All issues

Volume 31, Issue 3
Displaying 1-17 of 17 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 137
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (189K)
Original Papers
-
Mitsuru YASUDA, Takuo AKIMOTOArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 139-143
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHigh-contrast fluorescence imaging using an optical interference mirror (OIM) slide that enhances the fluorescence from a fluorophore located on top of the OIM surface is reported. To enhance the fluorescence and reduce the background light of the OIM, transverse-electric-polarized excitation light was used as incident light, and the transverse-magnetic-polarized fluorescence signal was detected. As a result, an approximate 100-fold improvement in the signal-to-noise ratio was achieved through a 13-fold enhancement of the fluorescence signal and an 8-fold reduction of the background light. View full abstractDownload PDF (1695K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1695K) -
Ju-Yen SUN, Chao-Min CHENG, Ying-Chih LIAOArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 145-151
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA simple and low-cost fabrication method for paper-based diagnostic devices (PBDDs) is described in this study. Street-available polymer solutions were screen printed onto filter papers to create hydrophobic patterns for fluidic channels. In order to obtain fully functional hydrophobic patterns for fluids, the original polymer solutions were diluted with butyl acetate to yield a suitable viscosity range between 30 – 200 cP for complete patterning on paper. Typical pH and glucose tests with color indicators were performed on the screen printed PBDDs. Images of the PBDDs were analyzed by computers to obtain calibration curves for pH between 2 and 12 and glucose concentration ranging from 10 – 1000 mmol dm−3. Detection of formaldehyde in acetone was also carried out to show the possibility of using this PBBD for analytical detection with organic solvents. An exemplar PBDD with simultaneous pH and glucose detection was also used to demonstrate the feasibility of applying this technique for realistic diagnostic applications.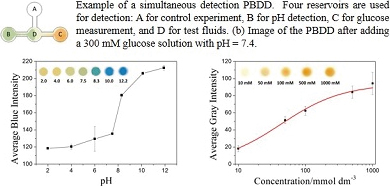 View full abstractDownload PDF (2046K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2046K) -
Sakon RAHONG, Takao YASUI, Takeshi YANAGIDA, Kazuki NAGASHIMA, Masaki ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 153-157
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialMolecular filtration and purification play important roles for biomolecule analysis. However, it is still necessary to improve efficiency and reduce the filtration time. Here, we show self-assembled nanowire arrays as three-dimensional (3D) nanopores embedded in a microfluidic channel for ultrafast DNA filtration. The 3D nanopore structure was formed by a vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) nanowire growth technique, which allowed us to control pore size of the filtration material by varying the number of growth cycles. λ DNA molecules (48.5 kbp) were filtrated from a mixture of T4 DNA (166 kbp) at the entrance of the 3D nanopore structure within 1 s under an applied electric field. Moreover, we observed single DNA molecule migration of T4 and λ DNA molecules to clarify the filtration mechanism. The 3D nanopore structure has simplicity of fabrication, flexibility of pore size control and reusability for biomolecule filtration. Consequently it is an excellent material for biomolecular filtration. View full abstractDownload PDF (997K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (997K) -
