All issues

Volume 30, Issue 9
Displaying 1-14 of 14 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 857
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (166K)
Special Reviews
-
Noritada KAJI, Yoshinobu BABAArticle type: Special Reviews
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 859-864
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNumerous nanobiodevices have been developed for cancer diagnosis through the analysis of cancer cells and cancer-related biomolecules, cancer gene therapy, and iPS cell-based regenerative medicine. A microchamber array, which is fabricated on a plastic chip, enables to develop a reliable circulating tumor cell (CTC) detection technique for cancer metastasis diagnosis. A nanopillar-array or a nanowire-array on a quartz chip allows ultrafast analysis of DNA and microRNA within 1 s for the molecular diagnosis of cancer. Immunopillar devices, which contain a tremendous amount of antibody-immobilized microparticles inside an immunopillar structure, have realized fast and low invasive “from blood to analysis” type biomarker detection of cancer with a pM detection sensitivity within 5 min. Quantum dots and gene delivery nanodevices are applied to single cancer cell diagnosis, in vivo imaging for iPS cell based regenerative medicine, and theranostic devices for cancer diagnosis and therapy. View full abstractDownload PDF (1946K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1946K)
Original Papers
-
Kenichiro TODOROKI, Tatsuki NAKANO, Hiroki WATANABE, Jun Zhe MIN, Koic ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 865-870
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have developed a convenient method for predicting the LC resolution of amino acid diastereomers through computational calculations. For acquiring experimental data, we derivatized 10 amino acids using o-phthalaldehyde and N-acetyl-L-cysteine as fluorogenic diastereomer-forming reagents and analyzed the diastereomers using reversed-phase LC and fluorescence detection. For theoretical chemical calculations, we used the publicly available semi-empirical calculation software MOPAC2012. Using the obtained experimental and theoretical data, we determined the change in analytical resolution with differences in the structure of the diastereomers. From the results obtained, we concluded that greater conformational change through diastereomeric derivatization induced an increase in the contact area with the stationary phase, leading to higher resolution.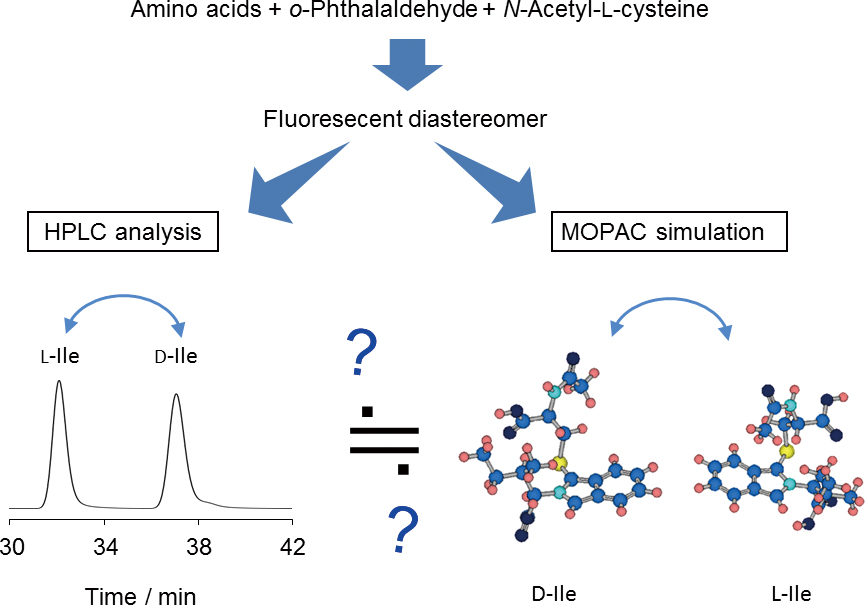 View full abstractDownload PDF (3845K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3845K) -
Naoko NONOSE, Akiharu HIOKI, Koichi CHIBAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 871-883
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn the present study the effects of the detector dead-time and its uncertainties on the accuracy and uncertainty of isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS) were considered through an interlaboratory study on the analysis of low-alloy steel by using an ICP-sector field mass spectrometer. Also, an optimized mixing ratio of the sample and the spike to obtain highly precise results was theoretically and experimentally investigated. The detector dead-time used in the interlaboratory study showed a negative value. However, it less affected the trueness of the analytical result if the dead-time correction for the measured isotope ratio was done properly. As many researchers have pointed out, the detector dead-time showed a clear mass dependence. Therefore, it is desirable to check the dead-time in every target element by using assay standards or isotopic standards, which would lead to an accurate result even if the detector dead-time is a negative value. On the other hand, the effect of the uncertainty of the detector dead-time can be minimized when both isotope ratios and ICP-MS signals of the [sample + spike] blend in IDMS are equal to those of [spike + assay standard] in reverse IDMS. From standpoints of error magnification theory and the precision of the isotope ratio measurement, an optimized isotope ratio of the sample-spike blend would be 1.0 for an element with a large difference in ten times and more between the atomic fractions of two isotopes used for IDMS. In the case of an element with no significant difference between the atomic fractions of two isotopes, an optimized isotope ratio can be calculated by a formula expressed as a function of the atomic fractions of the sample and the spike as well as the signal of ICP-MS. View full abstractDownload PDF (6213K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (6213K) -
