All issues

Volume 30, Issue 11
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1033
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (170K)
Rapid Communications
-
Yuta ARAI, Makoto HARADA, Tetsuo OKADAArticle type: Rapid Communications
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1035-1037
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA size-tunable micro-channel is fabricated in a gap between two probe electrodes by freezing aqueous KCl. The channel has been characterized by resistance measurements and channel blocking by resistive particles. The channel size can be varied by the temperature even after the preparation of the channel. The channel is potentially useful not only for size-selective particle counting but also for the size-selective separation or filtration of particles and macromolecules. View full abstractDownload PDF (646K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (646K)
Original Papers
-
Zhaohui HU, Yanhong ZHOU, Xiangtao XIE, Renjie JIANG, Ningning LIArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1039-1044
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSHighly sensitive detection of bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP6) mRNA is essential to monitor bone regeneration in the regenerating defects. In this work, we proposed a quantitative approach based on two-stage nicking enzyme signal amplification (NESA) and DNAzyme amplification for highly sensitive detection of BMP6 mRNA. The two-stage NESA involves two templates and two-stage amplification reactions under isothermal conditions. The first template contains two repeat sequences that could hybridize to the target RNA, triggering an exponential amplification. The amplified product was a short single-stranded DNA with the same sequence as the target RNA. The single-stranded DNA can trigger another linear NESA and produces a large amount of horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-mimicking G-quadruplex DNAzyme. This proposed assay showed a quantitative analysis of BMP6 mRNA in a wide range from 1 fM to 100 nM with a detection limit of 0.01 fM.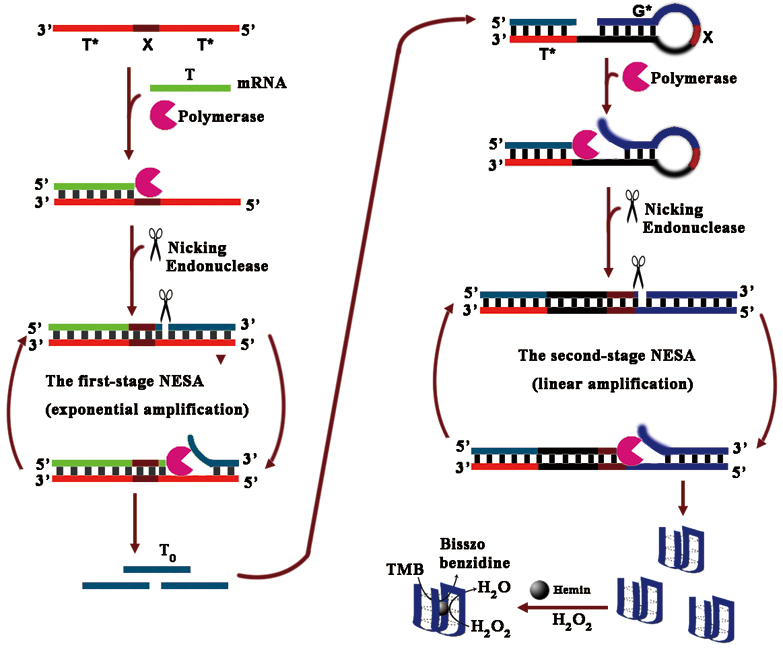 View full abstractDownload PDF (3249K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3249K) -
Hiroyuki KOBAYASHI, Kohei KATANO, Takeshi HASHIMOTO, Takashi HAYASHITAArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1045-1050
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe fluorescence behavior of a probe dpa-HC, which has a coumarin derivative that acts as a fluorophore and a dipicolylamine (DPA) unit that functions as a metal ion-recognition site, was investigated with various metal ions in aqueous and several non-aqueous solvents. In aqueous solution, the fluorescence of dpa-HC was enhanced by Zn2+ and Cd2+, but was quenched by other metal ions. On the other hand, in an acetonitrile solution, only Mg2+ enhanced the fluorescence, and the addition of a small amount of water quenched this fluorescence. This dramatic selectivity change is explained by stabilization of a metal-dpa-HC complex due to acetonitrile coordination and ON-OFF switching of the intramolecular photoinduced electron transfer (PET) from the nitrogen lone pair of DPA to the coumarin derivative.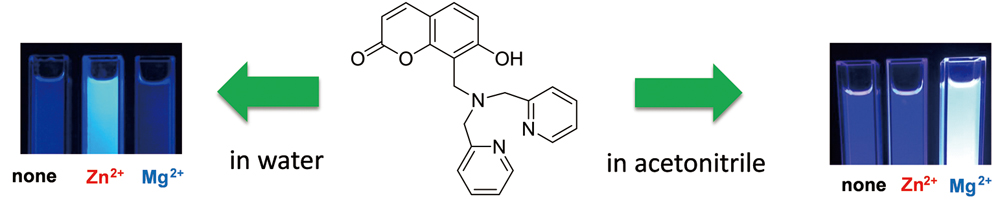 View full abstractDownload PDF (3280K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3280K) -
Stefan BAJ, Tomasz KRAWCZYK, Natalia PRADEL, Md. Golam AZAM, Takayuki ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1051-1056