Min-Jung SONG, Joon-Hyung JINArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 159-163
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA nanoporous silicon-based label-free DNA biosensor was fabricated to monitor rapidly enteric adenovirus types 40 and 41, a leading cause of viral gastroenteritis in children. Nanoporous silicon (NPS) was formed by an anodic etching process in a mixture solution containing hydrofluoric acid and ethanol. The polypyrrole (PPy) film was directly electropolymerized on The NPS substrate. Twenty-five base pairs of probe DNA (pDNA), derived from the fiber gene, was electrochemically doped on the PPy-coated NPS substrate. The conductivity change due to the immobilized pDNA and hybridized target DNA (tDNA) was expressed as an arbitrary factor, γ, which is a normalized numerical term used for the selective quantification of the tDNA. γ was inversely proportional to the concentration of complementary tDNA, but independent of the non-complementary tDNA. The sensitivity slope for detecting tDNAc was –1.54 μM−1, based on the factor γ in the range of 0.4 to 1.0 μM of tDNA. The surface roughness was characterized using atomic force microscopy. View full abstractDownload PDF (647K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (647K) -
Camila MARCHIONI, Fagner Moreira de OLIVEIRA, Cristiana Schmidt de MAG ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 165-172
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMany metals are toxic in human organism, as is the case of cadmium and lead. Therefore, the metal levels in food need to be controlled. In coffee, metals may present risks when they are extracted from the powder to be consumed as beverage. A flow injection analysis (FIA) system is proposed, with atomic absorption detection, to metal adsorption studies in coffee powder. Kinetic study, best isotherms and time, and mass influences were determined. They allowed analyzing the high lead and cadmium adsorption percentage in organic and conventional ground coffee. Metal adsorption occurs in multilayers, following Freundlich’s model, and the kinetic model obeyed is the pseudo-second order. The cadmium adsorption suffered higher temperature influence, while the lead retention suffered higher mass influence. This study indicates that the majority of these toxic agents will be retained in the powder and will not be consumed by man, avoiding possible deleterious effects. View full abstractDownload PDF (1293K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1293K) -
Hirokazu SETO, Seiji KAMBA, Takashi KONDO, Yuichi OGAWA, Yu HOSHINO, Y ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 173-176
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA biosensor for protein detection was developed using antibody-immobilized metal mesh devices. Antihemoglobin antibodies were covalently immobilized on a metal mesh device. Extraordinary transmission with a dipped structure was observed for a metal mesh device immobilized with antihemoglobin antibodies as well as for the original metal mesh device. Hemoglobin in the mixture solution containing albumin at a hundred-fold concentration was detectable using antihemoglobin-immobilized MMDs. The detectability using the antihemoglobin-immobilized metal mesh device was similar to that of a commercially-available kit for the qualitative determination of hemoglobin. View full abstractDownload PDF (461K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (461K) -
Takuya OKAZAKI, Kenichiro IMAI, Shin Y. TAN, Yun T. YONG, Faidz A. RAH ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 177-183
