
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Tomohiro UCHIMURAArticle type: Highlights
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 285-286
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Nobumitsu OIDE, Taro UEDA, Kai KAMADA, Takeo HYODO, Yasuhiro SHIMIZUArticle type: Rapid Communications
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 287-290
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 07, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSToluene-sensing properties of mixed-potential type yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ)-based sensors attached with a thin CeO2-added Au sensing electrode (SE, CeO2 content: 4 – 16 mass%, thickness: 30 – 100 nm), which was fabricated by using a spin-coating method, were examined and the effects of their SE thickness and the additive amount of CeO2 on their toluene response were discussed in this study. The toluene response of the sensors attached with a 16 mass% CeO2-added Au SE increased with an increase in the SE thickness, and the sensor attached with the thickest 16 mass% CeO2-added Au SE showed the largest response, among all the sensors tested. This behavior probably arises from the increase in the number of active sites for electrochemical toluene oxidation in the CeO2-added Au SE.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2202K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2202K)
-
Kuniaki NAGAMINE, Ayako NOMURA, Yusuke ICHIMURA, Ryota IZAWA, Shiori S ...Article type: Reviews
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 291-302
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 03, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis review describes recent advances in biosensors for non-invasive human healthcare applications, especially focusing on sweat analysis, along with approaches for fabricating these biosensors based on printed electronics technology. Human sweat contains various kinds of biomarkers. The relationship between a trace amount of sweat biomarkers partially partitioned from blood and diseases has been investigated by omic analysis. Recent progress in wearable or portable biosensors has enabled periodic or continuous monitoring of some sweat biomarkers while supporting the results of the omic analysis. In this review, we particularly focused on a transistor-based biosensor that is highly sensitive in quantitatively detecting the low level of sweat biomarkers. Furthermore, we showed a new approach of flexible hybrid electronics that has been applied to advanced sweat biosensors to realize fully integrated biosensing systems wirelessly connected to a networked IoT system. These technologies are based on uniquely advanced printing techniques that will facilitate mass fabrication of high-performance biosensors at low cost for future smart healthcare.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1185K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1185K)
-
Wuye YANG, Wenming WANG, Ruoqiu ZHANG, Feiyu ZHANG, Yinran XIONG, Ting ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 303-309
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, a new variable selection method, named moving-window partial least-squares coupled with sampling error profile analysis (SEPA-MWPLS), is developed. With a moving window, moving-window partial least-squares (MWPLS) is used to find window intervals which show low residual sums of squares (RSS) of a calibration set. Sampling error profile analysis (SEPA) is a useful method based on Monte-Carlo Sampling and profile analysis for cross validation (CV). By combining MWPLS with SEPA, we can obtain more stable and reliable results. Besides, we simplify the plot of the RSS line so that it is easier to determine the informative intervals. In addition, a backward elimination strategy is used to optimize the combination of subintervals. The performance of SEPA-MWPLS was tested with two near-infrared (NIR) spectra datasets and was compared with PLS, MWPLS and Monte Carlo uninformative variable elimination (MC-UVE). The results show that SEPA-MWPLS can improve model performances significantly compared with MWPLS in the number of variables, root-mean-squared errors of CV, calibration and prediction (RMSECVs, RMSECs and RMSEPs). Meanwhile it also exhibits better performances than MC-UVE.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (794K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (794K) -
Tianlai XIA, Yuan GAO, Ling ZHANG, Xinyu WANG, Guangxing PAN, Zhenyuan ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 311-316
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe electrooxidation of phenolic groups of caffeic acid and rutin promote anodic electrochemiluminescence (ECL) luminol substantially. A sensitive, and cost-effective ECL method has thus been developed to detect caffeic acid, ranging from 0.1 to 5.0 μM, with a detection limit of 0.1 μM and rutin ranging from 0.2 to 25 μM with a detection limit of 0.12 μM. Contrarily, phenolic compounds quench the weak cathodic ECL of luminol. Both of anodic and cathodic ECL mechanisms of luminol in the presence of phenolic compounds are analyzed. The method based on the boomed anodic ECL of luminol is comparable to those based on Ru(bpy)32+ and S2O82−/O2 systems. A lower onset potential and price than the other ECL reagents would realize its widely applications in the detection of phenolic compounds in food and medicine.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (929K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (929K) -
Ali MEHDINIA, Maede SALAMAT, Ali JABBARIArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 317-322
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 18, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, amino groups were directly coated on reduced graphene oxide sheets and applied for the extraction of cadmium(II) ions from well water, aqueduct (water coming from mountain), lentils and rice prior to measurements by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The properties of the adsorbent were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and a vibrating sample magnetometer. Some parameters related to the adsorption and desorption stages were optimized. After preconcentration, the linear determination range of cadmium(II) was 0.5 – 40 μg L−1. The limit of quantification, relative standard deviation and preconcentration factor were obtained as 0.5 μg L−1, 0.39 – 2.18% and 100, respectively.
