All issues

Volume 32, Issue 9
Displaying 1-19 of 19 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Papers
-
Lu ZHANG, Hua ZHANG, Le LI, Peng ZUO, Feilang ZHAO, Manhua LIU, Bang-C ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 923-930
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this work, we prepared surface molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for selective recognition of pneumocandin B0 (PNB0). Methacrylic acid (MAA) was first grafted onto silica gel particles (SiO2) in the manner of “grafting from” by using 3-methacryloxypropyl trimethoxysilane as intermedium, and then PNB0 molecules were imprinted on the surface of the obtained particles in the presence of ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether as the cross-linker. The prepared MIP-PMAA/SiO2 was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermo-gravimetric analysis, which confirmed the successful grafting of MAA onto SiO2 and the grafting degree was calculated to be 12.50 wt%. The binding properties of the products were investigated and it is found that the binding process of PNB0 followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The as-prepared material also displays relatively quick adsorption kinetics and decent recognition affinity toward the template over its structurally related compound. View full abstractDownload PDF (6090K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (6090K) -
Yali KUANG, Bosai HE, Yiyang DU, Jiahui LI, Di WANG, Kaishun BI, Qing ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 931-936
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and reliable method using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a photodiode array detector (HPLC-PDA) was firstly established for the determinations of eleven bioactive compounds (neomangiferin, mangiferin, spinosin, liquiritin apioside, liquiritin, fumalic acid, 6′′′-feruloylspinosin, senkyunolide I, isoliquiritin, glycyrrhizic acid and senkyunolide A) in Suanzaoren decoction (SZRD) extract and its granules. The chromatographic analysis was performed on a C18 column at 30°C. Excellent linear behaviors over the investigated concentration ranges were observed with the values of R2 being higher than 0.9990 for all analytes. The developed method showed good precision and accuracy with overall intra- and inter-day variations of less than 2.0%, and overall recoveries in the range of 97.2 – 102.1%. The validated method was successfully applied to the determination of eleven components in SZRD samples from different production batches, including SZRD extract, lab-made SZRD granules and clinical medicine. This accurate and reliable HPLC-PDA method will be helpful for improving the quality evaluation of SZRD granules and its quality control in productive processes.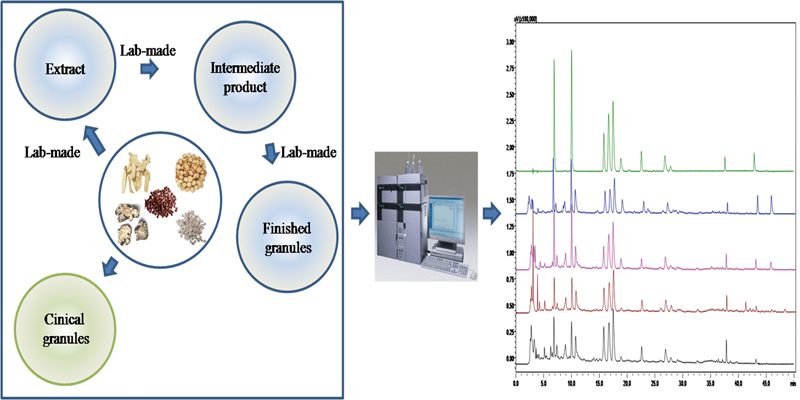 View full abstractDownload PDF (730K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (730K) -
Taku T. SUZUKI, Isao SAKAGUCHIArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 937-941
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA gas analytical technique with compact size, low cost, sufficient sensitivity, and excellent reproducibility is required in many fields including exhaled breath analysis for medical monitoring. In the present study, we examined selective acetone concentration by quench condensation at cryogenic temperature followed by temperature programmed desorption (cryogenic temperature programmed desorption (cryo-TPD)) for possible applications to breath analysis for medical monitoring. The essence of cryo-TPD is rough mass selection by thermal desorption followed by quantification of certain species using mass spectrometry. The performance of cryo-TPD was investigated in the acetone concentration range below 1 × 10−6 volume fraction (1 ppmv). It was found that acetone is selectively quench-condensed on a tungsten substrate at 50 K without the major components of air, such as N2 and O2. The concentrated acetone gas was obtained by the following thermal desorption at around 151 K. Under conditions of condensation for 1 min and pressure of 1 × 10−2 Pa, the lowest limit of detection reached well below 10 × 10−9 volume fraction (10 ppbv). The relationship between the cetone intensity of cryo-TPD and the acetone concentration in the gas was almost linear in the ppbv range. The separation of acetone and propanal using the fragmentation pattern, which have almost the identical molecular mass, was also demonstrated in the present study. View full abstractDownload PDF (4710K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4710K) -
