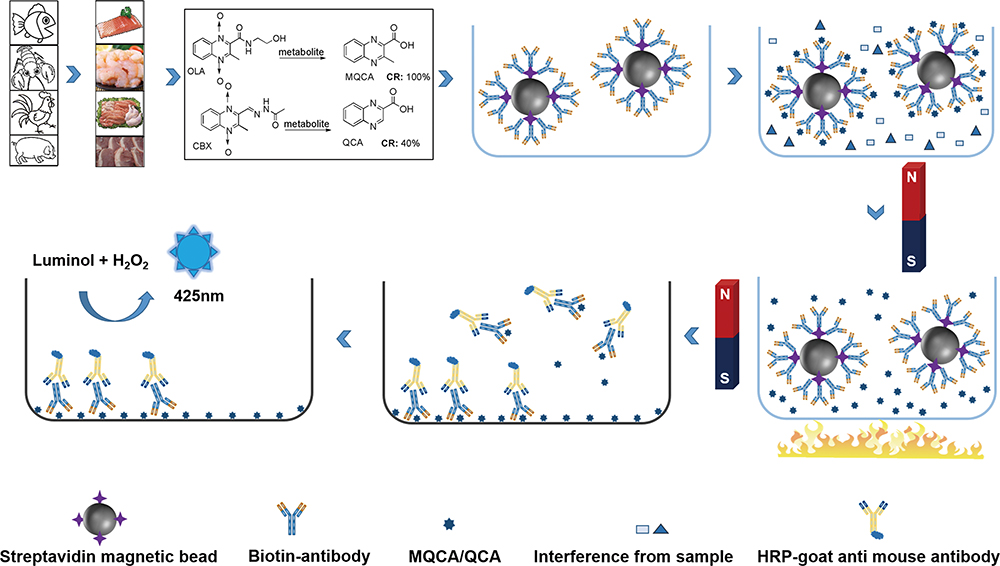
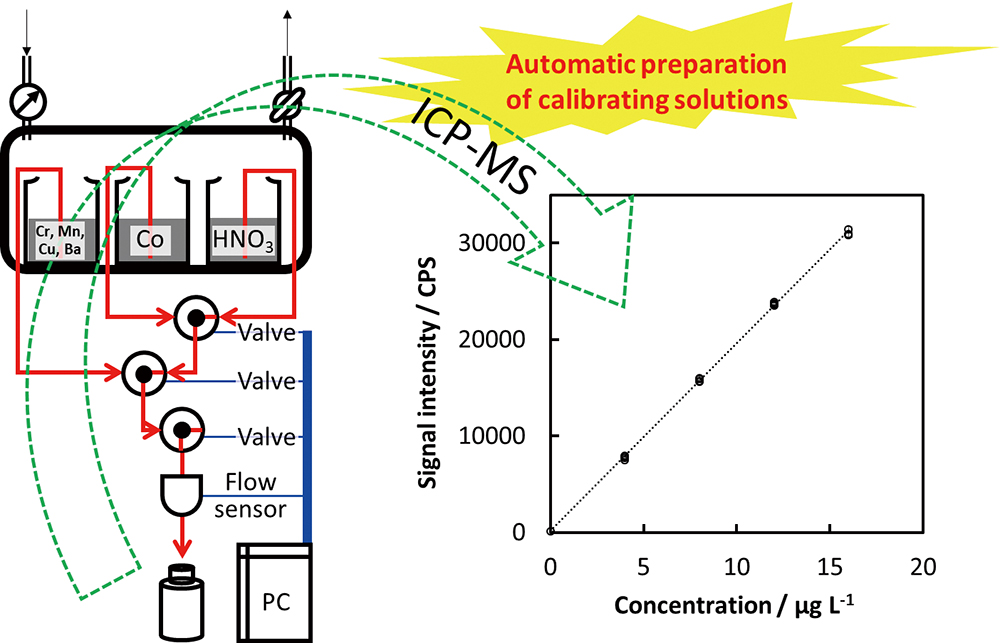
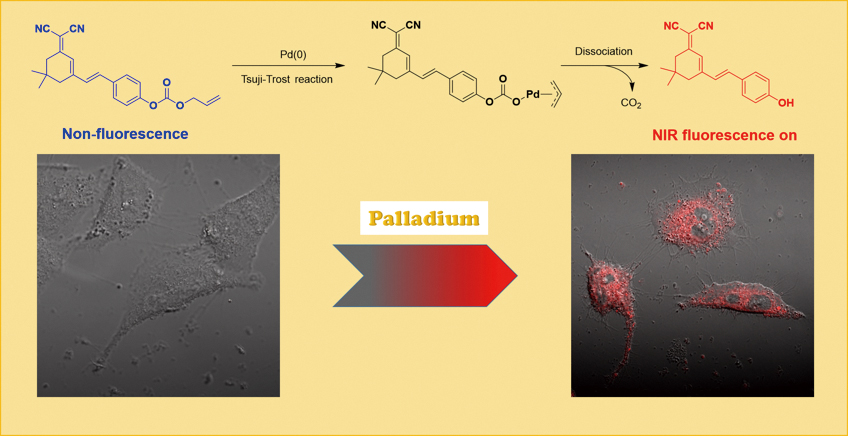
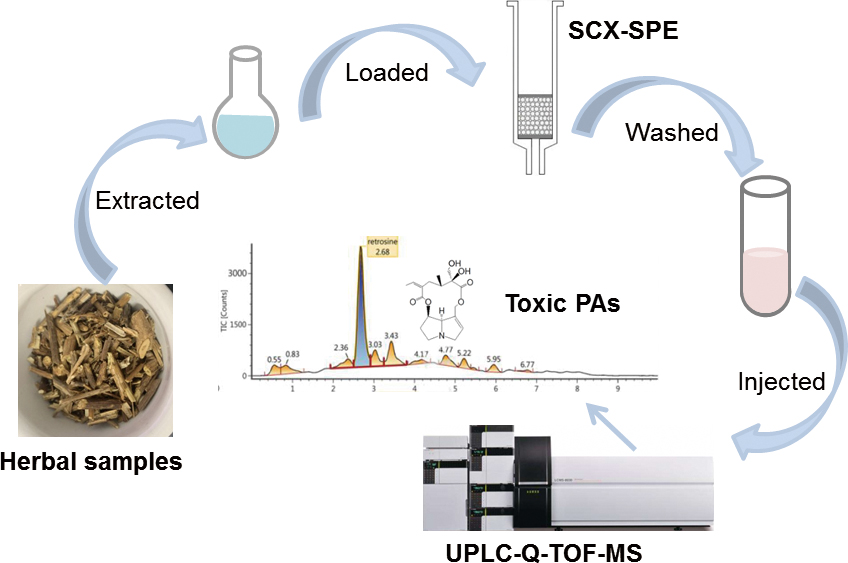
Volume 35, Issue 12
Displaying 1-19 of 19 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1289-1290
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Download PDF (66K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1291-1293
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 22, 2019Download PDF (2536K) -
Article type: Rapid Communications
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1295-1298
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 22, 2019Download PDF (196K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1299-1304
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: July 12, 2019Download PDF (805K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1305-1310
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: July 12, 2019Download PDF (839K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1311-1315
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Download PDF (337K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1317-1325
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 09, 2019Download PDF (2258K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1327-1331
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 09, 2019Download PDF (161K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1333-1340
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 16, 2019Download PDF (703K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1341-1345
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Download PDF (788K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1347-1352
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 16, 2019Download PDF (462K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1353-1360
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 23, 2019Download PDF (739K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1361-1365
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 23, 2019Download PDF (282K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1367-1373
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 30, 2019Download PDF (5696K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1375-1379
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 30, 2019Download PDF (118K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1381-1384
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 13, 2019Download PDF (413K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1385-1391
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Download PDF (362K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1393-1397
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 30, 2019Download PDF (303K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2019Volume 35Issue 12 Pages 1399
Published: December 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2019
Download PDF (1165K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|