SARENQIQIGE, Takamasa KODANI, Mari KAJIWARA, Kô TAKEHARA, Kazuh ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 885-889
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialBoric acid reacts with 5-fluorosalicylaldehyde (F-SA) and 8-amino-1-naphthol-3,6-disulfonic acid (HA) to form the boric acid-fluoroazomethine H complex (F-AzB) that is now being used for the flow-injection analysis (FIA) of boric acid. At pH 6.5, the F-AzB complexation proceeded fairly fast, whereas the fluoroazomethine H (F-AzH) formation was slow. Thus, highly sensitive measurement of F-AzB was possible if the reaction time was controlled using the FIA method to decrease the background absorbance of F-AzH at the analytical wavelength. The optimum conditions for the color developing reaction were investigated for single and dual channel systems. The former system was simple, applicable to the determination of boron in reversed osmosis (RO) desalination water with a detection limit (LOD) of 4 μg B dm−3. For the latter system, the calibration range was 0.005 to 10 mg B dm−3 with an LOD of 1 μg B dm−3, which can be applicable to natural water analyses of boron. These methods could analyze 15 – 20 samples in one hour. The results of the boron concentration measurement for water samples from an RO desalination plant, industrial wastewater and river water were in fairly good agreement with those obtained by other methods. View full abstractDownload PDF (883K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (883K) -
Shunsuke SAKURAI, Tomohiro UCHIMURAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 891-895
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialGas chromatography/multiphoton ionization/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC/MPI/TOFMS) coupled with a Curie-point pyrolyzer as a sample introduction technique was applied for the rapid and selective analysis of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) that are a part of aerosol particulate matter. Increasing the operating temperature of the pyrolyzer also increased the number of observed peaks, but the peak areas of a few PAHs decreased due to thermal decomposition. In the present study, more than 100 peaks were confirmed using 0.3 mg of an aerosol particulate matter, and further sensitive detection would be achievable. The advantages of MPI/TOFMS, such as optical selectivity and simultaneous determination properties, allowed the trace analysis of highly complicated particulate matter—even in the absence of pretreatment. Therefore, this method would help elucidate the origin of particulate matter when sampling from different points for short periods of time.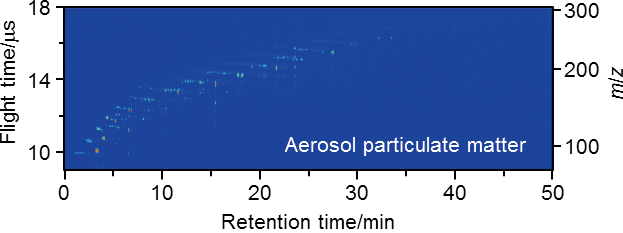 View full abstractDownload PDF (904K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (904K) -
En HAN, Xia LI, Jian-Rong CAI, Hai-Ying CUI, Xing-Ai ZHANGArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 897-902
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, we developed a highly sensitive amperometric biosensor for glucose detection based on glucose oxidase immobilized in a novel carbon nanosphere (CNS)/sodium alginate (SA) composite matrix. This hybrid material combined the advantages of CNS and natural biopolymer SA. This composite film was characterized by scanning electron microscope, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and UV-vis, which indicated that the hybrid material was suitable for immobilization of glucose oxidase. Various experimental conditions were investigated that influenced the performance of the biosensor, such as pH, applied potential and temperature. Under the optimum conditions, the biosensor showed excellent performance for glucose over a wide linear concentration range from 1.0 × 10−6 to 4.6 × 10−3 M with a detection limit of 0.5 μM based on a signal-to-noise ratio of 3. Furthermore, the biosensor exhibited excellent long-term stability and satisfactory reproducibility.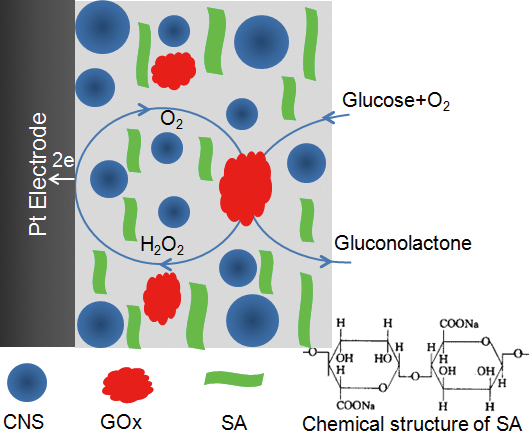 View full abstractDownload PDF (2034K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2034K) -
