
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yuko UENOArticle type: Highlights
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 121-122
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Sumaira NISHAT, Fazli Rabbi AWAN, Sadia Zafar BAJWAArticle type: Reviews
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 123-131
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 14, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn resource-limited settings, the availability of medical practitioners and early diagnostic facilities are inadequate relative to the population size and disease burden. To address cost and delayed time issues in diagnostics, strip-based immunoassays, e.g. dipstick, lateral flow assay (LFA) and microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (microPADs), have emerged as promising alternatives to conventional diagnostic approaches. These assays rely on chromogenic agents to detect disease biomarkers. However, limited specificity and sensitivity have motivated scientists to improve the efficiency of these assays by conjugating chromogenic agents with nanoparticles for enhanced qualitative and quantitative output. Various nanomaterials, which include metallic, magnetic and luminescent nanoparticles, are being used in the fabrication of biosensors to detect and quantify biomolecules and disease biomarkers. This review discusses some of the principles and applications of such nanoparticle-based point of care biosensors in biomedical diagnosis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (8057K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (8057K)
-
Longjie ZHONG, Jiadi SUN, Ying GAN, Shuqi ZHOU, Zijian WAN, Quchao ZOU ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 133-140
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSaxitoxin (STX) is one of the paralytic shellfish poisons (PSP) that endanger people’s health. It is necessary to develop methods for the on-site rapid detection for STX in order to prevent safety accidents. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is timesaving and effective, but it is not suitable for large-scale in-field tests due to the expensiveness of commercial ELISA kits and the bulkiness of a microtiter plate reader (MTPR). In this study, a portable smartphone-based colorimetric analyzer (SBCA) with a cost-effictive enhanced gold nanoparticle-based ELISA (EGNB-ELISA) was proposed for STX detection. In a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay (R2 = 0.9939) and a glucose assay (R2 = 0.9937), SBCA was shown to be in good agreement with MTPR. EGNB-ELISA had a 12.5-fold lower detection limit (0.4 ng/mL) and a lower detection range (1 – 50 ng/mL, Y = 0.4037X + 0.3564, R2 = 0.9797) than the classical ELISA. The recovery rate ranged over 89.1 – 112.2%. The whole detection system, combining both homemade SBCA and ENGB-ELISA, is expected to satisfy the needs of on-site STX sample tests to guarantee seafood safety.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4908K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4908K) -
Riou KAWAMURA, Momoka SATOU, Takuya YONESAKA, Akio YUCHIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 141-145
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 14, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialPenetration of salt solutions into cation exchange resins was used to measure the volume of a space within the resin phase (the inner space), which was usable for ion exchange in principle but not fully in practice. The average volume of the inner space per functional group was significantly dependent on the type and the concentration of the salt (250 – 450 Å3) for a resin having the cross-linking degree of 8%, while being less dependent on the type and the concentration of the salt (160 – 240 Å3) for a resin having the cross-linking degree of 12%. The salt concentration ratio of the solution filling the inner space to the outer solution decreased with a decrease in concentration of the outer salt solution due to the osmotic pressure, and decreased with an increase in cross-linking degree due to the smaller volume and the higher independency of the inner space.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (181K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (181K) -
Yan Jun JU, Na LI, Shi Gang LIU, Yu Zhu FAN, Yu LING, Na XIAO, Hong Qu ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 147-152
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA fluorescence method for the determination of picric acid (PA) using phosphorus-doped carbon dots (P-CDs), synthesized from β-cyclodextrin and sodium pyrophosphate, is described. The P-CDs are very uniform and monodisperse with a diameter of about 2.8 nm. Under an excitation of 350 nm, the P-CDs emit bright blue fluorescence with an emission peak at 440 nm. The as-synthesized P-CDs serve as a sensitive, selective, and label-free fluorescent probe for the detection of PA. Based on an inner filter effect between PA and P-CDs, a linear response is obtained for PA from 0.1 to 10 μM with a detection limit of 82 nM. Finally, this sensing system has been demonstrated to have practicability for PA detection in the environmental water samples.