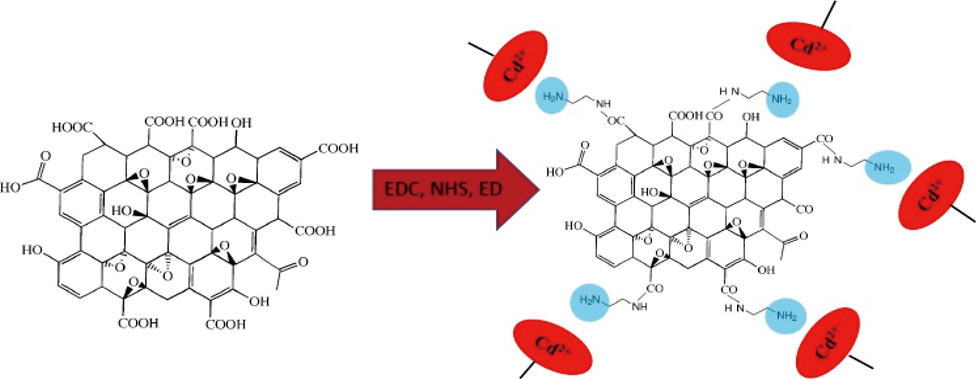 View full abstractDownload PDF (2255K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2255K) -
Yanan LI, Xiaoming WU, Shaoxiang YANG, Sen LIANG, Hongyu TIAN, Baoguo ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 323-327
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 18, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA natural light visible colorimetric responses fluorescent probe (Probe 1) was developed for N2H4 detection. The recognition mechanism of Probe 1 for hydrazine is based on addition-cyclization. The LOD of Probe 1 for N2H4 was 80.3 nM (0.0026 mg/L), which is below the national limited standard (0.02 mg/L). When various concentrations of N2H4 were added, the color of the Probe 1 solution was graded gradually from yellow to colorless, which could be observed under natural light. The changing course only takes 5 min. Furthermore, Probe 1 was successful applied to detect N2H4 in mineral water, seawater, tap water and river water. The obtained recovery ranged from 91.91 – 100.00%. Probe 1 has great potential, developed as a visual tool for N2H4 rapid detection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (965K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (965K) -
Chao ZHAO, Jinyan SHANG, Heping LI, Chunsong YANG, Zhiwei LI, Jingheng ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 329-333
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 18, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe content of sulfur dioxide derivatives in cells is closely related to life and health. Therefore, it is essential to detect the content of sulfur dioxide derivatives in cells under physiological conditions to ensure life and health. In this paper, a novel sulfur dioxide derivative fluorescent water-soluble probe ((E)-1,1,3-trimethyl-2-(2-(naphthalen-1-yl)vinyl)-1H-3λ4-benzo[e]indole, TNB) was synthesized by using naphthalene formaldehyde (1) and 1,1,2,3-tetramethyl-1H-3λ4-benzo[e]indole (2) as raw materials. Based on the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) mechanism of the naphthalene ring to benzoindole, TNB exhibits very weak fluorescence emission in PBS buffer (pH 7.4). The olefin unit of TNB can be combined with HSO3−/SO32− with high selectivity to make the π–π conjugate interrupt. ICT is blocked, TNB produces a strong fluorescence emission, and the color visible to the naked eye changes from yellow to colorless. The effect of TNB on HSO3−/SO32− can be completed in 40 s, the fluorescence intensity is increased by 91 times, and the detection limit is as low as 0.089 μM. It is expected to be able to rapidly detect low levels of sulfur dioxide derivatives in cells, which has important application prospects in maintaining life and health.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (740K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (740K) -
Shiro MIYAKE, Yuki HIRAKAWA, Tomomi YAMASAKI, Eiki WATANABE, Ayako HAR ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 335-340
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 18, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSix pesticides, azoxystrobin, boscalid, chlorfenapyr, imazalil, isoxathion, and nitenpyram, were simultaneously detected by using a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) immunosensor. The working ranges were 3.5 – 19 ng/mL for azoxystrobin, 4.5 – 50 ng/mL for boscalid, 2.5 – 25 ng/mL for chlorfenapyr, 5.5 – 50 ng/mL for imazalil, 3.5 – 50 ng/mL for isoxathion, and 8.5 – 110 ng/mL for nitenpyram. They showed adequate recovery results in tomato samples: 104 – 116% for azoxystrobin, 94 – 101% for boscalid, 90 – 112% for chlorfenapyr, 96 – 106% for imazalil, 107 – 119% for isoxathion, and 104 – 109% for nitenpyram. The correlation coefficient with liquid chromatography (HPLC or LC-MS/MS) using vegetable samples also agreed well: 0.91 – 0.99 as R2 without strong bias, except for nitenpyram for which the SPR immunosensor sensitivity was too low. The SPR immunosensor will have high applicability for pesticide residue analyses in vegetable samples.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (858K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (858K) -
Lin WU, Ya-Nan YAO, Zi-Cheng YUAN, Dandan DI, Lei LI, Bin HUArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 341-346
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 25, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDirect characterization of native protein binding to ligands in raw biological samples is a challenging task, because the ligand solution might induce proteins to aggregation, flocculation and denaturation. In this work, we developed a reactive wooden-tip electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) for formation and characterization of protein-ligand complexes upon rapid mixing in electrospray droplets. Raw viscous hen egg white (HEW) was directly loaded onto a wooden tip to induce spray ionization, and sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) solution was directly loaded into the HEW spray by a pipette tip, and thus lysozyme-DS complexes were then formed in the electrospray droplets and were detected subsequently by mass spectrometry. The new approach was successfully applied to investigate interaction of SDS and native lysozyme in electrospray droplets of standard solution and raw egg white. Our results showed that wooden-tip ESI-MS is a promising method to form and characterize protein-ligand complexes.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1036K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1036K) -