Xiangheng NIU, Hongwei ZHANG, Meihua YU, Hongli ZHAO, Minbo LAN, Cheng ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 943-949
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHere, the combination of Nafion with microporous hollow carbon spheres (MHCS) is first proposed to fabricate a disposable metal-free electrode for heavy metal stripping sensing. The MHCS–Nafion composite film electrode is prepared by drop-casting a mixture of MHCS and Nafion onto the lab-made screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE*). Results demonstrate that the interfusion of MHCS into Nafion offers enhanced performance for the electro-enrichment and stripping of lead and cadmium over the only Nafion film: 1) abundant MHCS immobilized on the electrode surface serve as effective nucleation sites for metal ion reduction; 2) the mixing of MHCS into Nafion enlarges the active surface of negative-charged Nafion for the electrostatic adsorption of metal cations. The proposed MHCS–Nafion/SPCE* provides linear responses for Pb2+ and Cd2+ in the range of 2 – 200 μg/L, with a detection limit of 1.37 and 1.63 μg/L, respectively. Practical applications of the sensor in water sample detection with good accuracy have also been confirmed.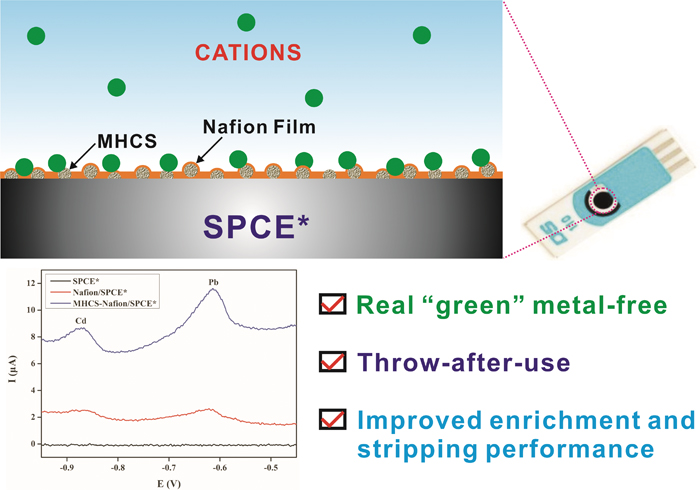 View full abstractDownload PDF (3366K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3366K) -
Nian Chun GONG, Yan Le LI, Xi JIANG, Xiao Fang ZHENG, Ya Ya WANG, Shua ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 951-956
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe present article reports a novel biosensor for organophosphorus pesticides based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between nitrogen-doped carbon dots (NC-dots) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The effective NC-dots/AuNPs assembly through the Au–N interaction results in good fluorescence quenching. Active acetylcholinesterase (AChE) catalyzes the hydrolysis of acetylthiocholine into –SH containing thiocholine to replace the NC-dots and trigger the aggregation of AuNPs. In the presence of paraoxon, the activity of AChE is inhibited, and thus preventing the generation of thiocholine, causing fewer NC-dots to be replaced. As a consequence, the fluorescence intensity gradually decreases with increasing amount of paraoxon. This biosensor does not require any complex synthesis or modification, and the results show a wide detection range of from 10−4 to 10−9 g/L with a detection limit of 1.0 × 10−9 g/L (3.6 × 10−12 mol/L). Two linear response regions have been reported with a turning point at about 10−6 g/L and three different factors that would influence the response behavior. These phenomena discussed in detail so as to explain the special response mechanism. View full abstractDownload PDF (3602K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3602K) -
Takahiro IWAI, Koichi CHIBA, Tomohiro NARUKAWAArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 957-962
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe concentrations of arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd) in the tobacco leaves, ash and smoke of 10 kinds of cigarettes collected from different countries worldwide were determined by ICP-MS after microwave-assisted digestion. Total As and Cd concentrations in the tobacco leaves ranged from 0.20 to 0.63 and 1.8 to 9.9 mg kg−1, respectively. By the speciation analysis of As in tobacco leaves and ash by HPLC-ICP-MS following acid extraction, arsenite [As(III)] and arsenate [As(V)] were determined and trace amounts of monomethylarsonic acid (MMAA), dimethylarsinic acid (DMAA), trimethylarsine oxide (TMAO), tetramethylarsonium (TeMA) and some unidentified As species were also found. Arsenic speciation for smoke absorbed in an aqueous solution was carried out. The sum of the As species in tobacco leaves, ash and smoke was in good agreement with the result of total As determination in each sample, and the recoveries of speciation were 100 ± 10%. The distributions and the behaviors of As species were clarified. View full abstractDownload PDF (900K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (900K) -