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study proposes an optical fiber sensor for calcium carbonate (CaCO3) scale formation in water. The sensor is easily fabricated by removing the cladding of a multimode fiber to expose the core towards the surrounding medium in order to detect refractive index change. A variation of the transmittance response from the high refractive index of CaCO3 which precipitated on the fiber core surface was observed. The proposed setup can be used to analyze the transmittance response over wide range of wavelength using white light as a source and also a spectroscopy detector. The curve of the transmittance percentage over time showed that a fiber core with 200 μm has higher sensitivity as compared to a fiber core with 400 μm. The findings from this study showed that the sensor detection region at near infrared (NIR) wavelengths showed better sensitivity than visible light (VIS) wavelengths. Field tests were conducted using natural geothermal water at Matsushiro, Japan in order to verify the performance of the proposed sensor. The optical response was successfully evaluated and the analytical results confirmed the capability of monitoring scale formation in a geothermal water environment. View full abstractDownload PDF (844K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (844K) -
Makoto SAGA, Tatsuya ANAMUSHI, Wakayo MIYAHARA, Shigeo YAMAZAKI, Keiit ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 185-189
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe fluorescence ligands N,N′-bis(2-methylquinolyl)dimethylethylenediamine (BQDMEN) and N,N′-bis(2-methylquinolyl)dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine (BQDMPN) were synthesized. [Cu(II)(bqdmen)]2+ and [Cu(II)(bqdmpn)]2+ were prepared, and their reduction to [Cu(I)(bqdmen)]+ and [Cu(I)(bqdmpn)]+ was confirmed by the observed UV-Vis spectral change. Then, the fluorescence of [Cu(I/II)(bqdmen)]+/2+ and [Cu(I/II)(bqdmpn)]+/2+ in aqueous solution was characterized; [Cu(I)(bqdmen)]+ and [Cu(I)(bqdmpn)]+ were found to fluoresce in aqueous solution, whereas the fluorescence of [Cu(II)(bqdmen)]2+ and [Cu(II)(bqdmpn)]2+ was completely quenched. On the basis of these findings, fluorometric detection of reductants with a flow-injection system using a [Cu(II)(bqdmen)]2+ or [Cu(II)(bqdmpn)]2+ solution as a carrier was explored.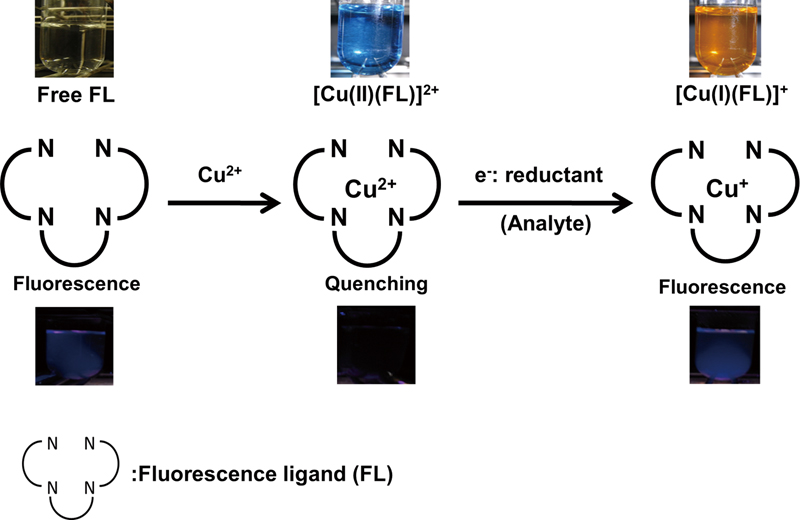 View full abstractDownload PDF (777K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (777K) -
Yan ZENG, Guanxin ZHANG, Deqing ZHANGArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 191-195
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA tetraphenylethylene-based compound with the property of aggregation-induced emission was designed and synthesized. It exhibited good sensitivity and selectivity to Cu2+ over other metal ions (Zn2+, Cd2+, Ba2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Co2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Ag+, K+, and Hg2+) in an aqueous solution by the “turn-off” UV-vis absorbance and fluorescence signals. More interesting, with the subsequent addition of histidine rather than other amino acids such as proline, alanine, aspartic acid, lysine, arginine, leucine, glutamine or cysteine, the complex between the compound and Cu2+ was disrupted, and the UV-vis absorbance and fluorescence signals were recovered, indicating that the complex from the compound and Cu2+ could be used as a “turn-on” fluorescent probe for histidine. View full abstractDownload PDF (758K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (758K) -
Yugo FUKUI, Yoshinori IIGUNI, Shinya KITAGAWA, Hajime OHTANIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 197-203