QiaoQin YU, YanYan ZHAO, WenJing DENG, TingTing CHEN, Xia CHUArticle type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 347-352
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 25, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialGlutathione (GSH) plays an important role in cells, which is an essential endogenous antioxidant. Here, we have developed a new detection platform to analyze GSH levels. In our system, fluorescent polydopamine (PDA) nanoparticles, as signal indicators, were obtained by oxidation through cobalt oxyhydroxide (CoOOH) nanosheets. When CoOOH was present, CoOOH could quickly oxidize dopamine to fluorescent PDA nanoparticles. However, once GSH existed, CoOOH nanosheets were decomposed into Co2+, and oxidation between CoOOH and dopamine was prevented with weaker fluorescence occurring. Thus, we could realize detection of the GSH concentration according to the decreased fluorescence value of the fluorescent polydopamine. This method provides a fast, simple, high sensitivity and desirable selectivity platform for GSH monitoring.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1230K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1230K) -
Sifan XU, Shuqi YE, Yunhui XU, Feifan LIU, Yushun ZHOU, Qian YANG, Hai ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 353-360
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 25, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTo achieve a rapid, sensitive, and economical method for the detection of ascorbic acid (AA) in the presence of Fe3+, a nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots (N,S-co-CDs) based fluorescence sensing system was developed. In this work, N,S-co-CDs were successfully synthesized via a one-step microwave-assisted method within 2.5 min using ammonium citrate and L-cysteine as precursors. The fluorescence of N,S-co-CDs was quenched (off ) by Fe3+ through a static-quenching mechanism. Subsequently, the fluorescence was recovered (on) after introducing AA into the quenched system, which was attributed to the reduction effect of AA for Fe3+. Therefore, a switch-on sensor (N,S-co-CDs/Fe3+ system) was developed for AA detection. Under optimal conditions, the limit of detection (LOD) of 2.31 μmol/L for AA was obtained over a linear range from 0 to 150 μmol/L. Furthermore, the proposed sensing method was successfully applied to detect AA in processed fruit juice with satisfactory results. The most important is that the sensor derived from a microwave-assisted method has simple and eco-friendly synthesis processes, is rapid, and has high detection efficiency. Therefore, such a switch-on sensor may be a promising candidate sensor for AA detection in processed fruit samples.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1886K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1886K) -
Muhammad Naeem KHAN, Waqar ALI, Zarbad SHAH, Muhammad IDREES, Hussain ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 361-366
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: November 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis research work presents a simple, sensitive, selective, economic, and widely applicable and interferences-free spectrofluorimetric method estimating moxifloxacin in the pure form, commercial formulations and biological samples. The method is based on the reaction of moxifloxacin with Ce(IV) in an acidic medium to generate fluorescent active species Ce(III). The excitation and emission of the fluorescent species are 250 and 362 nm, respectively. Different variables that might influence the oxidation of moxifloxacin, including the Ce(IV) concentration and volume, the effect of temperature and the heating time, the type of acids and its concentration were analyzed and boosted. The linearity was observed in the concentration range of 0.2 – 5.0 μg mL−1 with a correlation coefficient of 0.9991. The limit of detection and the limit of quantification were calculated and observed to be 0.016 and 0.056 μg mL−1 respectively. The effects of the common excipients and some co-administrated drugs usually used in the determination of moxifloxacin were investigated, and no interferences were noted. The planned method has been successfully practical for the analysis of moxifloxacin in its pure form, in pharmaceutical products and in biological samples. The obtained percent recoveries ranged from 95.50 to 101.37% for pharmaceutical products and from 95.15 to 103.18% for human blood plasma and urine.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (524K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (524K) -
