- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Nobuaki SOHArticle type: Highlights
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 515-516
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Tatsumi MIZUTA, Kenichi MAENO, Kenji SUEYOSHI, Tatsuro ENDO, Hideaki H ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 517-519
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA novel method for the intact immobilization of a very-thin and soft PVC membrane on a convex-shaped poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) surface is described. The present method using PVA film as a sacrificial layer allowed successful immobilization of an intact PVC membrane using an ionic liquid-based dye on only the convex-shaped PDMS surface without any deformation or increase of the inhomogeneity. In addition, two different kinds of PVC membranes were successfully immobilized simultaneously toward multiplexed detection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (215K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (215K) -
Takafumi KOZAKAI, Takanori HARASHIMA, Manabu KIGUCHI, Tomoaki NISHINOArticle type: Rapid Communications
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 521-523
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
Advance online publication: April 20, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe report on a method to measure the electron transport of a single molecular assembly by scanning tunneling microscopy (STM). The STM molecular tip together with a chemically modified substrate was utilized to form an assembly with a single target molecule. This method was successfully applied to a heme peptide to reveal the transport property of a single peptide-containing assembly. The present work opens a way to create functional single molecular devices using biomolecules.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (390K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (390K)
-
Hiroshi YUKAWA, Yoshinobu BABAArticle type: Reviews
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 525-532
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSQuantum dots (QDs) have excellent fluorescence properties in comparison to traditional fluorescence probes. Thus, the optical application of QDs is rapidly expanding to each field of analytical chemistry. In this review paper, we reviewed the application of QDs to regenerative medicine, especially stem cell transplantation therapy. The labeling of stem cells using QDs composed of semiconductor materials in combination with a chemical substance, poly-cationic liposome and cell penetrating peptide is reported. In addition, the influence of QD labeling on the pluripotency of stem cells is also reported. Finally, the in vivo imaging of transplanted stem cells in mice by QDs emitting fluorescence in the near-infrared region, which can be detected by in vivo fluorescence imaging systems such as IVIS and SAI-1000, is described. The future prospects for stem cell imaging technology by QDs are also discussed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2765K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2765K)
-
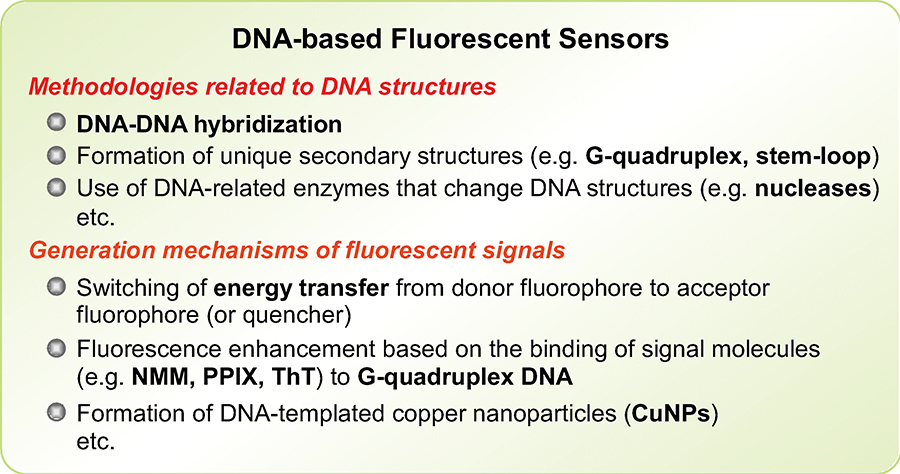
Yuki HIRAKAWA, Tomomi YAMASAKI, Ayako HARADA, Seiji IWASA, Hiroshi NAR ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 533-539