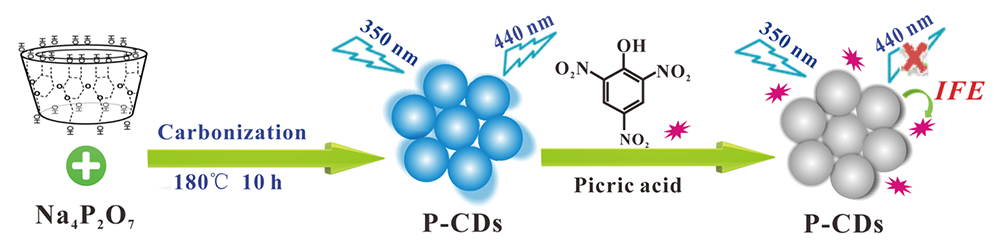 View full abstractDownload PDF (933K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (933K) -
Masami K. KOSHIKAWA, Mirai WATANABE, Masanori TAMAOKI, Shoko ITO, Take ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 153-158
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTo evaluate the mobility and bioavailability of 137Cs in soils, we compared the extraction of 137Cs with stable Cs and ammonium solutions from 137Cs-contaminated minerals and soils. The extraction yields of 137Cs with stable Cs were significantly lower than those with ammonium for minerals with frayed edge sites, but such differences were not observed for minerals without frayed edge sites. The amount of 137Cs extracted with stable Cs from soils was lower than, or equal to, that extracted with ammonium. The above results suggest that stable Cs extracted the 137Cs from easily accessible sites. Plant available 137Cs was assessed using Kochia (Bassia scoparia) cultivated in pots of contaminated soils, and compared with soil parameters including extractable 137Cs and K, and radiocesium intercept potential. The 137Cs/K ratio extracted with stable Cs solution was found to be a potential index for evaluation of the easily mobile and bioavailable fraction of 137Cs in soil.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (414K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (414K) -
Yue YALING, He YIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 159-163
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 28, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe report a visual chronometric method for the detection of copper(II) ions (Cu2+) using the clock reaction between methylene blue (MB) and hydrazine (N2H4). The addition of Cu2+ greatly accelerates the clock reaction due to the formation of the Cu cluster between Cu2+ and N2H4. By recording the change of the reaction time and solution color, different concentrations of Cu2+ in buffer and environmental water have been detected. As low as 300 nM Cu2+ can be visually identified by the naked eye without the assistance of any advanced instruments. This visual chronometric assay shows a dynamic range from 0.2 to 16 μM with a limit of detection of 20 nM. Additionally, it has good selectivity toward Cu2+ and against other common metal cations.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (780K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (780K) -
Felipe M. FORTUNATO, Tiago Augusto CATELANI, Mario Siméon POMARES-ALFO ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 165-168
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 28, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA multi-energy calibration method was applied for the determination of chromium and nickel in nickeliferous ores by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. For the optimization of the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy parameters, such as laser fluence and delay time, an experimental study was conducted. The best results in terms of trueness were observed using a laser fluence and a delay time of 2500 J/cm2 and 1.1 μs, respectively. A study of sample matrix effects and the determination of emission lines for calibration and normalization of the spectra were undertaken, and appropriate values of those variables were selected for each analyte. The trueness values for chromium and nickel varied from 89 to 114% when certified reference samples (nickeliferous laterite, rock phosphate and contaminated soil) were analyzed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (245K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (245K) -
Kanako ITO, Shinya KITAGAWA, Hajime OHTANIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 169-174
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 28, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPoly(ethylene oxide), poly(propylene oxide), and their copolymer (poly(EO-co-PO)) were analyzed by electrospray ionization–ion mobility spectrometry–mass spectrometry (ESI-IMS-MS). ESI produced multiply charged analytes of 2 to 5 Na+ additions, and they were separately observed in a 2D map of m/z value vs. drift time. The collision cross-section of the analyte polymers was almost linearly proportional to (molecular weight)0.644, except for the analytes with 2Na+ addition; a nonlinear relation called “folding” was significantly observed for the analytes with 2Na+ addition. An increase in electrostatic repulsion, because of the increase in Na+ addition, suppressed the folding of the polymer. Analyses of poly(EO-co-PO) with different EO compositions revealed that the copolymer with high EO composition tended to show folding. The separation of highly multiply charged poly(EO-co-PO)s with different EO contents by ESI-IMS-MS was successfully demonstrated.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1864K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1864K) -
Jincui GU, Chengfeng XU, Menglu LI, Boyi CHEN, Yating SHANG, Hailing Z ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 175-180
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 28, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSpecies identification is of key significance for exploring the origin and transmission of ancient silks. In this study, two novel methods, i.e. western blot (WB) and proteomics analyses, were proposed and established to identify the differences between silks from Bombyx mori (B. mori) and two other distinctive species (Eri silkworm and Chestnut silkworm). Three diagnostic antibodies, a polyclonal anti-silk fibroin (anti-SF) antibody (pAb), a polyclonal anti-SF-specific peptide antibody (pAsb), and a monoclonal anti-SF antibody (mAb) were designed and prepared to distinguish silk species using the antibody-based WB technique. Proteomics analysis by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry was performed to further identify silk species at the protein level. WB results indicated that the three antibodies showed high specificity and affinity and could discern B. mori silk from Eri and Chestnut silks. Biomarkers for each SF were obtained using proteomics analysis, and they have the potential to serve as standards for identifying silk species. Thus, combining WB and proteomics analyses with conventional methods can provide more accurate silk information and may be suitable for identifying other proteinaceous materials in archaeological field.
