
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yusuke MORISAWAArticle type: Highlights
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 833-834
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Mizuki ENDO, Masashi MIYASAKI, Qiaojing LI, Genki KAWAMURA, Takeaki OZ ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 835-838
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: July 05, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialGlucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) is an insulin-regulated glucose transporter, which is vital for blood glucose homeostasis. To clarify the physiological roles of GLUT4, quantitative measurement of GLUT4 exocytosis is indispensable. Herein, we show a rapid detection system for GLUT4 on the cell surface using spontaneous split-luciferase reconstitution. Upon insulin-induced GLUT4 exocytosis, GLUT4 was exposed outside, where luciferase is reconstituted and emitted luminescence. Pretreatment with inhibitors reduced the insulin-induced signal elevation. The results indicate that the developed method is applicable to high-throughput analysis on GLUT4 trafficking, which will greatly accelerate comprehensive research on the physiological roles of GLUT4.
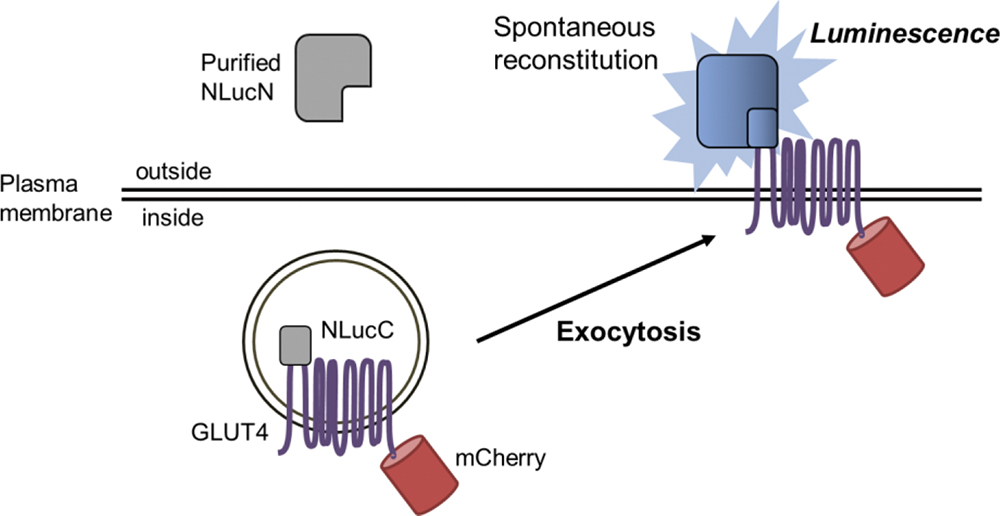 View full abstractDownload PDF (273K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (273K)
-
Nadine LOBSIGER, Wendelin J. STARKArticle type: Reviews
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 839-847
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 14, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis review summarizes the development of whole-cell biosensors with a special focus on device development and cell immobilization. Integration of biosensor functions in a device will pave the way for field applications in remote areas and resource-limited settings. Firstly, an introduction to the field of whole-cell biosensors is provided, followed by examples of genetic engineering of cells in order to fulfill sensor functions. A framework of requirements to enable future field applications of biosensors is elaborated. A special focus is on different cell immobilization techniques ranging from polymers, to microfluidic devices, immobilization on paper and combinations of these methods. Looking at globally successfully implemented point of care devices such as a home pregnancy test or a blood glucose meter, we conclude the review with thoughts on long-term stability, portability, ease of use and user safety design guidelines for whole-cell biosensor devices.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (807K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (807K)
-
Xintong LI, Fang LIU, Huifang WANG, Fan HE, Rui YANG, Mingqin ZHAOArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 849-854
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 29, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialOne method based on QuEChERS sample preparation is presented in this study, which leads to simultaneously detect nine alkaloids in tobacco and tobacco products. Nicotine, nornicotine, myosmine, N-methyl anabasine, β-nicotyrine, anabasine, anatabine, isonicotenine and cotinine can all be found in fresh tobacco leaves, cigars, Virginia-type and blended-type cigarettes. The samples were purified via a certain proportion of adsorbents consisting of anhydrous magnesium sulfate, PSA and carbon after extracting, then centrifuged and filtered before analyzing by GC-MS. The matrix effects were all among 88 – 105%. The limit of detection of all were within the range of 0.0065 – 0.1509 μg/g and limit of quantification were among 0.0217 – 0.5031 μg/g. The recovery rates were higher than 89%. This is the first time that the QuEChERS sample preparation method has been applied for tobacco alkaloids, where more varieties of alkaloids could be quantified regarding sensitivity and reproducibility.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (623K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (623K) -
Ikuo UETA, Risa TAKENAKA, Koji FUJIMURA, Shoji NARUKAMI, Tomohiro SASA ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 855-859