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA carbon nanofiber-based luminol-biotin probe was synthesized for the sensitive chemiluminescence (CL) detection of a target protein by grafting luminol and biotin onto an oxidized carbon nanofiber. This carbon nanofiber was prepared by chemical vapor-deposition with methane in the presence of the Ni–Cu–MgO catalyst, which was followed by oxidization with HNO3–H2SO4 to produce a carboxyl group on the surface of the nanofiber. The material was grafted with luminol and biotin by means of a standard carbodiimide activation of COOH groups to produce corresponding amides. The substance was water-soluble and thus could be utilized as a sensitive CL probe for a protein assay. The probe showed highly specific affinity towards the biotin-labeled antibody via a streptavidin–biotin interaction. The detection limit for this model assay was approximately 0.2 pmol of the biotinized IgG spotted on a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. Nonspecific binding to other proteins was not observed. Therefore, the synthesized carbon nanofiber-based CL probe may be useful for a sensitive and specific analysis of the target protein. View full abstractDownload PDF (749K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (749K) -
Susana S. M. P. VIDIGAL, António O. S. S. RANGELArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1057-1062
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe present paper describes a flow-injection system coupled to a Micro-Guard cartridge and a miniaturized optical CCD detection system used to monitor the sugars (glucose/fructose) and ethanol content during alcoholic fermentation. The carrier stream (mobile phase) is composed of an aqueous sulfuric acid solution. The flow parameters were studied in order to obtain a good resolution and a wide dynamic concentration range, with a good repeatability. The relative standard deviation (RSD) obtained was inferior to 4%, for n = 3. It was possible to achieve a linear range of up to 12 g L−1 of sugars and up to 2% (v/v) of ethanol with a detection limit of 2.3 g L−1 and 0.4% (v/v), for sugars and ethanol concentrations, respectively. The proposed system was successfully applied to monitor a vinification process by the quantification of sugars and ethanol, and also in some finished port wines. View full abstractDownload PDF (1102K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1102K) -
Po-Ting CHEN, Hsiao-Ping CHEN, Chia-Hung HUNG, Shau-Chun WANGArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1063-1068
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSStatic light-scattering (LS) detection can determine the molecular weight (MW) of polymers eluted with size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) without using any standards when the differential refraction index (RI) of solutes are obtained. On the other hand, the noisy chromatographic signal peak acquired using a static LS detector often causes difficulty in peak-width recognition. This disadvantage limits the determination accuracy and precision of the MW values. This study developed one second-order derivative filtering procedure by convolving the original LS chromatogram against the second-derivative curve of one artificial Gaussian-shape chromatographic peak to suppress the noises and to correct the baseline of the chromatogram. More accurate estimations of the chromatographic peak widths of pullulan samples were achieved to improve the MW determination accuracy. For noisy original chromatography peaks of pullulan 5 k (SNR of approximately 10), the non-ideal determination accuracy of the MW values (9.3%) is improved to −1.3% with the assistance of the filtering procedures.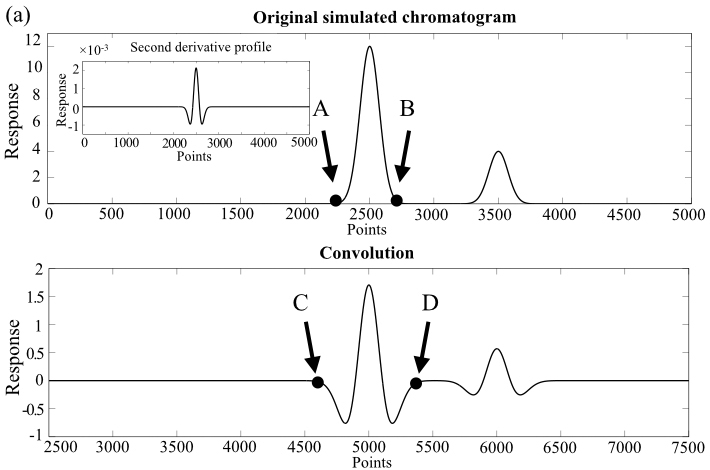 View full abstractDownload PDF (746K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (746K) -