Jie BAI, Xiaojuan WANG, Yuning MENG, Hui-Min ZHANG, Liangti QUArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 903-909
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSGraphene, as a novel carbon nanomaterial, exhibits superior performance in electrochemical sensors. Here, graphene was applied to the microelectrode system by a simple method. A novel graphene coating carbon fiber microelectrode (G-CFM) was fabricated by electrodepositing graphene on the surface of carbon fiber. The fabrication method is fast and simple. Scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy demonstrated that carbon fiber was successfully modified by graphene. The electrochemical behavior of G-CFM was characterized by potassium ferricyanide and dopamine (DA). The electrode exhibited much larger current response and less overpotential response, compared to CFM. The microsensor for DA showed good sensitivity and selectivity, and the electrode had good stability. It is believable that the unique characteristic of graphene holds promise for the advanced microelectrode system for highly sensitive detection of various targets.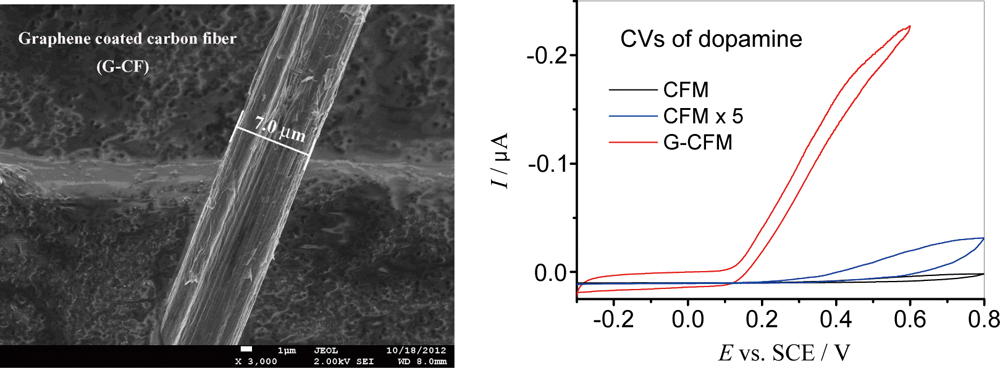 View full abstractDownload PDF (1088K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1088K) -
Hadi Hassani NADIKI, Meissam NOROOZIFAR, Mozhgan KHORASANI-MOTLAGHArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 911-918
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA glassy carbon electrode modified with ruthenium red and functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube has been developed. The electrochemical response characteristics of the modified electrode toward epinephrine (EP) and acetaminophen (AC) was investigated by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Linear calibration plots were obtained over the range of 0.3 – 333.3 μM for both EP and AC with sensitivities of 0.221 and 0.174 μA μM−1 for EP and AC, respectively. The detection limits for EP and AC were 0.04 and 0.06 μM, respectively. The diffusion coefficients for the oxidation of EP and AC at the modified electrode were calculated as 2.74 ± 0.05 × 10−5 and 1.75 ± 0.07 × 10−5 cm2 s−1, respectively. The practical analytical utilities of the modified electrode were demonstrated by the determination of EP and AC in human urine and serum as well as AC tablet samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (1800K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1800K) -
Toshio TAKAYANAGI, Kinuyo OGURA, Tomoki YABUTANIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 919-924
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe ion-association equilibrium of the dipicrylaminate ion (DPA−) was investigated in an aqueous solution with alkali metal ions and with its 18-crown-6 ether complexes as pairing cations by capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE). Although DPA− is precipitable with the pairing cations of K+ and Cs+ in a homogenous aqueous solution, a low concentration of DPA− below its solubility suppressed the formation of the precipitates, and DPA− was detected as a usual CZE signal. Changes in the electrophoretic mobility of DPA− was analyzed for its ion-association equilibrium. The ion association constants determined were almost comparable among alkali metal ions, while the ion association constants were meaningfully large with a hydrophobic 18-crown-6 ether complex of K+. The CZE separation was also proved to be useful for the equilibrium analysis under precipitating conditions. It was suggested that the precipitable property of DPA− with K+ and Cs+ could not be attributed to the ion-association process in an aqueous solution, but to the condensation process concerning the intermolecular CH···O bond in the precipitate crystals, as reported. View full abstractDownload PDF (629K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (629K) -
