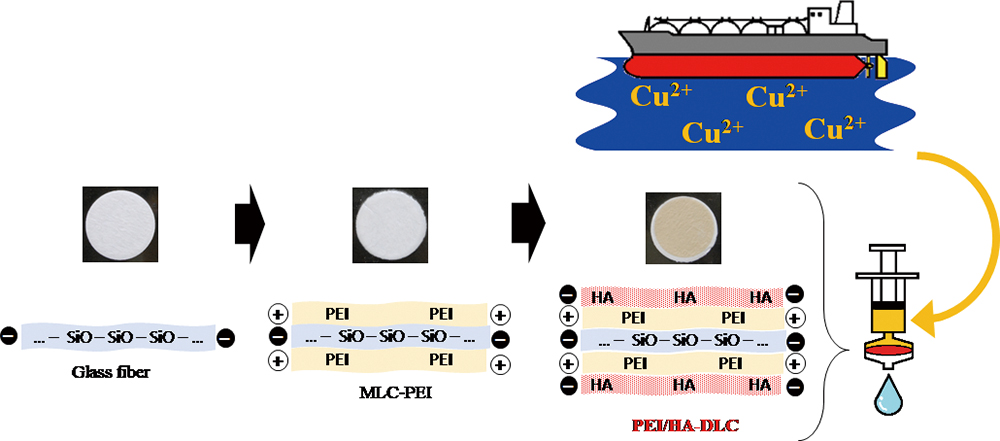
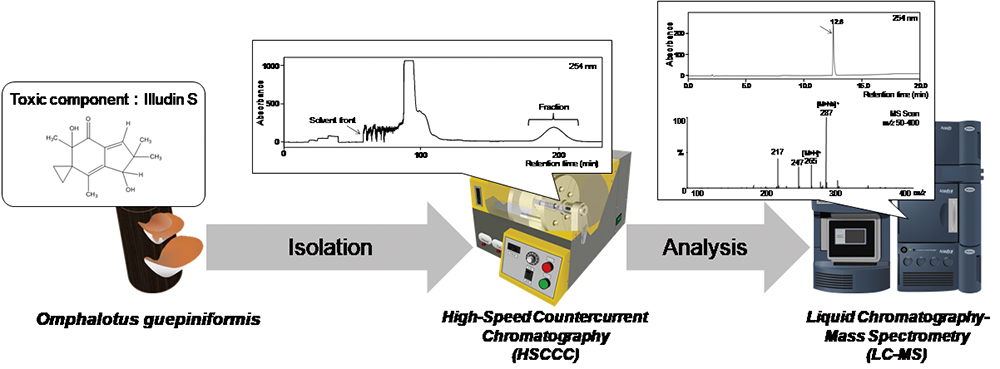
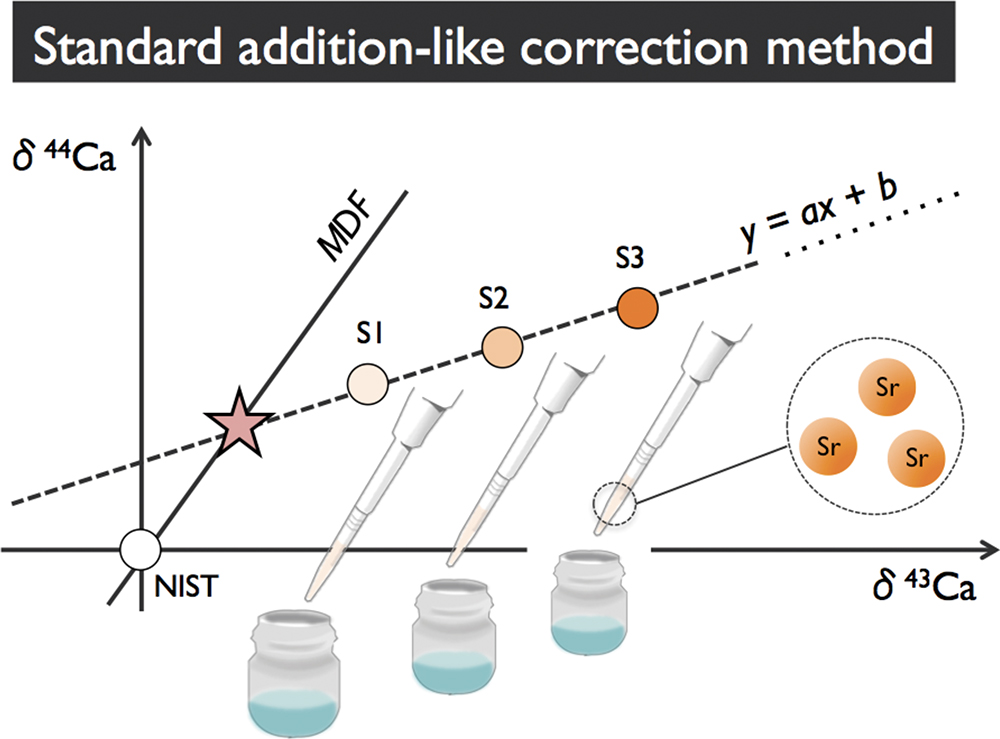
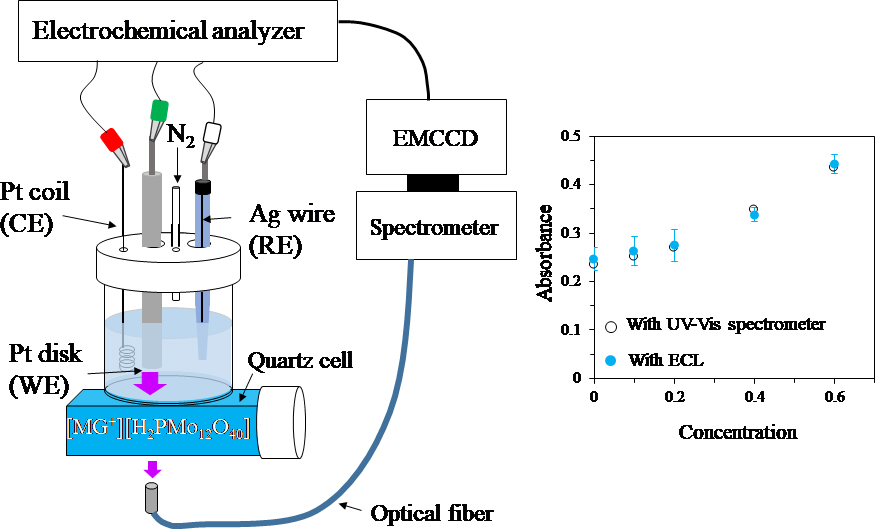
Volume 35, Issue 7
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 715
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Download PDF (29K)
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 717-718
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Download PDF (1522K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 719-732
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 22, 2019Download PDF (2474K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 733-738
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 08, 2019Download PDF (1082K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 739-743
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Download PDF (278K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 745-750
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 01, 2019Download PDF (501K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 751-757
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 08, 2019Download PDF (455K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 759-762
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 22, 2019Download PDF (364K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 763-767
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 22, 2019Download PDF (1977K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 769-775
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 22, 2019Download PDF (711K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 777-782
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 22, 2019Download PDF (809K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 783-787
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 29, 2019Download PDF (694K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 789-792
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 29, 2019Download PDF (243K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 793-798
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 05, 2019Download PDF (254K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 799-802
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Download PDF (1543K) -
Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 803-806
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 22, 2019Download PDF (181K) -
Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 807-809
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 29, 2019Download PDF (156K) -
Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 811-813
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 29, 2019Download PDF (977K) -
Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 815-819
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: April 05, 2019Download PDF (239K) -
Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 821-825
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 17, 2019Download PDF (7378K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2019 Volume 35 Issue 7 Pages 827
Published: July 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2019
Download PDF (1108K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|