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA simultaneous immunosensor based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was developed for determination of 3 pesticides —boscalid, clothianidin and nitenpyram— instead of the direct competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (dcELISAs) widely used as individual determination methods. Carboxy groups that introduced compounds to their pesticides were designed, and conjugates of them and bovine serum albumin were immobilized onto separate channels of the same sensor chip. When a mixture of 3 monoclonal antibodies reacted to each pesticide, and 3 pesticides were injected into the SPR immunosensor, each channel showed specific reactivity at 15 – 93 ng mL−1 for boscalid, 6.7 – 27 ng mL−1 for clothianidin, and 7.3 – 62 ng mL−1 for nitenpyram. Recovery tests using vegetables spiked with a mixture of 3 pesticides showed good results: 75 – 90%, 88 – 104%, and 72 – 105%, respectively, with a high correlation to results of the dcELISAs. The SPR immunosensor would be useful for the determination of pesticide residues in vegetables.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1332K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1332K) -
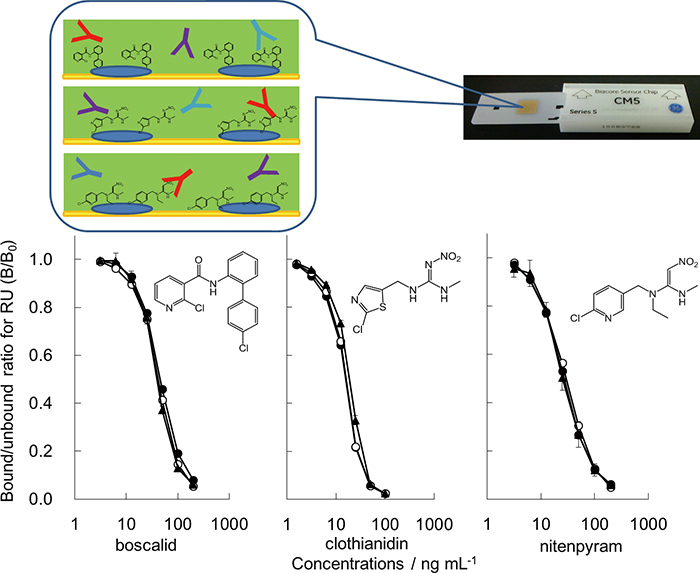
Yong MENG, Hong-Ze GANG, Shi-Zhong YANG, Ru-Qiang YE, Bo-Zhong MUArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 541-545
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFluorescent derivatization of the carboxyls in surfactin peptide rings is an effective way to improve the sensitivity of trace detection of surfactin, but very little is known about the reaction selectivity of surfactin containing multiple carboxyls in derivatization. In this paper, the reaction selectivity in fluorescent derivatization of a surfactin containing two carboxyls in its peptide ring with 1-bromoacetylpyrene and the catalysis role in the reactions were investigated using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry. It showed that only one carboxyl was labeled with 1-bromoacetylpyrene in derivatization reactions, and the connection of the Asp residue with 1-bromoacetylpyrene was confirmed. It also showed that triethylamine as a catalyst was connected with surfactin to liberate more nucleophilic groups beneficial to promote the derivatization rate. This would contribute to better understanding the mechanism of derivatization of surfactin and its analogues with 1-bromoacetylpyrene, and with other fluorescent labeling reagents.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (711K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (711K) -
Seiji KAMBA, Hirokazu SETO, Takashi KONDO, Yoshiko MIURAArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 547-552
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA metal mesh device has a structure in which through-holes of the same shape are periodically placed on a thin metal film, and the selection of such a structure makes it possible to sense objects of various sizes. In this study, we showed the structure of the metal mesh device and the relationship between the detectable optical domain and the size of the objects to be measured. In addition, from measurement of changes in electromagnetic wave transmission characteristics of the metal mesh device due to specific adsorption of particles with a mean diameter of 100 nm with surface modification with Streptavidin to a metal mesh device fixed with biotin, we showed that even large particles can be sensed. Based on these examinations, we showed that, by using a metal mesh device with detectable optical domain corresponding to the size of objects, even objects that are larger than protein can be sensed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1482K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1482K) -
Sota MATSUBA, Ryo KATO, Koichi OKUMURA, Kazuaki SAWADA, Toshiaki HATTO ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 553-558