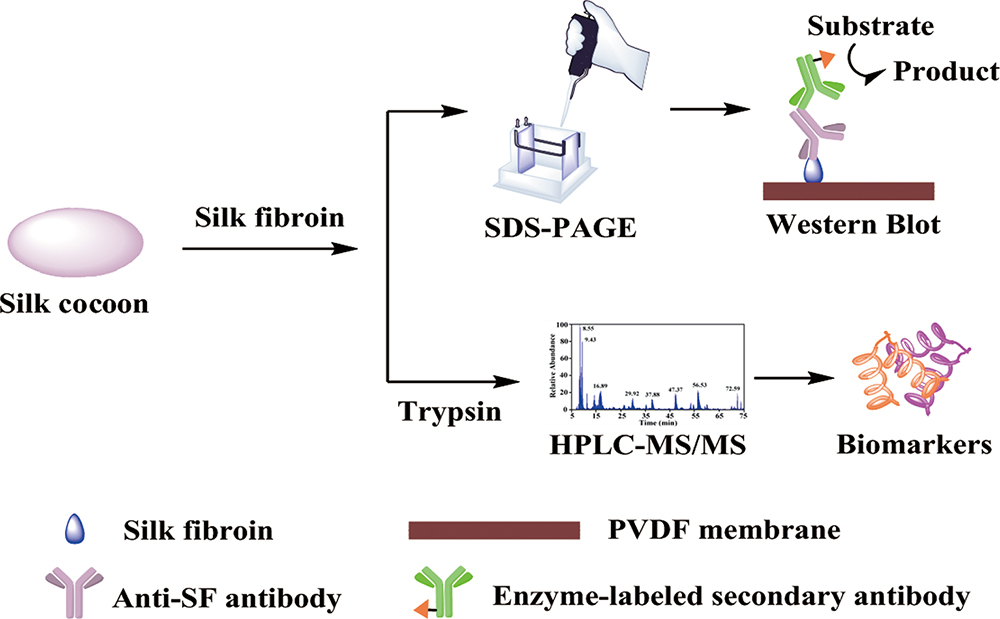 View full abstractDownload PDF (609K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (609K) -
Yingying ZHANG, Luhui WANG, Yafei DONGArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 181-187
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDue to structual polymorphism, excellent binding activity and functional significances in biological regulation, G-quadruplex has become the focus of research as an innovated module for analytical chemistry and biomedicine. Meanwhile, in the biosensor fields, new nanomaterial graphene oxide (GO) has also received extensive attention due to its brilliant physical and chemical properties. Herein, we propose a non-label and enzyme-free logic operation platform based on G-quadruplex structure and GO instead of any expensive modification. Taking advantage of the quenching ability of GO to AgNCs and the fluorescence enhancement of NMM (N-methylmesoporphyrin IX) mediated by the split G-quadruplex, a series of binary logic gates (AND, OR, INHIBIT, XOR) have been constructed and verified by biological experiments. Subsequently, two combinatorial logic gates were successfully realized conceptually on the basis of the same BGG platform, including half adder and half subtractor. Taken together, such a universal platform has great potential in applications, such as biocomputing, bio-imaging and disease diagnosis, which cultivate a new view for future biological research.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1098K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1098K) -
Manal A. EL-SHAL, Hassan A. M. HENDAWYArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 189-194
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 05, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSElectrochemical techniques were used for estimating xylazine HCl (XLZ) in bulk powder, medicinal manufacturing and human serum. Electro-oxidation of XLZ at carbon multiwalled nanotube (MWCNT), 1-n-butyl-3-methylpyridinium hexafluorophosphate ion crystal (BMH) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) MWCNT-BMH-SDS electrode in 0.04 M Britton–Robinson buffer (BR) with pH 7.0, was studied in numerous buffer structures and at different pH values. The experimentation and instrumental parameters to assessable commitment of XLZ had been optimized, and a detection limit was observed as 4.80 nM. The precision and accuracy for the recognized method was tested by retrieval studies with good repeatability and reproducibility of the estimated method. The projected method was practiced successfully to the dosage form and spiked serum.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (410K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (410K) -
Zhejian LI, Shumin WANG, Xuemei FAN, Baoyue CAO, Chunsheng ZHOUArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 195-199
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 05, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel gold nanoprobe for a sensitive and simple determination of a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was designed on the basis of homogeneous detection and a peptide cleavage reaction. The gold nanoprobe (AuNPs-peptide-Ru1) consisted of a specific peptide tagged with a ruthenium(II) complex (Ru1) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) conjugated with the peptide via the strong Au–S bond between the AuNPs surface and the thiol group of the peptide. The electrochemiluminescence (ECL) enzymatic-cleavage-reaction-based bioanalytic system based on homogeneous detection has overcome shortcomings from a complicated fabrication process of traditional electrodes. In the presence of the target PSA, it specifically cleaved the peptide of the AuNPs-peptide-Ru1, and the ECL signal substance (Ru1) part dissociated from AuNPs-peptide-Ru1. This resulted in an increase in the ECL intensity. The ECL biosensor could detect PSA concentrations in the range from 1.0 × 10−12 to 1.0 × 10−9 g/mL, the detection limit was 4.0 × 10−13 g/mL. The assay with the advantages of a simple method for PSA was selective and fast. It is superior to the immunoassay, and is a promising strategy to develop biosensors based on enzymatic cleavage including electrochemistry and optics.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (730K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (730K) -
Qi CHANG, Yun SHAO, Yang YANG, Han YU, Renqi WANGArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 201-206