Kotaro BESSHO, Naoki KANAYA, Saki SHIMADA, Shoichi KATSUTA, Hideaki MO ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1069-1074
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe adsorption behavior of Be(II) on CuO nanoparticles dispersed in water was studied as a model for colloid formation of radioactive 7Be nuclides in the cooling water used for electromagnets at high-energy proton accelerator facilities. An aqueous Be(II) solution and commercially available CuO nanoparticles were mixed, and the adsorption of Be(II) on CuO was quantitatively examined. From a detailed analysis of the adsorption data measured as a function of the pH, it was confirmed that Be(II) is adsorbed on the CuO nanoparticles by complex formation with the hydroxyl groups on the CuO surface (>S–OH) according to the following equation:
n > S–OH + Be2+ ⇔ (>S–O)n Be(2−n)+ + nH+ (n = 2, 3) S : solid surface.
The surface-complexation constants corresponding to the above equilibrium, β(s,2) and β(s,3), were determined for four types of CuO nanoparticles. The β(s,2) value was almost independent of the type of nanoparticle, whereas the β(s,3) values varied with the particle size. These complexation constants successfully explain 7Be colloid formation in the cooling water used for electromagnets at the 12-GeV proton accelerator facility. View full abstractDownload PDF (612K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (612K) -
Shoji ISHIZAKA, Kunihiro YAMAUCHI, Noboru KITAMURAArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1075-1079
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNoncontact levitation of single micrometer-sized water droplets in air can be achieved by a laser trapping technique. The equilibrium size of a water droplet is quite sensitive to relative humidity in the surrounding gas phase. In order to investigate the physical and chemical properties of single water droplets in air as a function of the droplet size or solute concentration, laser trapping experiments were conducted under controlled humidity conditions. In this study, we developed a trapping chamber equipped with a relative humidity controller and demonstrated the reversible control of the equilibrium size of a single droplet levitated in air through a change in relative humidity. Furthermore, relative humidity was successfully evaluated by means of cavity enhanced Raman spectroscopy of a trapped water droplet. View full abstractDownload PDF (521K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (521K) -
Hongmei YU, Jing PANG, Mei WU, Qiaoli WU, Cuixiu HUOArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1081-1087
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe ues of corn silk modified with diluted nitric acid (HNO3-MCS) as a novel biosorbent has been established for solid-phase extraction of Cr(III) and chromium speciation in water samples. The functional groups of the HNO3-MCS surface are favorable for the adsorption of Cr(III). Effective extraction conditions were optimized in both batch and column methods. At pH 3.0 – 6.0, a discrimination of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) is achieved on the HNO3-MCS surface. Cr(III) ions are retained onto the HNO3-MCS surface, however, the adsorption of Cr(VI) is negligible under the