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn biochemistry, Ca2+ and K+ play essential roles to control signal transduction. Much interest has been focused on ion-imaging, which facilitates understanding of their ion flux dynamics. In this paper, we report a calcium and potassium multi-ion image sensor and its application to living cells (PC12). The multi-ion sensor had two selective plasticized poly(vinyl chloride) membranes containing ionophores. Each region on the sensor responded to only the corresponding ion. The multi-ion sensor has many advantages including not only label-free and real-time measurement but also simultaneous detection of Ca2+ and K+. Cultured PC12 cells treated with nerve growth factor were prepared, and a practical observation for the cells was conducted with the sensor. After the PC12 cells were stimulated by acetylcholine, only the extracellular Ca2+ concentration increased while there was no increase in the extracellular K+ concentration. Through the practical observation, we demonstrated that the sensor was helpful for analyzing the cell events with changing Ca2+ and/or K+ concentration.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2675K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2675K) -
Jiaming WANG, Patima NIZAMIDIN, Yuan ZHANG, Nuerguli KARI, Abliz YIMITArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 559-565
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe sensitive detection of trimethylamine has been accomplished by using a homogeneous optical waveguide sensor system. Also the sensor can be easily fabricated by using tetraphenylporphyrin manganese (MnTPP) as sensitive materials to detect different volatile organic compounds (VOC). NMR (1H-NMR), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), infrared (IR), and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) instrumental means were used to characterize its structure. Gas-sensing measurements indicated that the sensing element has shown good selectivity, high sensitivity and a low detection limit level of 0.1 ppm to trimethylamine (TMA) with the presence of interference gases at room temperature. For a range of trimethylamine concentrations from 0.1 to 1000 ppm, the sensor has shown a short response time. Also the response time and recovery time are 1.5 and 50 s, respectively. Simulation experiments (dichloromethane, chloroform and carbon tetrachloride were selected as interference gases) showed little interference with its gas sensing. That may provide an ideal candidate for detecting the freshness of fish and seafood.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1908K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1908K) -
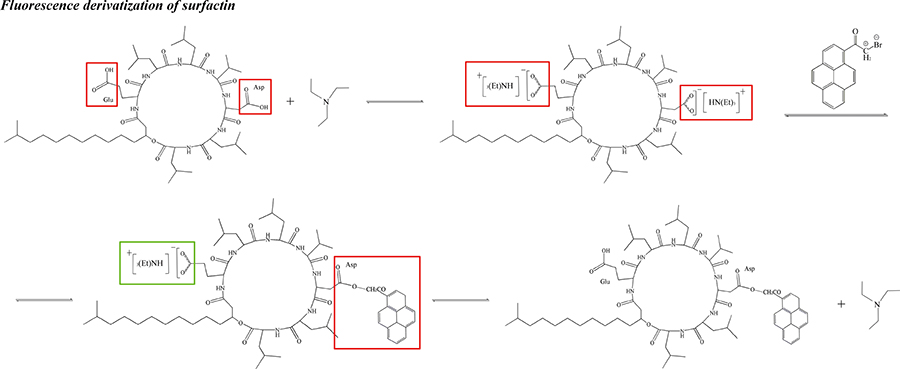
Hatam HASSANVAND, Payman HASHEMIArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 567-570
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA highly sensitive and selective colorimetric method was developed for the detection of CN− ion based on the surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) embedded in a transparent agarose matrix. The AgNPs were prepared by chemical reduction of Ag+ in the presence of sodium borohydride as the reducing agent and agarose as the stabilizing agent. Characterization of the nanoparticles was performed with UV/Vis spectrometry and scanning electron microscopy. A calibration curve was derived for the absorbance of the sensor at 410 nm, that was linear over a range from 1.5 to 120 μmol L−1 with an R2 value of 0.998 (n = 8). A detection limit of 0.69 μmol L−1 and a relative standard deviation of 3.8% were obtained for CN− for 8 replicates. A reproducibility of about 6.1% was also obtained for four batches of the sensor. The sensor showed excellent selectivity for CN− ion at the presence of a number of interfering ions with concentrations exceeding 50 times of that of the analyte. The results showed successful application of the AgNPs–agarose as a colorimetric sensor for easy and selective monitoring of CN− ion in aqueous solutions.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (469K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (469K) -
Kazuhiro KOBAYASHI, Masaharu TANAKA, Yoichi YATSUKAWA, Soichi TANABE, ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 571-574