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel microchip separation method for microparticles based on electromagnetophoresis was developed. In this method, a double Y-shape microchip with two inlets and two outlets was used for particle separation. Microparticles of two different sizes were suspended in an aqueous solution and introduced into the microchannel from one inlet with a stream of the aqueous solution without particles from another inlet by a hydrodynamic flow. Then, the particles with two different sizes were migrated orthogonal to the flow by elctromagnetophoresis and separated to different outlets based on the difference in their electromagnetophoric velocities, which depended on the size of particle. Using this method, at one outlet, 89% of 3 μm polystyrene latex particles were isolated from a mixture of 3 and 10 μm particles. By combining hydrodynamic focusing, both 3 and 10 μm particles were recovered at the different outlets with 100% purity and recovery, respectively. Even the separation of 3 and 6 μm particles was also achieved with about 98% recovery and purity. Moreover, yeast cells and polystyrene particles could be separated with high separation efficiency by this technique.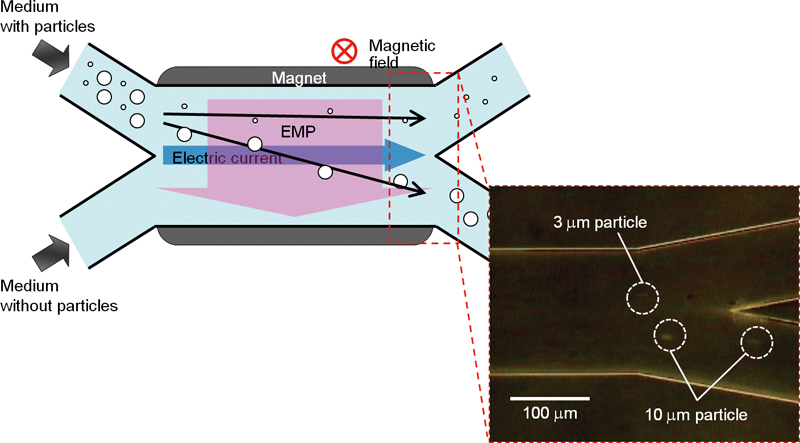 View full abstractDownload PDF (796K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (796K) -
He-Gang GAO, Wen-Jie GONG, Yong-Gang ZHAOArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 205-210
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSynthetic pigments are still used instead of natural pigments in many foods and their residues in food could be an important risk to human health. A simple and rapid analytical method combining the low-cost extraction protocol with ultra-fast liquid chromatography–tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (UFLC-MS/MS) was developed for the simultaneous determination of seven synthetic pigments used in colored Chinese steamed buns. For the first time, ethanol/ammonia solution/water (7:2:1, v/v/v) was used as extraction solution for the synthetic pigments in colored Chinese steamed buns. The results showed that the property of the extraction solution used in this method was more effective than critic acid solution, which is used in the polyamide adsorption method. The limits of quantification for the seven synthetic pigments ranged from 0.15 to 0.50 μg/kg. The present method was successfully applied to samples of colored Chinese steamed buns for food-safety risk monitoring in Zhejiang Province, China. The results found sunset yellow pigment in six out of 300 colored Chinese steamed buns (from 0.50 to 32.6 μg/kg).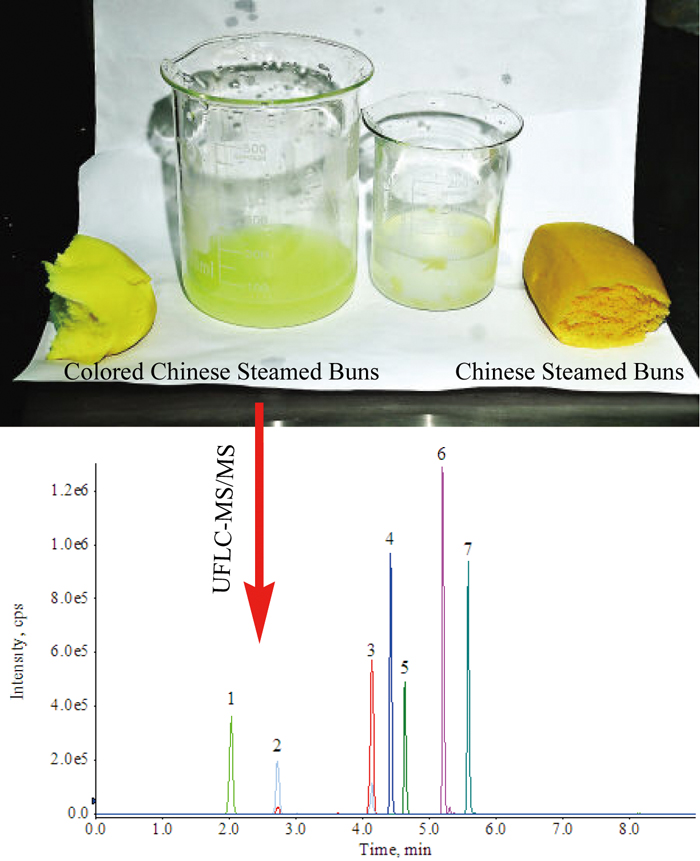 View full abstractDownload PDF (1116K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1116K) -
Kazufusa SHINOMIYA, Kazunori YOSHIDA, Koji TOKURA, Etsuhiro TSUKIDATE, ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 211-218
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSProtein separation was performed using the high-speed countercurrent chromatograph (HSCCC) at both synchronous and nonsynchronous type-J planetary motions. The partition efficiency was evaluated with two different column configurations, eccentric coil and toroidal coil, on the separation of a set of stable protein samples including cytochrome C, myoglobin and lysozyme with a polymer phase system composed of 12.5% (w/w) polyethylene glycol 1000 and 12.5% (w/w) dibasic potassium phosphate. Better peak resolution was obtained by the eccentric coil than by the toroidal coil using either lower or upper phase as the mobile phase. The peak resolution was further improved using the eccentric coil by the nonsynchronous type-J planetary motion with the combination of 1066 rpm of column rotation and 1000 rpm of revolution. View full abstractDownload PDF (1503K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1503K) -