Juan PERIS-VICENTE, Samuel CARDA-BROCH, Josep ESTEVE-ROMEROArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 925-930
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper describes a micellar liquid chromatographic method used to analyze tamoxifen (TAMO) in pharmaceutical formulations, while focusing in its interesting features. Solid samples were solved in a micellar solution, irradiated at 254 nm, filtered and injected. Extraction steps were avoided and thus expediting the procedure. Tamoxifen was resolved in <5 min, using a mobile phase containing 0.15 M sodium dodecyl sulfate–7% pentanol at pH 3, running at 1.5 mL/min under an isocratic mode at 40°C through a C18 column. Detection was achieved by fluorescence by excitation at 260 nm and emission at 380 nm. The validation was performed following the requirements of the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) Tripartite Guidelines in terms of: specificity, sensitivity, calibration range (0.2 – 20 mg/L), accuracy (98.8 – 101.7%), precision (<1.5%) and robustness (<6.2%). The method was applied to quantify TAMO in TAMO citrate tablets supplied in Spain, and was found appropriate for the quality control of TAMO formulations. View full abstractDownload PDF (506K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (506K) -
Ryuichi WATANABE, Tomoko HARADA, Ryoji MATSUSHIMA, Hiroshi OIKAWA, Yas ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 931-936
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe indirect identification and quantification of saxitoxin (STX) using other STX analogues by high-performance liquid chromatography with post-column oxidation and fluorescent detection (HPLC-FD) was investigated. Decarbamoylsaxitoxin (dcSTX) among the many STX analogues was selected as an external standard to identify and quantify STX. The retention time of STX in shellfish extracts by HPLC-FD was reproducibly estimated by using the retention time of dcSTX and the separation factor (α) between STX and dcSTX. Almost all of the columns tested to setup the method were useful to identify STX. Because a molar fluorescent coefficient of dcSTX was slightly different from that of STX, a factor used to correct the fluorescent coefficient in STX/dcSTX was determined to be 1.30. The indirect quantification of STX in scallop extracts by using the correction factor agreed to 80 – 100% precision with direct quantification using STX as an external standard. View full abstractDownload PDF (582K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (582K) -
Valerie FLEISCHAUER, Jinseok HEOArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 937-942
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis paper describes a whole cell sensor using E. coli entrapped within photocrosslinked hydrogel beads. Hydrogel beads containing organophosphorus hydrolase (OPH)-expressed E. coli were prepared by adding a hydrogel precursor solution containing the E. coli to an oil phase using a precision syringe pump, forming droplets, and photopolymerizing them. The beads showed good monodispersity with an average size of 1.2 mm. We detected organophosphates (OPs) using the beads. The detection relied on a pH-sensitive fluorescence dye that responds to protons produced from the intracellular OPH reaction with the OPs. This sensor could detect up to 80 μM of paraoxon with a detection limit of 3 μM. The enzyme activity of E. coli entrapped within the hydrogel beads showed stable enzyme activity for at least two weeks. This whole cell sensor will be implemented in a microfluidic system by directly photopolymerizing the hydrogel precursor solution within microfluidic channels. View full abstractDownload PDF (4977K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4977K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014 Volume 30 Issue 9 Pages 943
Published: September 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2564K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|