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRecent growing health awareness is leading to increasingly conscious decisions by consumers regarding the production and traceability of food. Stable isotopic compositions provide useful information for tracing the origin of foodstuffs and processes of food production. Plants exhibit different ratios of stable carbon isotopes (δ13C) because they utilized different photosynthetic (carbon fixation) pathways and grow in various environments. The origins of glutamic acid in foodstuffs can be differentiated on the basis of these photosynthetic characteristics. Here, we have developed a method to isolate glutamic acid in foodstuffs for determining the δ13C value by elemental analyzer-isotope-ratio mass spectrometry (EA/IRMS) without unintended isotopic fractionation. Briefly, following acid-hydrolysis, samples were defatted and passed through activated carbon and a cation-exchange column. Then, glutamic acid was isolated using preparative HPLC. This method is applicable to measuring, with a low standard deviation, the δ13C values of glutamic acid from foodstuffs derived from C3 and C4 plants and marine algae.
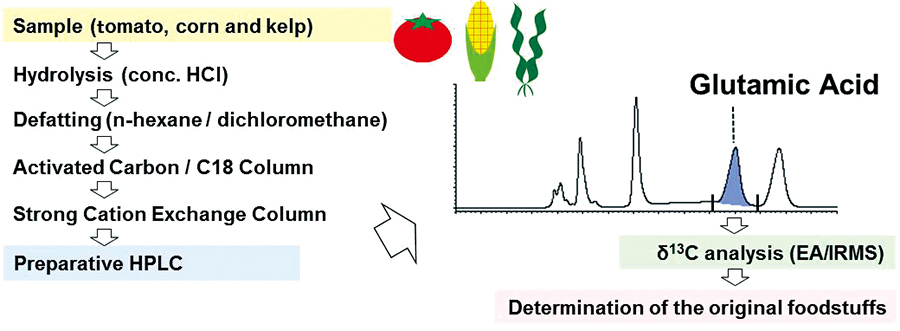 View full abstractDownload PDF (137K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (137K) -
Rojeet SHRESTHA, Yusuke MIURA, Ken-ichi HIRANO, Zhen CHEN, Hiroaki OKA ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 575-582
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFatty acid (FA) profiling of milk has important applications in human health and nutrition. Conventional methods for the saponification and derivatization of FA are time-consuming and laborious. We aimed to develop a simple, rapid, and economical method for the determination of FA in milk. We applied a beneficial approach of microwave-assisted saponification (MAS) of milk fats and microwave-assisted derivatization (MAD) of FA to its hydrazides, integrated with HPLC-based analysis. The optimal conditions for MAS and MAD were determined. Microwave irradiation significantly reduced the sample preparation time from 80 min in the conventional method to less than 3 min. We used three internal standards for the measurement of short-, medium- and long-chain FA. The proposed method showed satisfactory analytical sensitivity, recovery and reproducibility. There was a significant correlation in the milk FA concentrations between the proposed and conventional methods. Being quick, economic, and convenient, the proposed method for the milk FA measurement can be substitute for the convention method.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (538K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (538K) -
Kazuho INABA, Tomoyoshi MURATA, Shigeki YAMAMURA, Masaaki NAGANO, Kazu ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 583-588
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe contents and elution behavior of metals in consumer electronics parts were determined so as to understand their maximum environmental risk. Elements contained most in printed-circuit boards were Cu, Si, Br, Ca, Al, Sn, Pb, Sb, Ba, Fe, Ni, Ti, and Zn; in cathode-ray tube glass were Si, Pb, Ba, Sr, Zn, Zr, Ca, and Sb; in arsenic contained liquid-crystal displays were Si, Ca, Sr, Ba, As, and Fe; and in antimony contained liquid-crystal displays were Si, Ba, Ca, Sb, Sr, Fe, and Sn. The elements eluted most from printed-circuit boards were Zn, Pb, and Cu; from cathode-ray tube glass were Pb, Zn, B, Ba, and Si; and from liquid-crystal displays were B and Si, and the toxic As and Sb. The amount eluted was greatest at acidic pH. It was revealed that officially recommended 6-h-shaking with a pure water test was insufficient to understand the real environmental risk of waste electronics.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (266K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (266K) -
