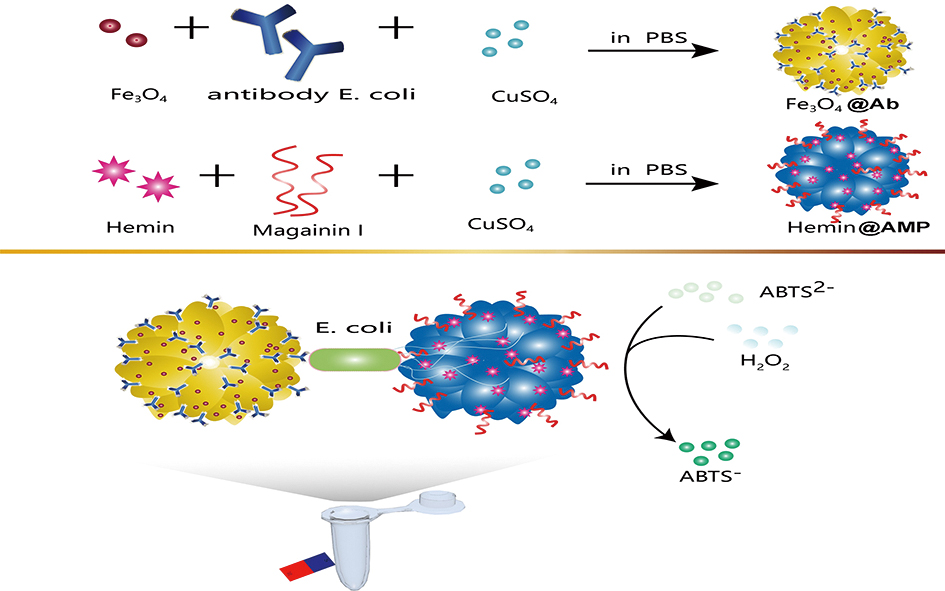
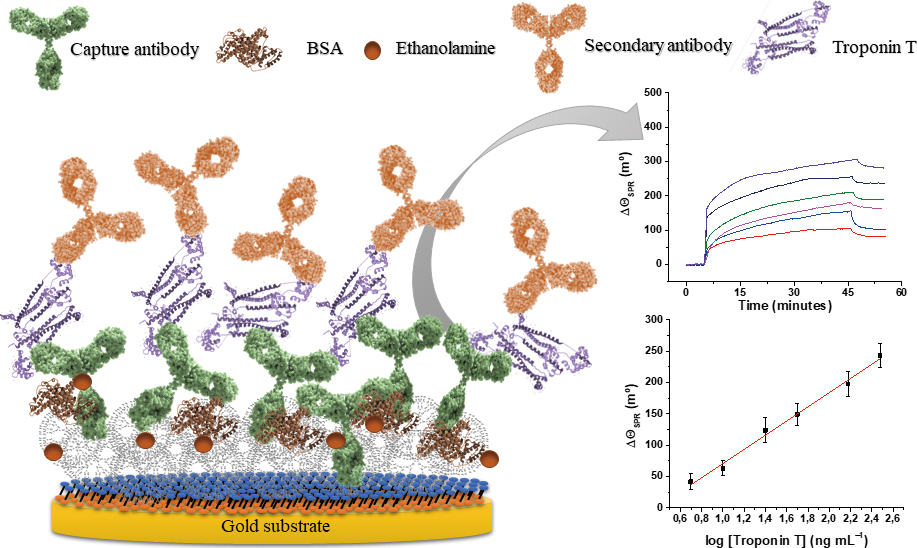
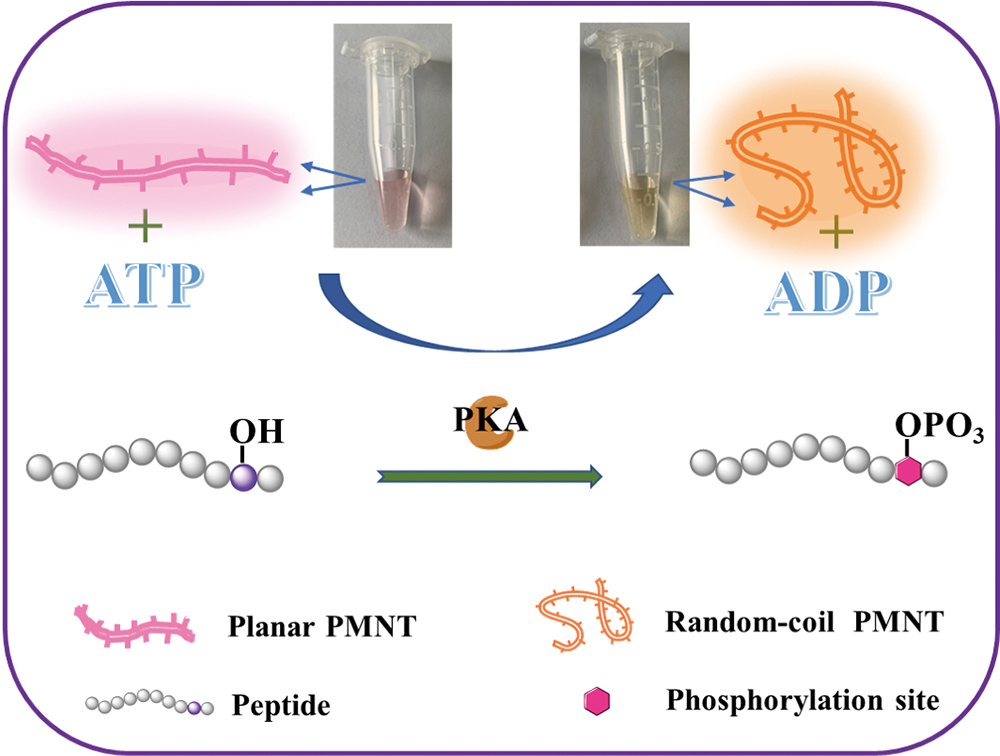
Volume 37, Issue 7
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 927-928
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Download PDF (96K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 929-940
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 30, 2020Download PDF (4286K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 941-947
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 04, 2020Download PDF (656K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 949-954
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 06, 2020Download PDF (781K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 955-962
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 13, 2020Download PDF (1680K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 963-969
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 20, 2020Download PDF (1072K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 971-976
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 27, 2020Download PDF (879K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 977-984
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 04, 2020Download PDF (448K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 985-990
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 04, 2020Download PDF (411K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 991-995
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 04, 2020Download PDF (1669K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 997-1001
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 11, 2020Download PDF (436K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1003-1006
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 11, 2020Download PDF (337K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1007-1013
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 08, 2021Download PDF (476K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1015-1021
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 15, 2021Download PDF (972K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1023-1027
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 16, 2020Download PDF (1383K) -
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1029-1032
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 13, 2020Download PDF (3812K) -
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1033-1037
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 27, 2020Download PDF (146K) -
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1039-1043
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 27, 2020Download PDF (542K) -
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1045-1048
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 11, 2020Download PDF (331K) -
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1049-1052
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 18, 2020Download PDF (215K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2021 Volume 37 Issue 7 Pages 1053
Published: July 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2021
Download PDF (204K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|