Vaibhavi Vishwajeet RAUT, Subbiah JEYAKUMAR, Dipti Jayesh SHAH, Uday K ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 219-223
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA method based on the pyrohydrolysis extraction of boron and its quantification with ion chromatography was proposed for paraffin waxes borated with H3BO3 and B4C. The optimum pyrohydrolysis conditions were identified. Wax samples were mixed with U3O8, which prevents the sample from flare up, and also accelerates the extraction of boron. Pyrohydrolysis was carried out with moist O2 at 950°C for 60 and 90 min for wax with H3BO3 and wax with B4C, respectively. Two simple methods of separation based on alkali extraction and melting wax in alkali were also developed exclusively for wax with H3BO3. In all the separations, the recovery of B was above 98%. During IC separation, B was separated as boron–mannitol anion complex. Linear calibration was obtained it between 0.1 and 50 ppm of B, and LOD was calculated as 5 ppb (S/N = 3). The reproducibility was better than 5% (RSD). View full abstractDownload PDF (402K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (402K) -
Jing-Jing SONG, Yong LU, Si-Wei ZHU, Qin-An HUANG, Yan WEIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 225-230
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNH3-plasma treated multi-walled carbon nanotubes (pn-MWCNTs) were prepared based on the plasma technique and developed as sensing materials for detection of quercetin and kaempferol with the differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and amperometric measurement. Such experimental parameters as pH values, accumulation potential and accumulation time were carefully investigated. The pn-MWCNTs modified electrode (pn-MWCNTs/GCE) was further explored for the analysis of quercetin and kaempferol in diluted blood serum and average recovery rates of 96.91 and 100.5% were obtained, respectively. In addition, the interference and stability measurements were evaluated under the optimized experimental conditions. More importantly, selective detection toward quercetin and kaempferol was achieved, and the proposed electrochemical sensing strategy was available to distinguish substances with similar oxidation potential. View full abstractDownload PDF (1587K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1587K)
Notes
-
Madhu BETA, Subramanian KRISHNAKUMAR, Sailaja V ELCHURI, Bindu SALIM, ...Article type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 231-235
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCirculating serum microRNAs (miRNAs) are promising biomarkers for disease diagnosis. The quantification of the serum miRNA copy number is a challenge due to the presence of low levels in the serum. Here, we report on a direct measurement of the miRNA copy number from human serum using a locked nucleic acid (LNA) modified beacon probe with a single step using fluorescence spectroscopy and microscopy. We had used a minimum volume of 0.1 μL healthy human serum and retinoblastoma serum to show the biological variation of the miRNA copy number.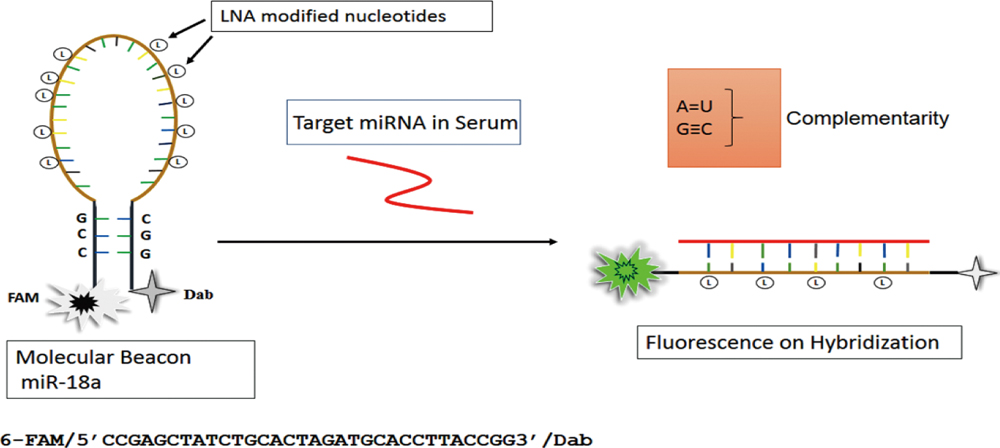 View full abstractDownload PDF (1084K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1084K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015 Volume 31 Issue 3 Pages 237
Published: March 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2654K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|