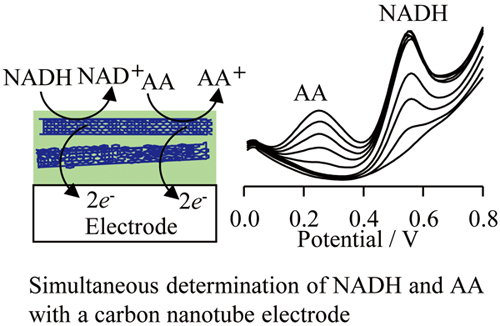
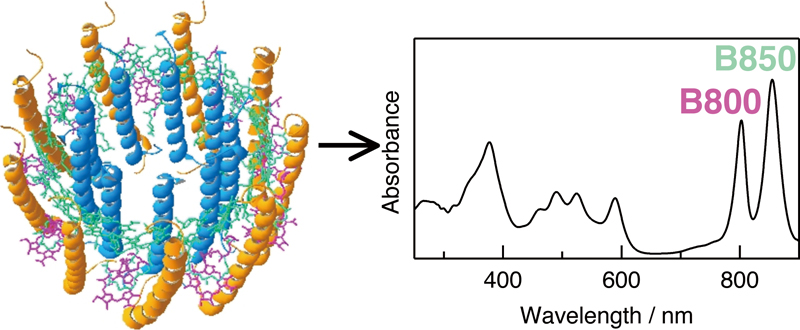
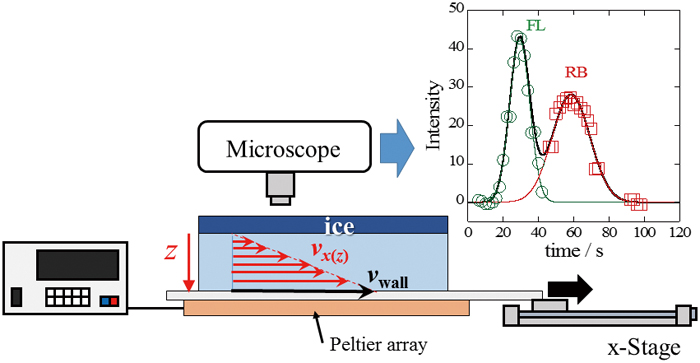
Volume 32, Issue 7
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 715-717
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1424K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 719-724
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (751K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 725-728
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (633K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 729-734
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (828K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 735-740
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1162K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 741-744
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (502K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 745-749
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1209K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 751-755
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1035K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 757-762
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1316K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 763-768
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (806K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 769-773
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1465K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 775-780
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1547K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 781-788
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (1365K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 789-795
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (2255K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 797-799
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (592K) -
Article type: Notes
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 801-804
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (545K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 805-808
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (3468K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2016Volume 32Issue 7 Pages 809
Published: July 10, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: July 10, 2016
Download PDF (2850K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|