Di LIU, Chao ZHAO, Hailin WANGArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 963-968
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), a newly recognized epigenetic mark, is essential to its functional study. Here, an efficient and simple two-step-amplification method to detect 5hmC mediated by glucosylation is reported, which combines rolling circle amplification (RCA) and a quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). In the first step RCA, the glucosylated 5hmC (5ghmC), but not 5hmC, 5-methylcytosine (5mC) or cytosine (C) bases, could directly and specifically inhibit the activity of phi29 DNA polymerase, resulting in less RCA product compared to that using C-/5mC-/5hmC-containing templates. Then, the second step qPCR is adopted to test and verify the difference of the product quantity of 5ghmC-related RCA. The results show that the delta cycle threshold, ΔCt, obtained by subtracting the cycle threshold value (Ct) of C-related qPCR from that of each qPCR, of 5ghmC-related qPCR reaches 1.59 ± 0.03, significantly different from that of C-/5mC-/5hmC-related qPCR (–0.00 ± 0.09, 0.06 ± 0.08 and –0.02 ± 0.03, respectively). Meanwhile, a linear relationship is observed between the 5ghmC levels and the ΔCt values. This suggests that the strategy has a potential application for 5hmC detection and quantification. View full abstractDownload PDF (1244K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1244K) -
Lulu SUN, Jing ZHANG, Surong ZHAO, Qiong PAN, Hongmin ZHANG, Hao LIU, ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 969-973
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSStatistical analyses of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-based chemical fingerprints of Bufo bufo gargarizans toad skin extracts were integrated with antitumor evaluations as a means to more effectively identify bioactive constituents. Specifically, chemical fingerprints of Bufo bufo gargarizans skin extract samples obtained from ten different regions in China were generated by HPLC, and then subjected to similarity analysis and principal component analysis (PCA). Concurrently, a MCF-7 breast cancer cell model was adopted to obtain the antitumor activity of different toad skin extracts. The chromatographic fingerprint–bioactivity relationships of the Bufo bufo gargarizans extracts were then evaluated by Pearson correlation analysis. The results demonstrated that all skin extract samples inhibited the proliferation of MCF-7 cells to some extent, and that there was a correlation between the chemical fingerprints and the anti-proliferative activity. Bufotalin, bufalin, and cinobufagin, three known components of Bufo bufo gargarizans that were identified in the chemical fingerprints, were highlighted as constituents responsible for the observed bioactivity. The activity of cinobufagin was confirmed by cell viability and colony formation assays using MCF-7 cells. The approach documented here provides a more effective means to associate chemical information on medicinal extracts with the principle components responsible for their bioactivity, and to therefore expedite drug discovery.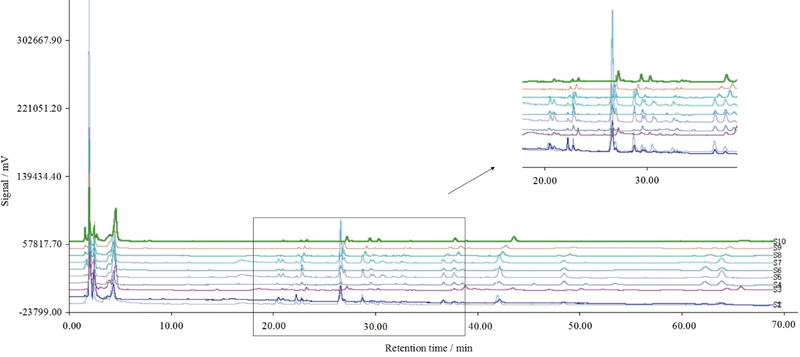 View full abstractDownload PDF (683K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (683K) -
Shanling HU, Xiaodong XIONG, Shuiying HUANG, Xiaoqi LAIArticle type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 975-980
