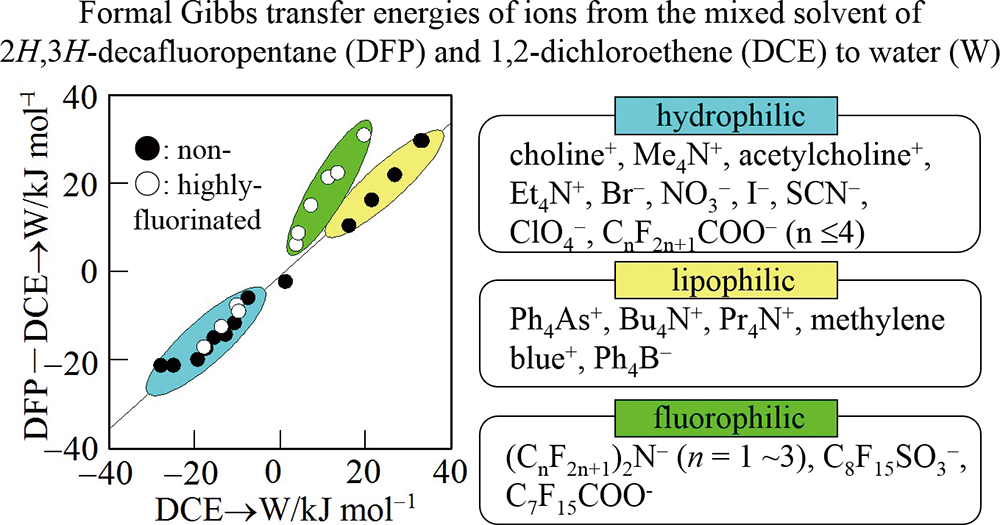
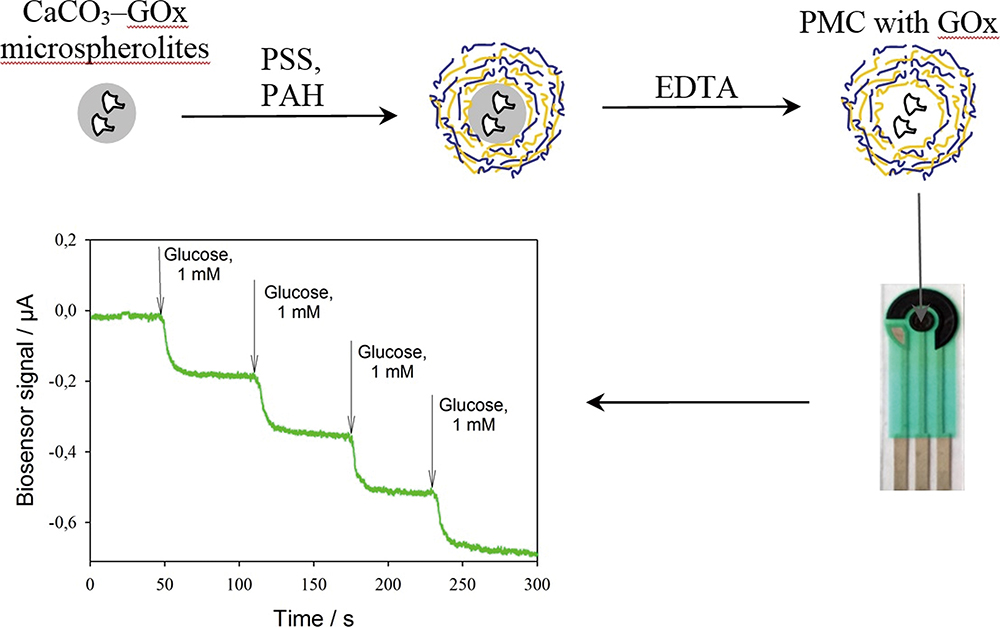
Volume 35, Issue 9
Displaying 1-19 of 19 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 949-950
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Download PDF (291K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 951-954
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 06, 2019Download PDF (2069K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 955-960
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 04, 2019Download PDF (1050K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 961-966
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 03, 2019Download PDF (370K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 967-972
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 10, 2019Download PDF (1625K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 973-978
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 10, 2019Download PDF (698K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 979-985
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 10, 2019Download PDF (1700K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 987-993
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 17, 2019Download PDF (1905K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 995-1001
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 24, 2019Download PDF (1823K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1003-1007
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 24, 2019Download PDF (611K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1009-1013
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 24, 2019Download PDF (608K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1015-1020
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 24, 2019Download PDF (517K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1021-1025
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 24, 2019Download PDF (465K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1027-1030
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 31, 2019Download PDF (401K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1031-1035
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 31, 2019Download PDF (325K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1037-1043
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 31, 2019Download PDF (572K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1045-1051
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 07, 2019Download PDF (651K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1053-1056
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 07, 2019Download PDF (427K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2019Volume 35Issue 9 Pages 1057
Published: September 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2019
Download PDF (1122K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|