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 05, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, in-door air semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) including 2-ethyl-1-hexanol, 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol monoisobutyrate (texanol), and 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate (TXIB), which are scheduled for adding as regulated compounds concerning indoor air reference values in Japan, were quantitatively extracted using a solid-phase extraction-type collection device, followed by sensitively determined by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The developed method has shown a good extraction recovery up to an air sampling volume of 900 L. The extracted analytes were quantitatively and rapidly eluted by 7 mL of acetone. The limit of quantification of the analytes were 0.7, 2.1 and 0.2 ng L−1 in air sample at a sampling volume of 300 mL without any concentration of a desorption solvent. The developed method was applied to simultaneous determinations of the investigated target analytes and phthalate esters in real indoor air samples.
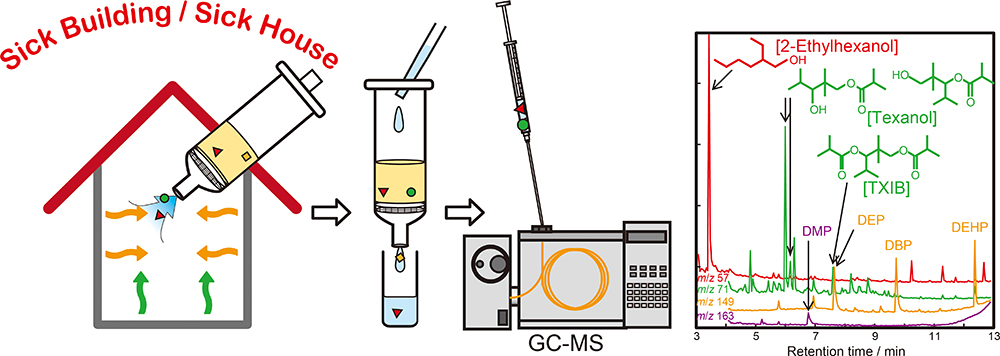 View full abstractDownload PDF (152K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (152K) -
Muhammad Shoaib KHAN, Muhammad ASGHAR, Mohammed YAQOOBArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 861-867
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 12, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and rapid flow injection chemiluminescence (FI-CL) method based on the reaction of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and quinine was established for the determination of lansoprazole in pharmaceutical formulations. A linear calibration curve was achieved over the range from 0.01 to 20.0 mg L−1 LNP (R2 = 0.9997 (n = 8); RSD = 1.1 – 3.7% (n = 4)) with a limit of detection of 3.0 × 10−3 mg L−1 (S/N = 3) and injection throughput of 150 h−1. By applying the Student t-test (calculated t-test value: t = 1.059907664, and tabulated t-distributed (95%) = 2.200985) it was found that the proposed method and reported spectrophotometric method were not significantly different. The LNP was efficiently extracted and the recovery of LNP from the spiked pharmaceutical formulations was in the range of 91.0 – 105.9% (%RSD = 1.6 – 3.6, n = 4). No significant interference activity was detected from the excipients commonly found in the drug samples analyzed. The possible chemiluminescence emission mechanism is discussed briefly.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (783K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (783K) -
Hideaki FUJIWARA, Hirohiko IMAI, Atsuomi KIMURAArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 869-873
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 12, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHyperpolarized (HP) 129Xe NMR and MRI have enabled 129Xe studies with extraordinarily enhanced sensitivity, stimulating new developments in magnetic resonance in chemistry, physics, biology and medicine. However, the standard method of HP 129Xe production inevitably demands Rb vapor for the excitation, which has made the method very sensitive to impurities such as water or oxygen. This is the case especially in the recirculating system. In the present study, stability of the hyperpolarizing system is discussed by proposing the “cell decay constant”, which symbolizes the decay rate of the NMR signal obtained from the system. The cell decay constant is effectively decreased to 1/3 by introducing separated chambers and mechanical stirring of the alkali metals used in the system, making it effective for accumulating FIDs over 30 to 100 h. The newly developed hyperpolarizing system has been successfully applied for newly detecting a broad signal at 190 ppm with an industrial material Nanofiber.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (509K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (509K) -
Xia WANG, Suyan ZHAI, Chao LIU, Xiaoshu WANG, Ya YANG, Yifeng TUArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 875-882
