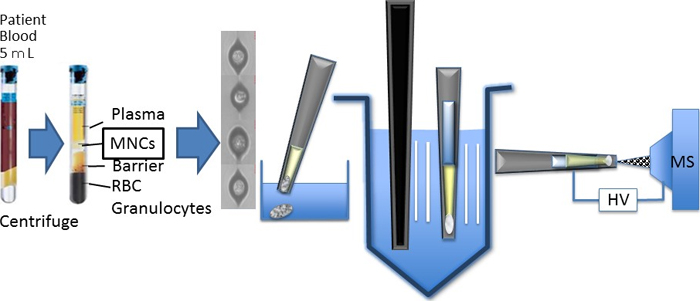
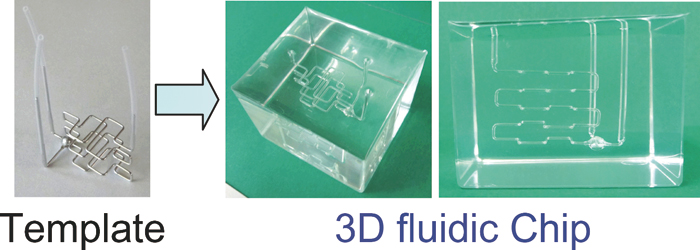
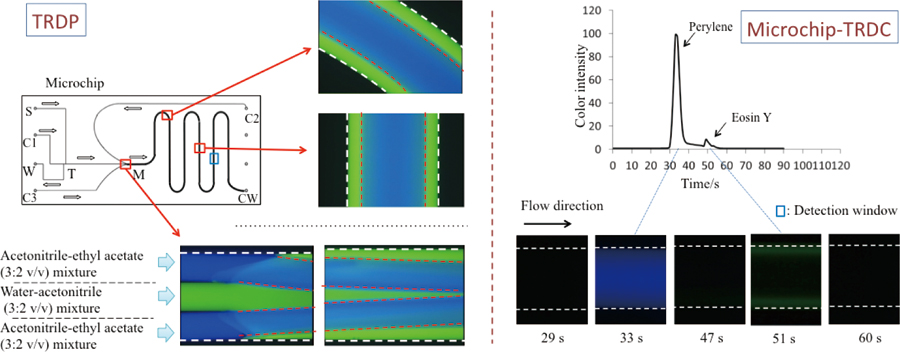
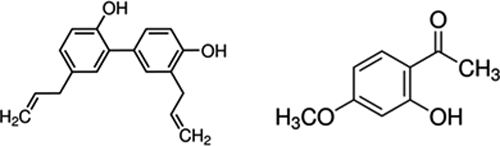
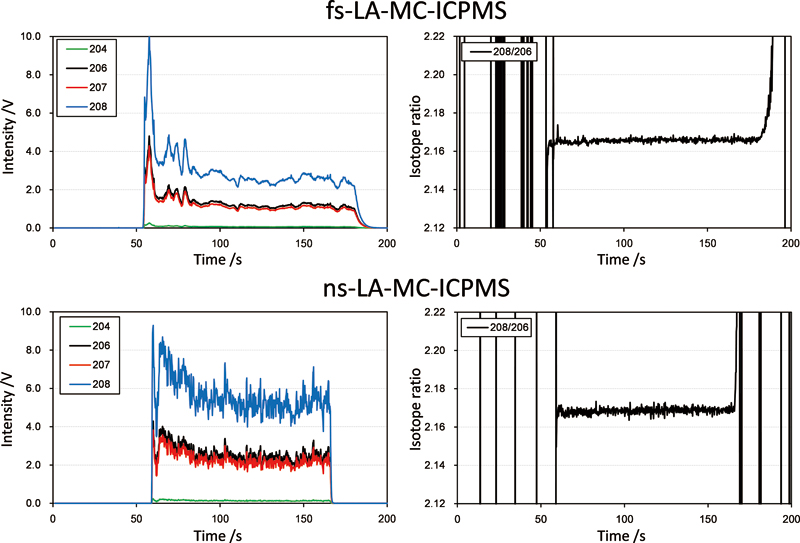
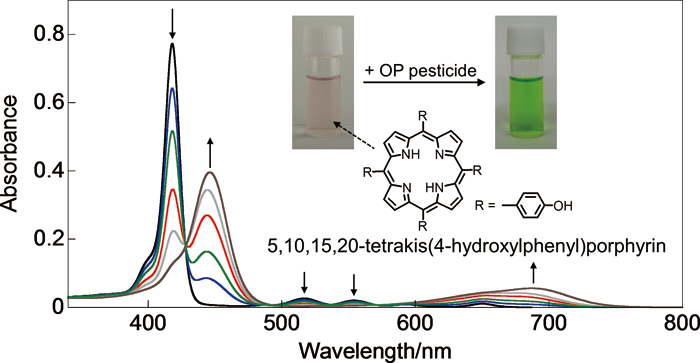
Volume 31, Issue 12
Displaying 1-23 of 23 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1211-1213
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (2610K) -
Article type: Rapid Communications
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1215-1217
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (1023K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1219-1224
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (3393K) -
Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine, Uric Acid and Guanine at Polyadenine Film Modified ElectrodeArticle type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1225-1231
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (3993K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1233-1240
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (925K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1241-1247
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (802K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1249-1253
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (894K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1255-1260
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (627K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1261-1266
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (879K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1267-1272
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (3050K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1273-1277
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (1113K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1279-1283
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (742K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1285-1289
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (3866K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1291-1295
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (2111K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1297-1302
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (867K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1303-1308
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (594K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1309-1315
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (3163K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1317-1323
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (1144K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1325-1328
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (459K) -
Article type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1329-1333
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (1206K) -
Article type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1335-1339
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (627K) -
Article type: Notes
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1341-1344
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (464K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015Volume 31Issue 12 Pages 1345
Published: December 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2015
Download PDF (2699K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|