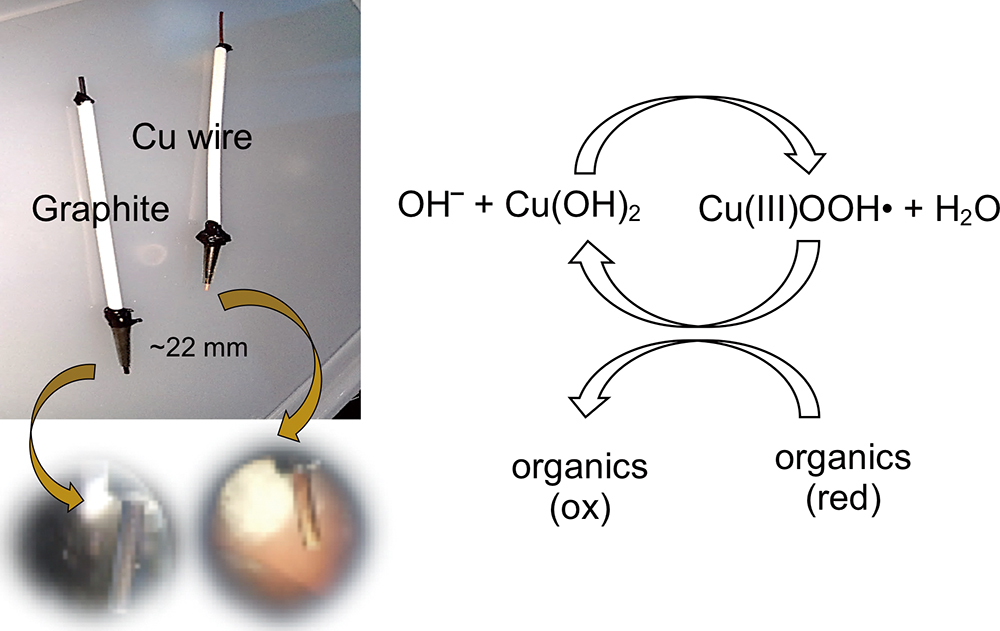
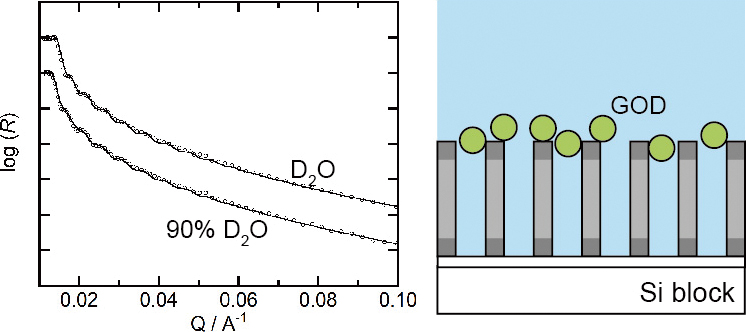
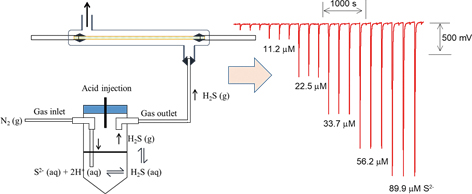
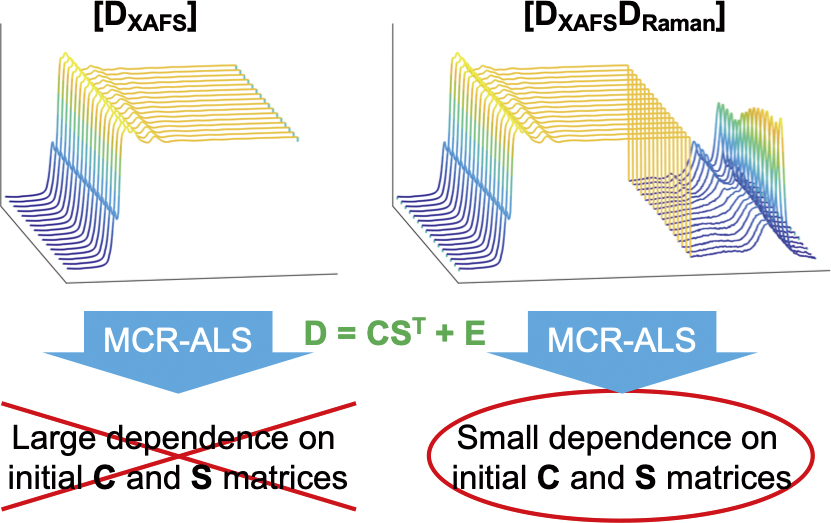
Volume 36, Issue 11
Displaying 1-22 of 22 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1295
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Download PDF (113K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1297-1302
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 05, 2020Download PDF (1170K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1303-1309
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 05, 2020Download PDF (575K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1311-1315
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 05, 2020Download PDF (1092K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1317-1322
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 12, 2020Download PDF (488K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1323-1330
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 12, 2020Download PDF (2222K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1331-1336
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 12, 2020Download PDF (593K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1337-1343
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 19, 2020Download PDF (1259K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1345-1352
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Download PDF (953K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1353-1358
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 03, 2020Download PDF (292K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1359-1364
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 10, 2020Download PDF (563K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1365-1369
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 10, 2020Download PDF (736K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1371-1378
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 10, 2020Download PDF (1490K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1379-1385
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 10, 2020Download PDF (567K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1387-1391
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 17, 2020Download PDF (196K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1393-1399
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 24, 2020Download PDF (162K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1401-1406
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 24, 2020Download PDF (667K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1407-1413
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 24, 2020Download PDF (3893K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1415-1421
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 24, 2020Download PDF (2021K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1423-1426
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 05, 2020Download PDF (422K) -
Article type: Notes
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1427-1430
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 24, 2020Download PDF (180K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2020 Volume 36 Issue 11 Pages 1431
Published: November 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2020
Download PDF (72K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|