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 12, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn antibody-based immunotherapy for methamphetamine (MA) addictive treatment is has been drawing more and more attention in recent years. However, studies about methamphetamine antibody (anti-MA) immunodetections are rare, owing to the lack of immunogenicity of small molecule MA. This study provides a simple and effective approach to develop a convenient electrochemiluminescent (ECL) immunosensor for the testing of anti-MA. In short, the synthetic holoantigen of MA is immobilized on a homemade gold nanoparticles modified electrode as the sensing host for the specific recognition and detection of anti-MA. The research suggested, under optimal experimental conditions, the ECL intensity on resultant immunosensor has a wide-linear regression toward the anti-MA quantity within the range from 0.03 to 3.07 ng with a detection limit of 2.32 pg. It responded to the dosage of anti-MA in spiked blood samples with satisfactory recovery. According to the research, the developed sensor shows promise as a portable Anti-MA fast seized device which performs quickly and offers convenience, and will be helpful for forensic identification and clinical treatment.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (735K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (735K) -
Hyeoun Ji PARK, Soo Suk LEEArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 883-888
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 19, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHere we present a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensor for the highly selective and sensitive detection of Hg2+ ion, a toxic chemical species and a hazardous environmental contaminant. Hg2+ ion can be quantitatively measured based on changes in the resonance frequency of QCM following mass changes on the QCM sensor surface. The high selectivity for Hg2+ ion in this study can be obtained using a thymine–Hg2+–thymine pair, which is more stable than the adenine-thymine base pair in DNA. On the other hand, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and their size-enhancement techniques were used to amplify the QCM signals to increase the sensitivity for Hg2+ ion. With this strategic approach, the proposed QCM sensor can be used to quantitatively analyze Hg2+ ion with high selectivity and sensitivity. The detection limit was as low as 98.7 pM. The sensor failed to work with other metal ions at concentrations 1000-times higher than that of the Hg2+ ion. Finally, the recovery does not exceed 10% of the original value for the detection of Hg2+ ion in tap and bottled water. The results indicate acceptable accuracy and precision for practical applications.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (553K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (553K) -
Fumihiko KITAGAWA, Shinichiro WAKAGI, Yuuki TAKEGAWA, Isoshi NUKATSUKAArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 889-893
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 19, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo achieve highly sensitive analysis without labor-intensive experimental procedures in capillary electrophoresis (CE), large-volume sample stacking with an electroosmotic flow pump (LVSEP)–field-amplified sample injection (FASI) was combined with a dynamic coating technique. In this study, poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) was employed for the dynamic coating additive. Since a standard fluorescent dye, fluorescein, was well concentrated in a conventional LVSEP, the PVP dynamically-coated capillaries can be also applied to the LVSEP-FASI analysis. In our home-made CE apparatus, however, current breakdown was often caused, especially at a longer electrokinetic injection time due to bubble formation. To avoid the interference of bubble formation, the distance between the tips of the electrode and the capillary in the vertical direction was changed from 0 to 2.5 cm under the magnetic stirring condition. This allowed for a long electrokinetic injection time of up to 20 min, resulting in a sensitive enhancement factor (SEF) of 34900 for fluorescein. The developed method was applied to the chiral analysis of amino acids in CE. As a result, leucine (Leu) was successfully separated in LVSEP-FASI with SEFs of 6420 and 4500 for the D- and L-Leu peaks, respectively.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (408K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (408K) -
Tomoyuki YASUKAWA, Asa MORISHIMA, Masato SUZUKI, Junya YOSHIOKA, Keita ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 895-901