same conditions. The adsorption isotherm of HNO3-MCS for Cr(III) has been demonstrated in accordance with a linear form of the Langmuir equation, and the maximum adsorption capacity is 35.21 mg g−1. The well fitted linear regression of the pseudo-second order model showed the indication of a chemisorption mechanism for the entire concentration range. Thermodynamic studies have shown that the adsorption process is spontaneous and endothermic. The adsorbed Cr(III) was quantitatively eluted by a nitric acid solution with detection by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). With a sample volume of 30 mL, a detection limit (3σ) of 0.85 μg L−1 and a precision of 2.0% RSD at the 40 μg L−1 level were achieved. The concentration of Cr(III) could be accurately quantified within a linear range of 3 – 200 μg L−1. After Cr(VI) has been reduced to Cr(III) with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, the total amount of chromium was obtained, and the content of Cr(VI) was given by subtraction. The procedure was validated by analyzing chromium in a certified reference material (GBW (E) 080039). It was also successfully applied for the speciation of chromium in wastewater samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (1175K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1175K) -
Thi Kim Dzung NGUYEN, Rainer LUDWIGArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1089-1092
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTrace concentrations of bromine and iodine in food samples and certified reference materials (CRMs) were determined by an inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) technique after low-power microwave digestion and extraction into an aqueous quaternary ammonium hydroxide solution. The recovery after sample preparation was quantitative. The internal standard for the measurement of the analyte on ICP-MS was optimized in this study. The detection limits were 0.19 and 0.68 ng g−1 for I and Br, respectively, when a 10 ng g−1 Te solution as an internal standard was used, applying the signal of 125Te. The high recovery and reproducibility are sufficient for the quantitative analysis of these elements, and the analytical procedure is recommended for the analysis of Br and I in various kinds of bio-samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (385K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (385K)
Notes
-
Naoto SHIRASU, Masahide KUROKIArticle type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1093-1096
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe developed a time- and cost-effective multiplex allele-specific polymerase chain reaction (AS-PCR) method based on the two-step PCR thermal cycles for genotyping single-nucleotide polymorphisms in three alcoholism-related genes: alcohol dehydrogenase 1B, aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and μ-opioid receptor. Applying MightyAmp® DNA polymerase with optimized AS-primers and PCR conditions enabled us to achieve effective and selective amplification of the target alleles from alkaline lysates of a human hair root, and simultaneously to determine the genotypes within less than 1.5 h using minimal lab equipment.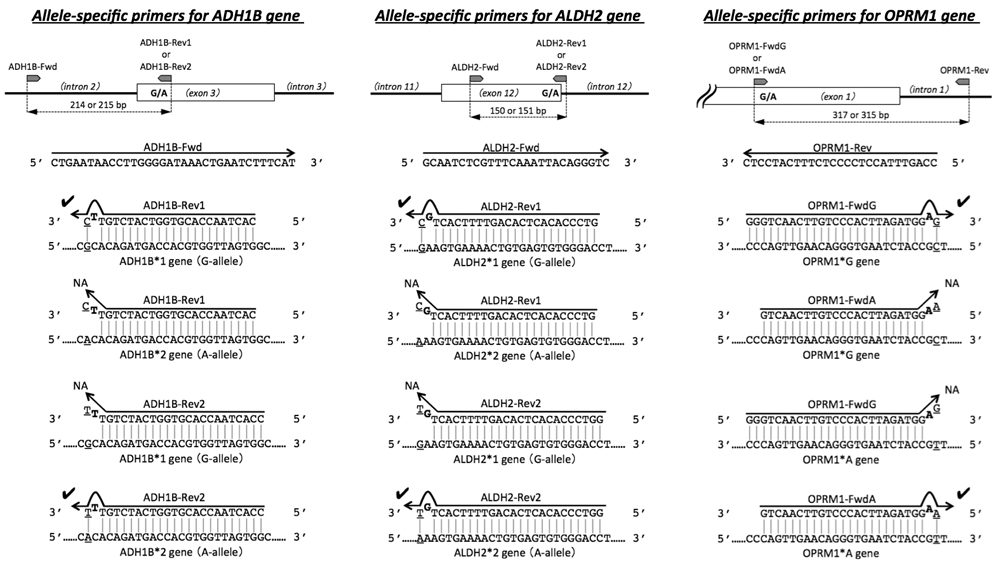 View full abstractDownload PDF (516K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (516K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014Volume 30Issue 11 Pages 1097
Published: November 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2618K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|