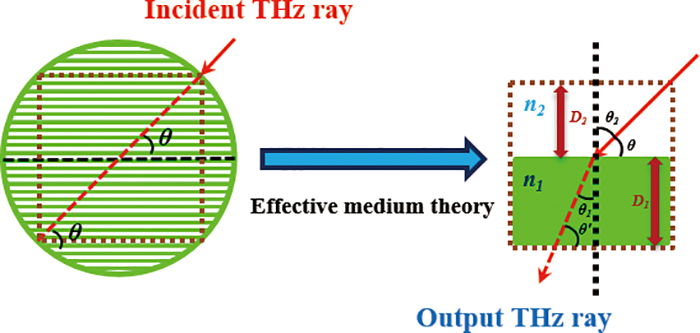
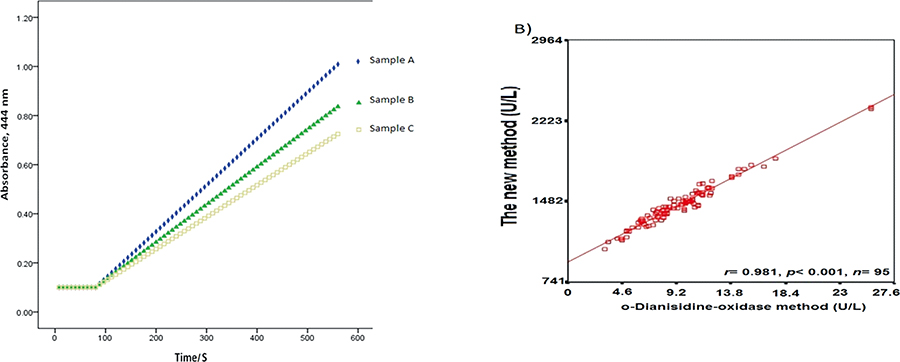
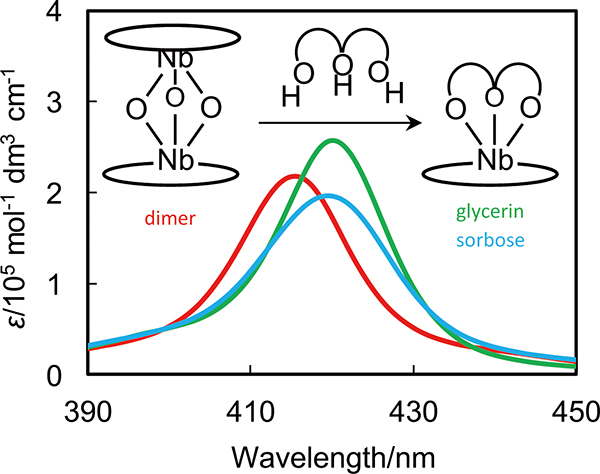
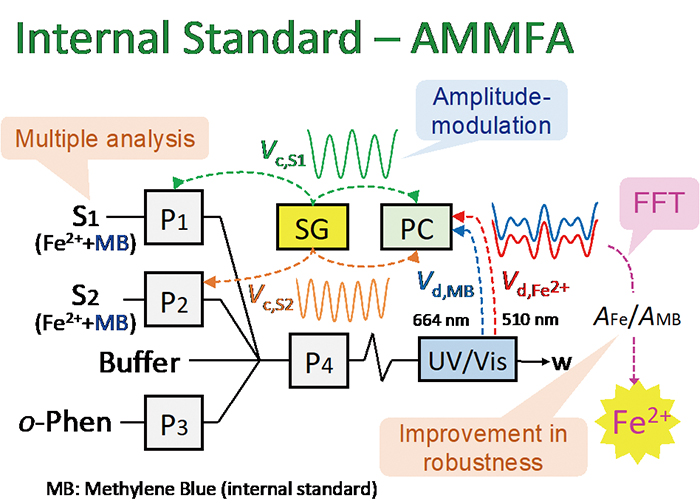
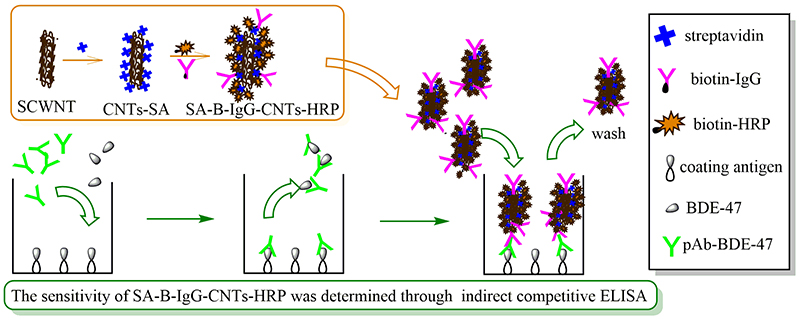
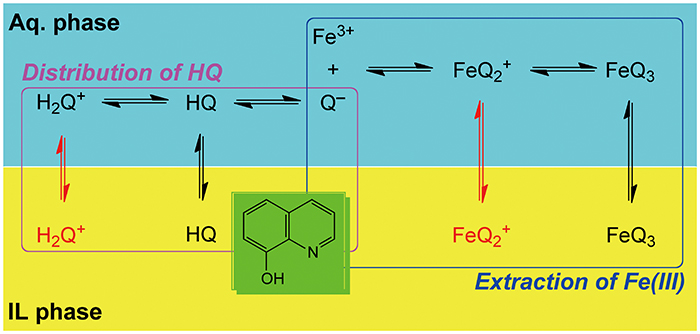
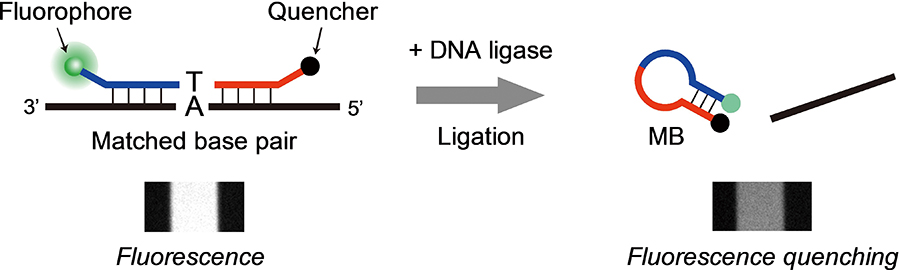
Volume 33, Issue 12
Displaying 1-27 of 27 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1321-1322
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (456K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1323-1325
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1085K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1327-1331
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (6657K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1333-1337
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (2259K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1339-1344
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (931K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1345-1350
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (908K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1351-1356
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1558K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1357-1361
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1595K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1363-1368
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1332K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1369-1374
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (2006K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1375-1380
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (941K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1381-1386
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1031K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1387-1394
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1023K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1395-1400
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1565K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1401-1405
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (3446K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1407-1413
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1130K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1415-1419
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1042K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1421-1425
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (731K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1427-1433
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (652K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1435-1440
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1066K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1441-1446
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (4592K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1447-1451
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (695K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1453-1456
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (827K) -
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1457-1460
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (1042K) -
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1461-1464
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (495K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1465-1468
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (998K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017Volume 33Issue 12 Pages 1469
Published: December 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2017
Download PDF (3219K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|