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 19, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe applied a fabrication method for the formation of island organization of cells based on a three-dimensional (3D) device for negative dielectrophoresis (n-DEP) to produce cell aggregates with uniform numbers of cells rapidly and simply. The intersections formed by rotating the interdigitated array (IDA) with two combs of band electrodes on the upper substrate by 90° relative to the IDA with two combs on the lower substrate were prepared in the device. The AC voltage was applied to a comb on the upper substrate and a comb on the lower substrate, while AC voltage with opposite phase was applied to another comb on the upper substrate and another comb on the lower substrate. Cells dispersed randomly were directed toward the intersections with relatively lower electric fields due to n-DEP, which formed by AC voltage applied bands with the identical phase, resulting in the formation of island patterns of cells. The cells accumulated at intersections were promoted to form the cell aggregates due to the close contact together. The production of cell aggregations adhered together was easily found by the dispersion behavior after switching the applied frequency to convert the cellular pattern. When cells were accumulated at the intersections by n-DEP for 45 min, almost accumulations of cells were adhered together, and hence a formations of cell aggregations. By using the present method, we can rapidly and simply fabricate cell aggregations with a uniform number of cells.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1151K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1151K) -
Xinmin HU, Fang LIU, Wenti LI, Xiaochun WANG, Hongyu DENGArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 903-909
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 26, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFerrocenylmethanol (Fc-OH) is included in β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) to form the β-CD-Fc-OH complex by host-guest supramolecular interaction. β-CD dissociates from the β-CD-Fc-OH complex due to the conversion of Fc-OH to Fc+-OH under a stimulus of oxidant. In our study, Fc-OH is oxidized after a series of enzymatic reactions of creatinine, which blocks the other means for oxidation of Fc-OH. And the background noise is reduced for testing for serum creatinine (sCr). The chronoamperometry signal for creatinine (with a constant potential –0.3 V vs. Ag/AgCl) increases linearly in the 1 – 1000 μM range, with a limit of detection as low as 0.5 μM. The amperometric potential of –0.3 V greatly prevents the interference of various redox substances in serum. The biosensor was used to test 120 clinical specimens and the results showed a linear correlation with the biochemical analyzer (R2 = 0.9885). The biosensor could be applied to clinical trials and offers good prospects for clinical sCr detection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1341K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1341K) -
Motohiro BANNO, Sumire TAKAHASHI, Hiroharu YUIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 911-915
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 26, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWater repellency of surfaces is realized by the roughness of the surfaces and the coating compounds on the surfaces. It is known that the water repellent surfaces are due to invasion of water into the trench structures on the surface, or due to air remaining in the trench structures. However, for more effective designing and fabrication of water-repellent surfaces, it is essential to measure the spatial distribution of water around the microstructures. In the present study, the SRS interferometer developed by the authors is applied to distinguish whether water or air is present in the trenches on the water-substrate interface buried by water. By obtaining the SRS interference signal generated from water while scanning the sample position, the phase shift of the SRS interference signal due to the microstructure on the interface was observed. From the quantitative analysis of the phase difference, it was revealed that the trench was filled with water. It is concluded that SRS interferometry is an effective method to observe experimentally the interface condition with chemical contrast along microstructures.