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn ion imprinted polymer (IIP) was synthesized by using Pb(II) as a template, methacrylic acid as a monomer, 8-hydoxyquinoline as a ligand, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as a crosslinker, and azobisisobutyronitrile as initiator. It can be applied to prepare lead ion selective voltammetric sensor for Pb(II) adsorption and trace detection. The Pb(II)-IIP was characterized by FTIR spectra and SEM image. Under optimized conditions of polymerization, the Pb(II)-IIP showed good adsorption behavior toward Pb(II), with a magnitude of three times higher than that of the non imprinted polymer (NIP). Also, it exhibited a favorable selectivity for Pb(II), compared with other heavy metal ions of Hg(II), Cd(II), Cu(II), and a negligible adsorption to the other cations. The synthesized IIP was used to determine trace levels of Pb(II) in food and water samples, with a calibration linear range over Pb(II) concentrations of 0.05 – 60 μM and a limit of detection at 0.01 μM. View full abstractDownload PDF (1798K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1798K) -
Youqiong WANG, Lipeng TANG, Wei YIN, Jiesi CHEN, Tiandong LENG, Xiaoke ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 981-988
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSensitive and specific biomarkers are required for the diagnosis and treatment of depression because the existing diagnostic criteria are subjective and could produce false positives or negatives. Some endogenous neuroactive steroids that have shown either antidepressant effects or concentration changes in individuals with depression could provide potential biomarkers. In this study, a simple and specific method was developed to simultaneously determine seven endogenous neuroactive steroids in biological samples: cortisone, cortisol, dehydroepiandrosterone, estradiol, progesterone, pregnenolone, and testosterone. After liquid–liquid extraction, chromatographic separation was achieved on a C18 column with gradient elution using water–methanol at a flow rate of 300 μL min−1. Detection and quantitation were performed by tandem mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and selected reaction monitoring. Plasma and brain neuroactive steroid levels were then determined in control rats and rats exposed to forced swimming, a classical rodent model of depression. The results showed that the plasma concentrations of testosterone, pregnenolone, and progesterone significantly increased in rats exposed to the forced swimming test. In contrast, brain homogenate levels of cortisol, estradiol, and progesterone decreased, while pregnenolone levels were elevated in this model of depression. In conclusion, a new method to quantify neuroactive steroids was successfully developed and applied to their investigation in rat plasma and brain. The findings of this study indicated that plasma testosterone, pregnenolone, and progesterone levels could provide potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of depression. View full abstractDownload PDF (853K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (853K) -
Mousumi CHATTERJEE, Bhavya SRIVASTAVA, Milan K. BARMAN, Bhabatosh MAND ...Article type: Original Papers
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 989-998
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA time-cost effective, chemically stable mesoporous resin (FSG-PAN), simultaneous binder of two different metal centers (both high (Cd(II)) and low (Tl(I)) oxidation states), has been synthesized by immobilizing azo-dye (1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-napthol: PAN) on functionalized silica gel (FSG). Its corresponding synthesized nano material possesses good luminescent properties, and has been utilized in fluoride sensing at trace levels (1.8 × 10−6 – 7.2 × 10−6 M). The composition ({Si[OSi]p=4[H2O]x=0.81}12[–Si(CH3)2–NH–C6H4–N=N–PAN]4.·51H2O) and structure (tetrahedral) have been well assessed. Under the optimum extraction conditions, the soft extractor (ηFSG-PAN = 1.31 eV), FSG-PAN quantitatively extracts the soft metal centers Cd(II), followed by Tl(I) at its respective HOMO and LUMO by soft-soft interactions. The extractor possesses a high Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area (SABET) (374 m2 g−1), high preconcentration factor (PF, 192), selective pore size and two kinds of break-through capacity (BTCHOMO, 945 μmol g−1; BTCLUMO, 120 μmol g−1). BTC is spelled out as a function of the electron density over the ligand binding site as analyzed from a DFT calculation. View full abstractDownload PDF (2147K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2147K)
