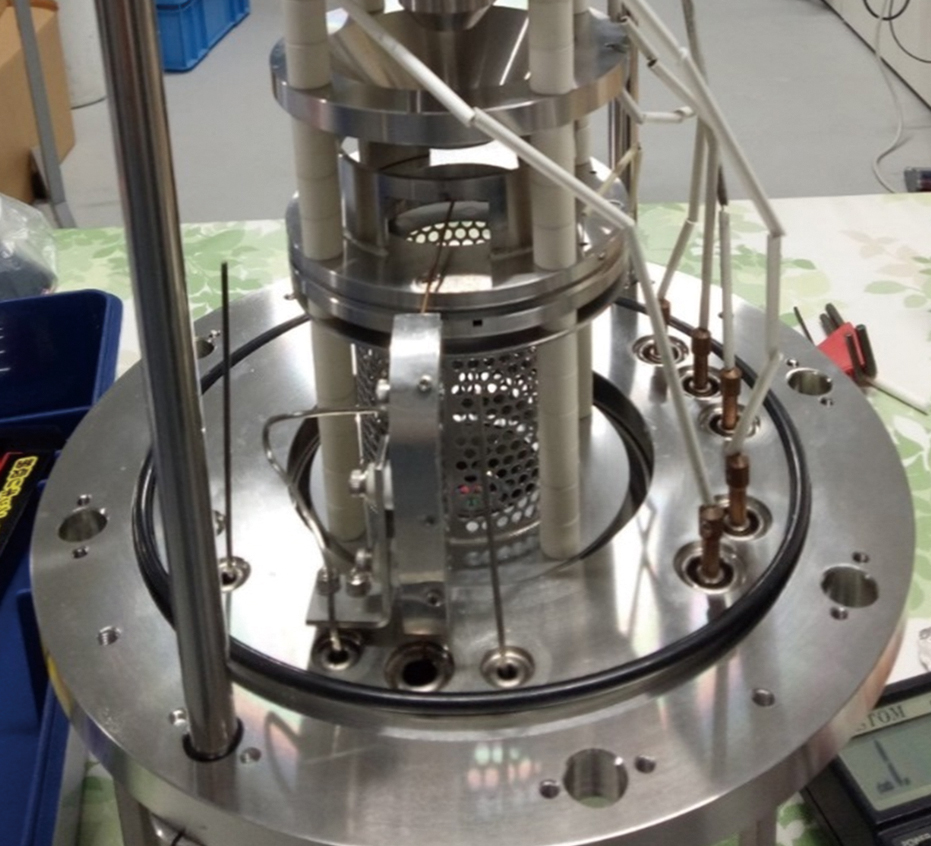
Volume 36, Issue 5
Displaying 1-24 of 24 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 507
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Download PDF (27K)
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 509-510
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Download PDF (115K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 511-514
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020Download PDF (1105K) -
Article type: Rapid Communications
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 515-517
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 01, 2020Download PDF (317K)
Guest Editorial
-
Article type: Guest Editorial
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 519
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Download PDF (24K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 521-530
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 13, 2020Download PDF (4209K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 531-538
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 13, 2020Download PDF (2497K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 539-543
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 17, 2020Download PDF (373K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 545-551
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Download PDF (2188K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 553-560
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 06, 2020Download PDF (2177K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 561-567
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 06, 2020Download PDF (297K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 569-575
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Download PDF (601K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 577-582
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 20, 2020Download PDF (1035K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 583-588
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 21, 2020Download PDF (1240K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 589-594
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Download PDF (4078K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 595-600
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 20, 2020Download PDF (344K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 601-609
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 27, 2020Download PDF (1754K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 611-615
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 07, 2020Download PDF (541K) -
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 617-620
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 28, 2020Download PDF (1684K) -
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 621-626
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 21, 2020Download PDF (320K) -
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 627-630
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: March 20, 2020Download PDF (292K) -
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 631-636
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 21, 2020Download PDF (332K) -
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 637-643
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 03, 2020Download PDF (485K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2020Volume 36Issue 5 Pages 645
Published: May 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2020
Download PDF (60K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|