Xingyu TONG, Ting YE, Yali YU, Longlong GAO, Yifan FEI, Qingqing ZHANG ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 367-372
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: November 01, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNatural sanguinarine (SG) was first used as a fluorescent probe to develop a novel ratiometric sensor for selective HSO3− detection. The nucleophilic addition reaction of HSO3− occurs at the C=N+ group of SG, and subsequent breakage of the conjugated π cycle leads to a decrease in the SG iminium fluorescence that is accompanied by an increase in the alkanolamine fluorescence. Therefore, a ratiometric fluorescence method with a large wavelength shift can be established for HSO3− detection. Furthermore, cucurbit[8]uril was used as an efficient host to encapsulate SG for an improved selectivity for HSO3− detection over H2S. Our method benefits include little interference from other common anions and cations for HSO3− detection, suggesting a promising application in real sample analysis. Besides sensor development, the interaction of the natural SG with HSO3− was first demonstrated in this work to further get an insight into SG’s pharmacology.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (697K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (697K) -
Yifan CHEN, Shu-Ping HUI, Yusuke MIURA, Sota KATO, Toshihiro SAKURAI, ...Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 373-378
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: November 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCholesteryl ester (CE) is an ester of cholesterol and fatty acid (FA). Plasma CE reflects complicated metabolisms of cholesterol, phospholipids, lipoproteins, and dietary FAs. An informatics approach could be useful for analysis of the CE species. In this study, two basic dimension reduction methods, principal component analysis (PCA) and factor analysis, were applied to serum CE species determined by LC-MS/MS in a Japanese population (n = 545). PCA and factor analysis both reflected the size (concentration), food source, fat solubility, and biological aspect of the CE species. In a comparison between PCA (PC4) and factor analysis (factor 4), the latter was found to be more suggestive from a biological aspect of n-6 FAs. Cholesteryl docosahexaenoate (DHA) was found to be unique by a factor analysis, possibly relevant to the unique accumulation of DHA in the brain. An informatics approach, especially factor analysis, might be useful for the analysis of complicated metabolism of CE species in the serum.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (393K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (393K)
-
Ryota SATO, Ryo YAMADA, Takashi MASADOMEArticle type: Notes
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 379-383
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: November 08, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA flow-injection analysis (FIA) method for assaying an anionic surfactant (AS) using AS optode detector was demonstrated. The optode membrane consists of 2-nitrophenyl octyl ether as a plasticizer, lactone form rhodamine B (L-RB) and poly(vinyl chloride). The linear response concentration range of the AS optode to AS was 20 – 100 μmol dm−3 in the FIA system. The sampling rate for an AS ion (40 μmol dm−3 sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate) in the proposed FIA system was ca. 5 samples h−1. The AS level in commercially available laundry detergents by the proposed FIA system was determined.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (376K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (376K) -
Tsutomu SUGIHARA, Masayasu MIE, Eiry KOBATAKEArticle type: Notes
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 385-387
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
Advance online publication: November 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA fusion protein, designated ELP-D-C, comprised of a hydrophobic elastin-like polypeptide unit, a hydrophilic aspartic acid-rich peptide unit, and an antibody-binding domain as a functional unit, was constructed. Upon heat induction, ELP-D-C forms micellar nanoparticles displaying antibody-binding domains on their surfaces. The protein nanoparticles were able to incorporate hydrophobic fluorescent compounds and subsequently detect target molecules via antibody binding by the resulting fluorescence intensity, which was proportional to the log of the concentration of the target molecule.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (261K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (261K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 389
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (194K)
-
Article type: Errata
2020 Volume 36 Issue 3 Pages 393
Published: March 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (29K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