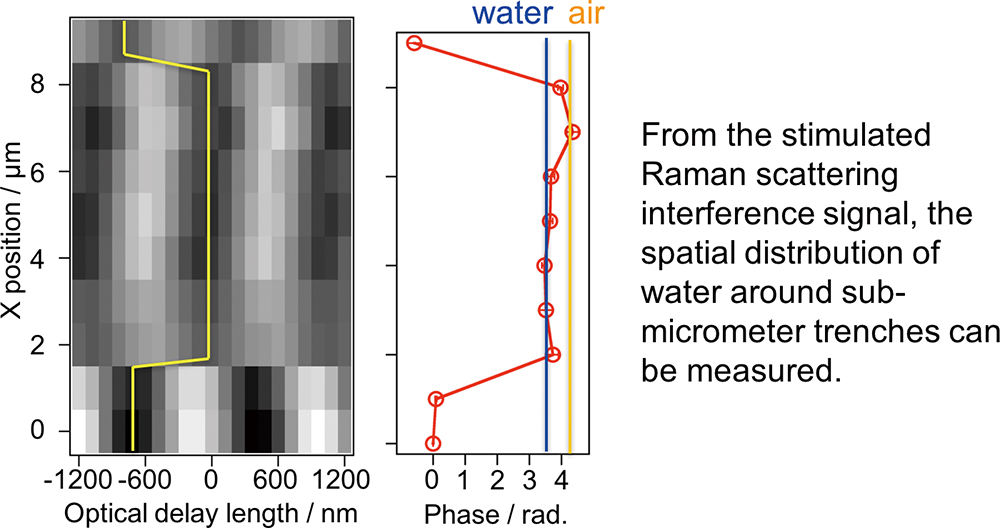 View full abstractDownload PDF (796K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (796K) -
Xiu WANG, Pingyue HU, Zhipeng WANG, Qiuyun LIU, Ting XU, Mengqian KOU, ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 917-922
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 26, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe detection of Ag+ ions in the environment and biological systems is important to both environmental monitoring and modern medicine. Herein, a novel and label-free method was developed for Ag+ detection, which utilizes a florescence strategy combining DNA-templated copper nanoclusters (Cu NCs) with cation exchange reactions. The method is primarily based on the effective detection of an Ag+-triggered cation exchange reaction and the release of free Cu2+ from CuS nanoparticles (CuS NPs), while the probe T30 serves as an effective template for the formation of fluorescence-inducing Cu NCs. Under optimal conditions, this sensing system displays high sensitivity with a 50 nM limit of detection and a range from 0 – 100 μM. In addition, the proposed method exhibits high selectivity and, therefore, was successfully applied to the analysis of real samples. Overall, these results demonstrate that our established method has advantages of design and operation simplicity, as well as cost-effectiveness.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2616K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2616K) -
Yukihiro SHINTANI, Shoji IBORI, Hiroshi KAWARADAArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 923-927
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 26, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper describes a deoxyribonucleic-acid-sensitive electrolyte solution-gate field-effect transistor (SGFET) sensor utilizing a partial carboxyl-terminated boron-doped polycrystalline diamond surface as a linker to connect a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) probe. A high density of carboxyl termination on the polycrystalline diamond surface that was employed as a FET channel was achieved using a vacuum ultraviolet system with oxygen gas. A single-stranded DNA probe was immobilized on the polycrystalline diamond channel via amino coupling. The current–voltage characteristics of the polycrystalline diamond SGFET sensor was examined with bias voltages within its potential voltage window. The characteristics of the drain-source current verses the drain-source voltage showed a pinch-off, a shift voltage of up to 40 mV with a coefficient of variation of 4 – 11% was obtained between hybridization and denaturation. In addition, a single nucleotide mutation of DNA sequence was selectively recognized by the shift voltage up to ca. 10 mV.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (785K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (785K) -
Xiaohui CHEN, Xuelin SHAN, Qiufeng LAN, Zhidong CHENArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 929-934
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 26, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this work, the electrochemiluminscence system of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) and K2S2O8 was built for the determination of crystal violet (CV). Meanwhile, a carboxylic carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode (CCNTs/GCE) was used as an ECL sensor. Thanks to the excellent electron transfer ability and large surface area of CCNTs, the ECL signal of N-GQDs@S2O82− was remarkablely amplified. With the presence of a low concentration of CV, a distinct decrease of the ECL signal was observed due to a quenching effect of CV on the ECL emission. Moreover, the quenched ECL intensity responded linearly to the logarithm of CV concentration within the range of 0.05 – 5 μmol/L, with a LOD of 45 nmol/L (S/N = 3). The proposed ECL system exhibited high sensitivity and specificity to CV, which was successfully applied in the practical detection of CV in real water samples from a local fishpond farm.