Notes
-
Shalini MENON, S. JESNY, Unni SIVASANKARAN, Krishnapillai GIRISH KUMARArticle type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 999-1001
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHerein, a simple, sensitive and selective turn-on fluorescent method for the determination of epinephrine (EP), an important hormone and neurotransmitter, is described. The method is based on the interaction of EP with PEG6000 coated carbon nanoparticles (PCN) resulting in the fluorescence enhancement of PCN. A linear relationship was obtained between the fluorescence intensity and concentration of EP in the 9.90 × 10−9 – 1.07 × 10−7 M range; the detection limit being 7.59 × 10−10 M. Furthermore, we demonstrated the application of the present approach in a synthetic urine sample, which suggested its great potential for diagnostic purposes.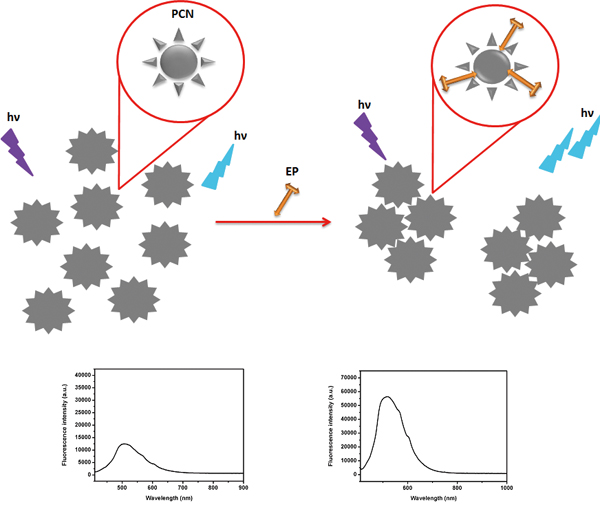 View full abstractDownload PDF (1852K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1852K) -
Masaki OHATAArticle type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 1003-1005
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe effect of long-time heating for both polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polypropylene (PP) resin pellet certified reference materials (CRMs) for heavy metal analysis, which contained Cd, Cr, Hg and Pb, was examined in the present study. The temperature of the drying oven was 80°C, which was used for drying these CRMs before analysis, and the long-time heating was carried out for up to 480 h. As a result, a relative decrease in mass of ca. 0.3% was observed for both CRMs. Moreover, a decrease in concentration of ca. 10% was observed for Cr, even though the concentrations for other elements did not change during the long-time heating. Since the chemical form of Cr was an organometallic compound with lower melting point, it was considered that concentration decreased due to the heat.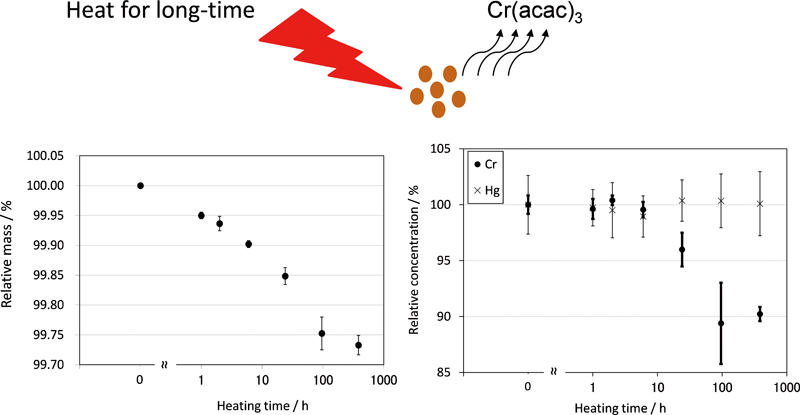 View full abstractDownload PDF (419K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (419K) -
Derong SHANG, Yanfang ZHAO, Yuxiu ZHAI, Jinsong NING, Delin DUAN, Yong ...Article type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 1007-1010
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA solid sampling method for the determination of lead in foods (including grains, vegetables and seafoods) using electrothermal vaporization atomic fluorescence spectrometry was established. The method introduced samples using electrothermal vaporization by quartz furnace and used on-line ashing and vaporization to remove matrix interferences for the specific trap of lead. It was proven by the certified reference material (CRM) and the recovery rate of the standards that the electrothermal vaporization was stable and there was no effect for sampling difference. The best operating program and parameters for the new method included ashing (850°C, 160 s), vaporization and trap (1050°C, 80 s; 800°C, 10 s), release (800°C, 10 s), and mixed Ar + H2 (85:15%, v/v) as carrier gas with flow rate of 500 mL/min. The relative standard deviations of repeated Pb measurements in CRMs were all below 5.0%, and the recovery rate ranged from 90.0 – 110.0%. The limit of detection (LOD) for the new method was 3.0 pg and the limit of quantification (LOQ) was 10.0 pg. The total time of analysis was less than 6 min. No significant differences existed between the results measured by the new method and microwave ICP-MS. View full abstractDownload PDF (485K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (485K) -
Akira KOTANI, Mizuki WATANABE, Kazuhiro YAMAMOTO, Fumiyo KUSU, Hideki ...Article type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 1011-1014