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 12, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA chromatographic retention assisted denoising and peak picking algorithm (CRAD) is developed for preprocessing liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) datasets of natural products. The retention behaviors of ions with the same m/z value are investigated under a series of elution conditions. The detected ions are identified as real compounds if their chromatographic retention behaviors fit well with the Snyder–Soczewinski model. Further, the ions with similar retention behaviors and isotope ratios are clustered. This method enables rapid identification of precursor ions when chemical standards or databases are unavailable. It also helps eliminate unexpected baseline disturbances and improve the resolution of LC-MS chromatograms. Unlike conventional deconvolution strategies, this method distinguishes the chemical properties of precursor ions through their dynamic retention behaviors. The algorithm is demonstrated with LC-MS datasets of control samples. In the application of such algorithms on a more complicated natural extract from Lycium ruthenicum Murr., 206 precursor ions were facilely determined.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1078K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1078K) -
Anna-Cathrine NEUMANN, Stanislav MELNIK, Reinhard NIESSNER, Eva STOEGE ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 207-214
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 12, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSEutrophication of water bodies can promote cyanobacterial (blue-green algae) blooms, which has become a source of increasing concern for both recreational and drinking water use. Many bacterial species can produce toxins that pose threats to wildlife, domestic animals and humans. Microcystin-leucine-arginine (MC-LR) is the most frequent and most toxic microcystin congener. For the first time, lab-scale investigations were performed to test the application of a recombinant plant-derived anti-MC-LR antibody immobilized on an immunoaffinity support material to selectively extract the toxin from spiked freshwater samples. As a comparison, its hybridoma-derived counterpart (murine monoclonal antibody) was evaluated. The antibody-doped material was prepared via an optimized sol-gel process; its stability and binding efficiency of MC-LR in spiked freshwater samples were thoroughly tested using the ELISA and orthogonal LC-MS methods. For removal, two column-based procedures with sequential or continuous cyclic sample addition and a suspension mode (moving adsorbent) were tested. Noteworthy the results obtained with a crude antibody fraction were fully compatible with the highly purified preparation. This study paves the way for further investigation being focused on novel applications of plant-derived anti-MC-LR antibodies in bioremediation to selectively deplete the toxin from freshwater: a green and promising technology without secondary pollution.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1785K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1785K)
-
Manami NAKAMURA, Hiroyasu MURATA, Kiichi SATO, Kin-ichi TSUNODAArticle type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 215-218
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 14, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA liquid-core liquid-cladding optical waveguide based on thermal gradients across laminar flow was built with the laminar flow of water in a stainless capillary tube placed in a heat source. Its characteristics were studied with both experiments and a computational fluid dynamics simulation, firstly showing that it had the nature of a graded index optical fiber.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (707K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (707K) -
Pathinan PAENGNAKORN, Saiphon CHANPAKA, Kanchana WATLA-IAD, Wasin WONG ...Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 219-221
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA downscaling in true titration based on a simple sequential injection analysis-lab-at-valve (SIA-LAV) has been proposed. A titrant solution was stepwise aspirated into a titration LAV chamber and a titration curve was obtained by monitoring the change in the solution color spectroscopically. This fully-automated SIA-LAV system required less volume of the sample/reagents, only a micro-liter scale, compared to the conventional method. The system was investigated with complexometric titration and acid-base titration. Application of the developed technique to some real samples has been demonstrated.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (137K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (137K) -
Shiro MIYAKE, Daisuke IRIKURA, Tomomi YAMASAKIArticle type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 223-225
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn immunosensor based on surface plasmon resonance was developed for detection of c-Kit expressed on a cell surface. The combination of the antibody solution modified with gelatin before immobilization to the sensor chip and its blocking with gelatin drastically decreased the nonspecific reaction. The condition may be useful for the detection of various cells by using antibody against cell surface marker including the c-Kit.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (433K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (433K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2019 Volume 35 Issue 2 Pages 227
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1085K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