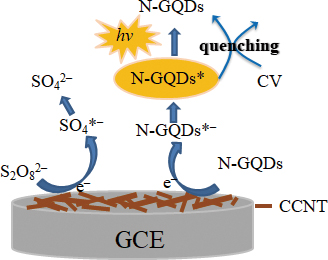 View full abstractDownload PDF (420K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (420K)
-
Hajime KATANO, Shota NOBA, Shu TAIRA, Taiho KAMBE, Masakazu TAKAHASHIArticle type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 935-937
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 05, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis note describes a simple and rapid method to separate specific soyasaponins, including the major and multi-functional bioactive species soyasaponin Bb, from the whole soybean flour. The method is based on the difference in solubility of the soyasaponins and other components in methanol, aqueous borax solution, and 1-octanol. First, the whole soybean flour was mixed with methanol to extract hydrophobic components, and the methanol solution was concentrated. Second, the methanol solution was mixed with a larger volume of aqueous borax solution, and the supernatant was acidified to obtain a precipitate. The precipitate was found to be containing mainly four group B soyasaponins. Two of those are non-conjugated molecules, soyasaponins Bb and Bc, and the other two are 2,3-dihydro-2,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one conjugated ones, soyasaponins βg and βa. All of them have two cis-diol groups in their structure. Therefore, although they are fundamentally insoluble in water, they became soluble in the aqueous medium in the form of divalent anionic species by the borate ester formation, and that they were re-precipitated by the hydrolysis. Furthermore, the non-conjugated group B soyasaponins could be separated by washing with 1-octanol to remove highly hydrophobic soyasaponins βg and βa. The solubility-based technique would be useful as pretreatment in the purification of these group B soyasaponins.
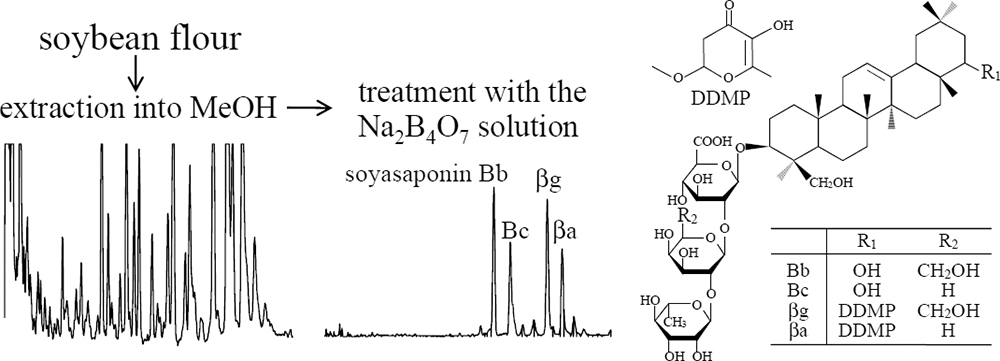 View full abstractDownload PDF (304K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (304K) -
Takeshi KATO, Yuki NAGASHIMA, Atsushi MANAKA, Chihiro NAKAMURA, Shigek ...Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 939-942
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 26, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe rapid determination of sub-ppm heavy metals in the solution state was examined via portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) based on homogeneous liquid–liquid extraction (HoLLE) in the water–ethanol–dimethyl phthalate ternary component system. The percentage of cadmium extracted into the sedimented liquid phase was 91.3%. After phase separation, the volume ratio (Va/Vs) of the aqueous phase (Va) and the sedimented liquid phase (Vs) was 121 (29.0 → 0.240 mL). Based on an analysis of the sedimented liquid phase in the solution state via the portable XRF, the presence of cadmium was determined over a concentration range of 0.100 – 4.00 mg L−1.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (543K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (543K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2019 Volume 35 Issue 8 Pages 943
Published: August 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1162K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
