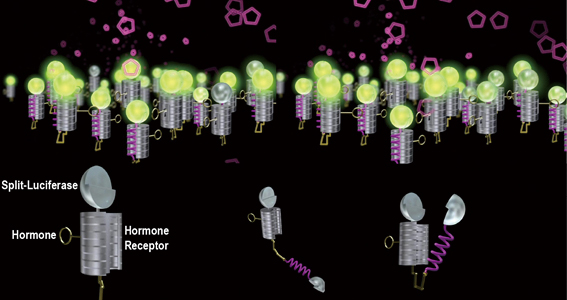
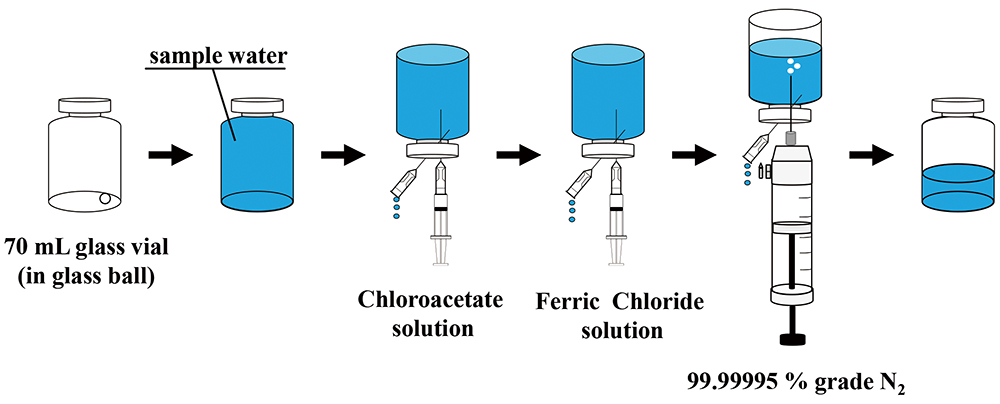
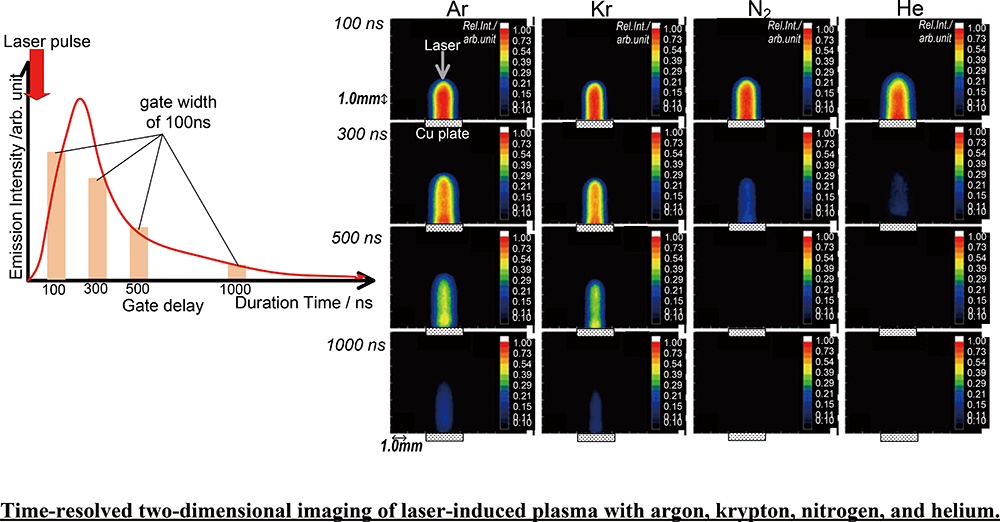
Volume 37, Issue 2
Displaying 1-24 of 24 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 227
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Download PDF (92K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 229-232
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 01, 2021Download PDF (883K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 233-247
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 18, 2020Download PDF (1053K) -
Article type: Reviews
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 249-260
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 06, 2020Download PDF (1953K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 261-266
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: May 15, 2020Download PDF (558K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 267-274
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: August 07, 2020Download PDF (1027K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 275-281
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: August 28, 2020Download PDF (636K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 283-292
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: August 28, 2020Download PDF (1887K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 293-299
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: August 28, 2020Download PDF (3400K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 301-307
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 04, 2020Download PDF (1081K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 309-314
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 18, 2020Download PDF (524K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 315-320
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 04, 2020Download PDF (1782K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 321-327
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 11, 2020Download PDF (1413K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 329-335
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 11, 2020Download PDF (397K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 337-340
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 11, 2020Download PDF (441K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 341-345
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 02, 2020Download PDF (278K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 347-351
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 02, 2020Download PDF (226K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 353-358
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 02, 2020Download PDF (370K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 359-365
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 23, 2020Download PDF (1033K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 367-375
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 23, 2020Download PDF (19967K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 377-380
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 11, 2020Download PDF (826K) -
Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 381-386
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 11, 2020Download PDF (312K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 387-391
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 18, 2020Download PDF (497K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2021 Volume 37 Issue 2 Pages 393
Published: February 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2021
Download PDF (85K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|