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD) system was developed for the simultaneous determination of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and arachidonic acid (AA) in human plasma. In the present HPLC-ECD system, EPA, DHA, and AA were separated using a reverse-phase C30 column and detected based on the voltammetric reduction of 3,5-di-tert-butyl-1,2-benzoquinone (DBBQ). Chromatographic peak areas were proportional to the concentration of EPA, DHA, and AA from 0.75 μM to 0.1 mM (r > 0.998). The concentrations of EPA, DHA, and AA in plasma from healthy human subjects after overnight fasting were determined, and the ratio of EPA to AA was obtained by the present HPLC-ECD method, which required 40 μL of human plasma and a simple procedure of sample preparation using diethyl ether extraction. Moreover, changes in EPA, DHA, and AA concentrations in a human subject were monitored before and after fish oil supplement administration by the present HPLC-ECD system. View full abstractDownload PDF (522K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (522K) -
Shuhei MIURA, Tomohiro UCHIMURAArticle type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 1015-1017
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe describe a new technique for evaluating the translational temperature of molecules by applying online concentration via analyte adsorption/laser desorption, which is a sample-introduction technique for resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (REMPI-TOFMS). In the present study, analyte molecules were adsorbed via a narrowed capillary tip once, and then the flow of the carrier gas containing the analyte was stopped. After laser desorption, the ion signals induced by REMPI were monitored. Finally, the translational temperature could be calculated from the velocity distribution of the desorbed molecules by applying a Maxwell distribution. View full abstractDownload PDF (477K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (477K) -
Takao KATO, Yasuhiro SUZUKI, Makoto HANDAArticle type: Notes
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 1019-1022
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNine disperse dyes extracted from colored polyester threads and single fibers of manufactory-supplied textiles by using centrifugal filtration were analyzed using liquid chromatography/linear ion trap tandem mass spectrometry (LC/LIT-MSn). Based on diode array detector data, dimethylformamide (DMF) was found to be a more effective extraction solvent than acetonitrile/water (4:3, v/v) or methanol/water (1:1, v/v) mixtures. The precursor, [M+H]+ ions, were detected for the dyes extracted using DMF. The MS2 and MS3 spectra also matched those of the standard disperse dyes. Without relying on comparison clothes, disperse dyes extracted from the single fibers (5 mm in length) were successfully identified by LC/LIT-MSn and the custom-built database. View full abstractDownload PDF (637K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (637K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Guangfu JIANG, Xia LIU, Yaqin WANG, Sanpeng RUAN, Honglan QI, Yong YAN ...Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 1023-1027
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA multi-functional eletrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) imaging analyzer including both a photomultiplier tube and charged coupled device as detectors has been developed. The ECL imaging analyzer can effectively work for electrochemical study, ECL intensity detection at electrode array, and ECL imaging at bipolar electrodes or electrode array. As an ECL imaging example, an ECL biosensor for visual detection of matrix metalloproteinase 7 in the range from 0.05 to 1 ng/mL is demonstrated.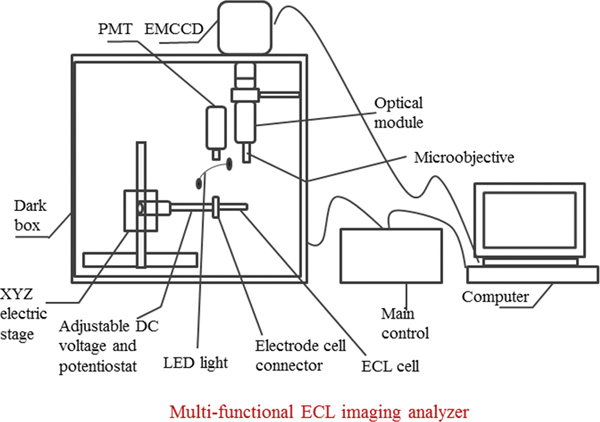 View full abstractDownload PDF (4537K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4537K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2016 Volume 32 Issue 9 Pages 1029
Published: September 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2899K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|