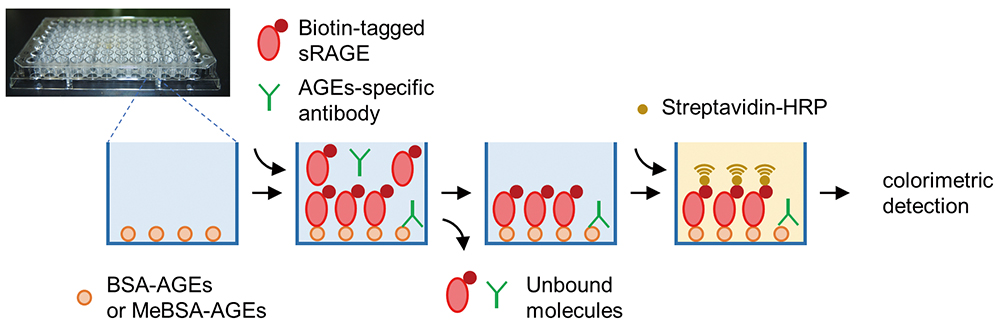
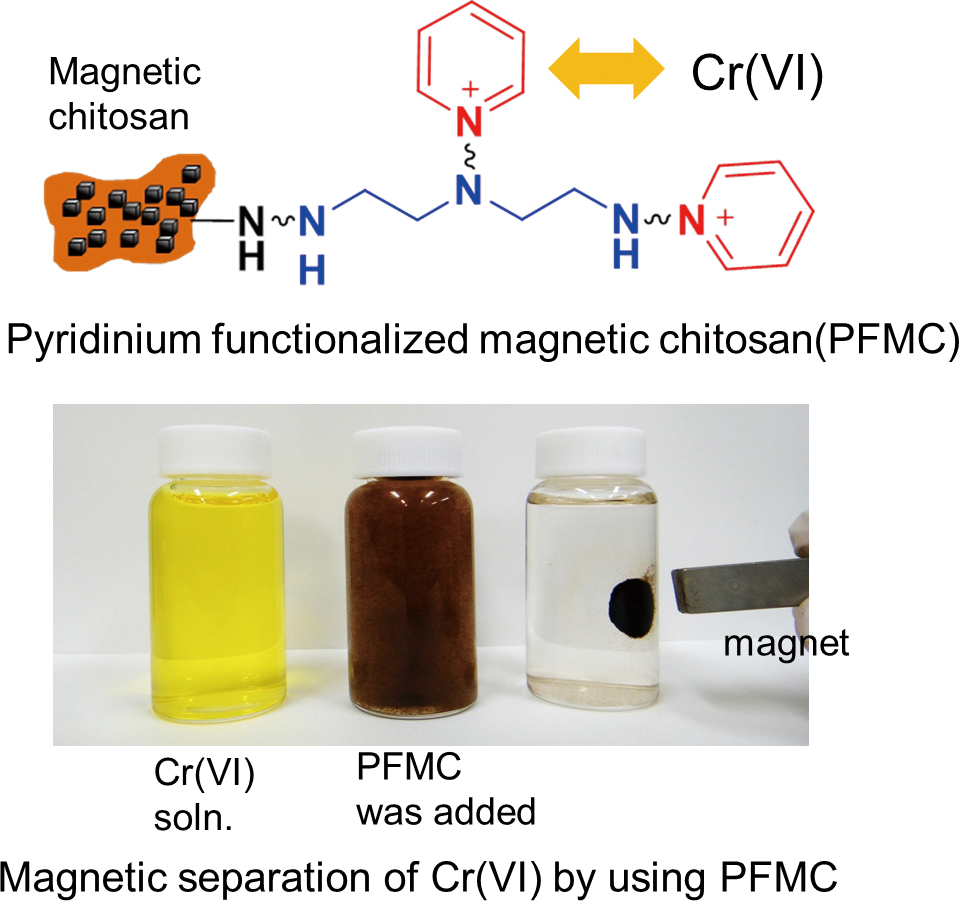
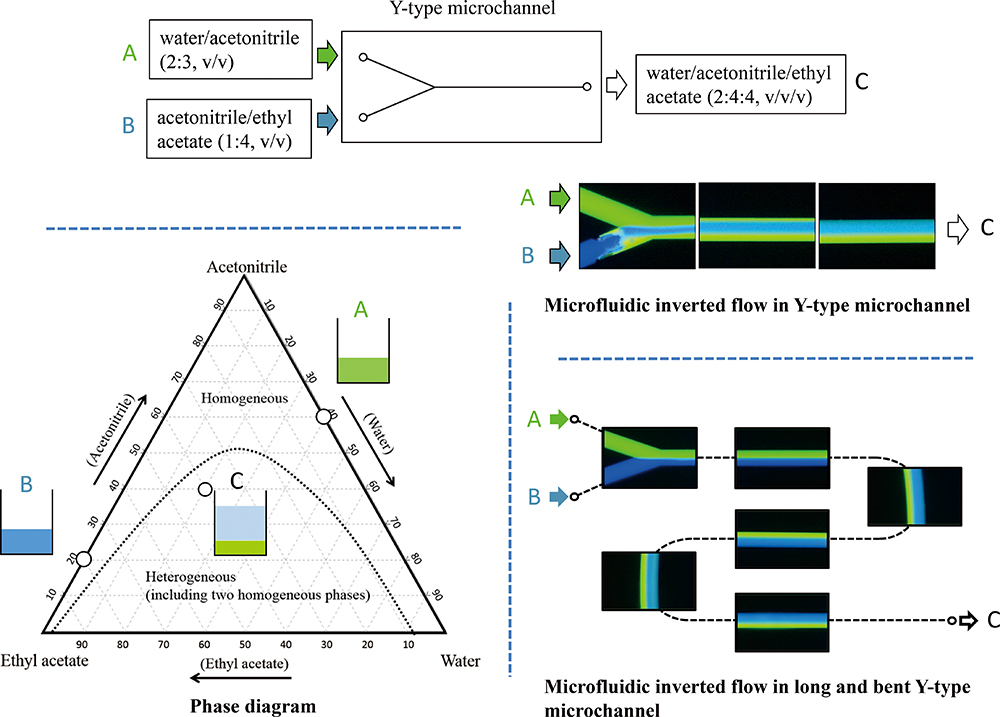
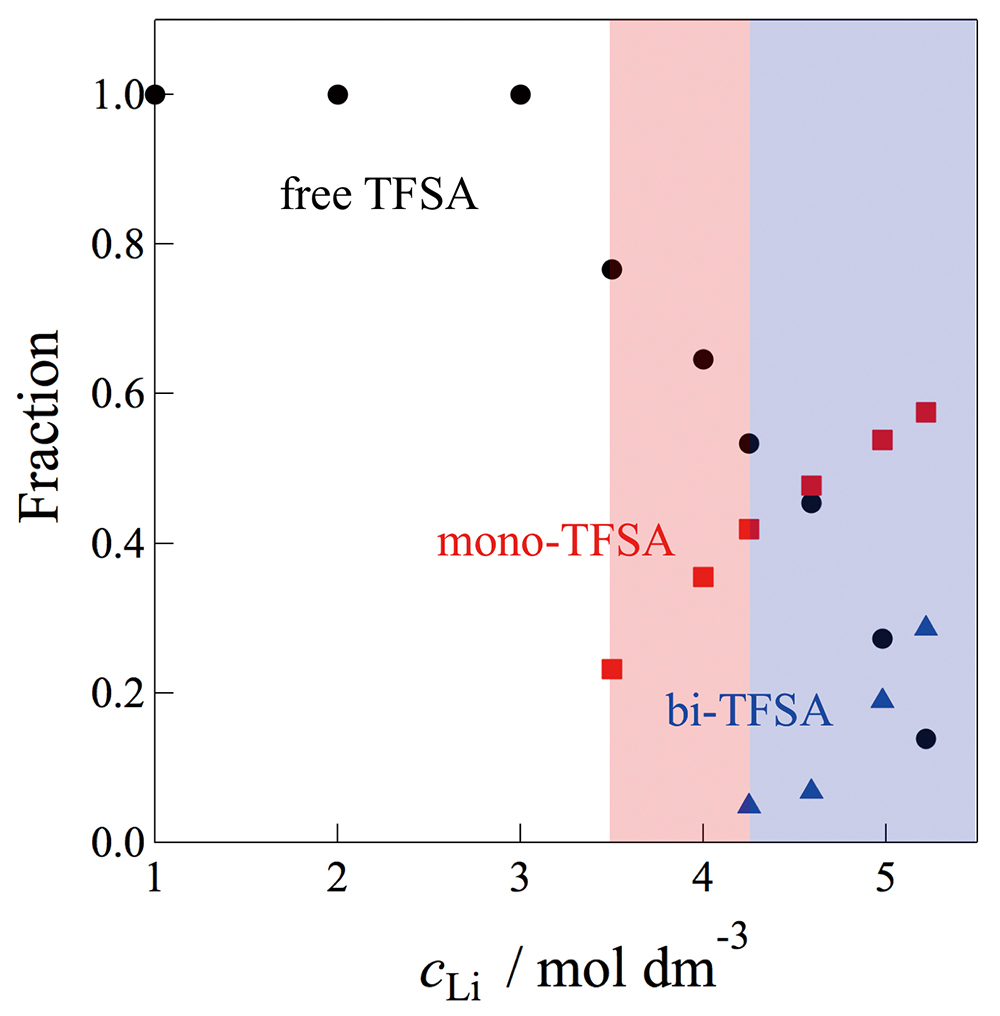
Volume 35, Issue 3
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 233
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Download PDF (28K)
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 235-236
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Download PDF (208K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 237-240
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 11, 2019Download PDF (765K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 241-248
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (1055K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 249-256
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 12, 2018Download PDF (11208K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 257-263
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 19, 2018Download PDF (890K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 265-269
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 26, 2018Download PDF (978K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 271-276
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 26, 2018Download PDF (1132K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 277-282
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (870K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 283-287
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (83K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 289-294
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (1385K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 295-300
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (556K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 301-305
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 09, 2018Download PDF (274K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 307-313
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 09, 2018Download PDF (634K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 315-321
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 16, 2018Download PDF (3054K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 323-328
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 16, 2018Download PDF (388K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 329-335
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 16, 2018Download PDF (614K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 337-341
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 16, 2018Download PDF (1520K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 343-346
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 12, 2018Download PDF (197K) -
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 347-350
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 19, 2018Download PDF (58K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2019Volume 35Issue 3 Pages 351
Published: March 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2019
Download PDF (1117K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|