Shoji IMAI, Yuhei YAMAMOTO, Takashi YAMAMOTO, Kenji KODAMA, Jun NISHIM ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 589-598
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialUsing a commercially available wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WDXRF) spectrometer, the chemical composition and S-Kα spectrum of rime and snow samples collected in remote and rural areas of Japan were measured with a membrane filter sample technique to investigate the long-range transport of aerosol from the East Asian continent. Insoluble substances are derived into three categories: 1) conventional mineral origin (crustal substance), 2) urban dust origin (Fe-Zn-Ca) and 3) coal origin (S-As). Assuming that (i) S(VI) was found as a plaster-like substance in hard rime, depending on [Ca], and that (ii) S(-II) was found as non-crustal sulfur compounds, fractions of S(VI) and S(-II) in rime could be calculated as 35 ± 6 and 66 ± 7% by [Ca], which is in agreement with 32 ± 8 and 68 ± 8%, respectively, by the chemical shift of the S-Kα line. During a one-day meteorological event that included the accumulation of both rime and snow, differences to the snow-like content corresponded to characteristics typical of rime since the chemical compositions of rime also includes the composition of the snow. The fractions of 22 ± 12% of S(VI) and 76 ± 12% of S(-II), respectively, were found in rime. The fraction of S(-II) decreased from the Chugoku district towards the Shikoku district. Along the coast of the Japan Sea, the fraction of S(-II) decreased from Chugoku district toward the Northeast Japan. It can be proposed that other analytical techniques of S, Al, and Ca in that are favorable to this fractionation.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (860K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (860K) -
Md. Abdul AZIZ, Rakan ALMADI, Zain Hassan YAMANIArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 599-604
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn electrochemical sensor based on an indium tin oxide nanoparticle (ITONP)-modified glassy carbon electrode (ITONP/GCE) was developed for the detection of sulfides in alcoholic medium. The ITONP/GCE was prepared by simply dropping the aqueous solution of ITONP on the GCE surface and then drying at 40°C. The homogeneous distribution of ITONP on the GCE surfaces was confirmed by recording the camera photographs and field emission scanning electron microscopic images. The ITONP/GCE was further characterized with energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray diffractometry to identify the surface chemical composition and crystallinity. The ITONP/GCE showed much better electrocatalytic properties toward sulfide electro-oxidation than that of bare GCE electrodes. The obtained amperometric detection limit of sulfide in alcoholic solutions of sodium acetate was 0.3 μM. The enhanced sensitivity, good selectivity and high stability are promising features of the ITONP/GCE for sulfide sensing.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (739K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (739K) -
Thiphol SATARPAI, Atitaya SIRIPINYANONDArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 605-612
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA rapid, easy, and cost effective fabrication method for paper-based analytical devices (PADs) is described. This newly developed method is based on the use of nail polish as an alternative hydrophobic reagent, and the nail polish was resistant to basic and organic solvents. Three approaches for fabrication of paper-based analytical devices (PADs) were investigated, namely writing, stamping, and spraying. The writing approach was carried out by drawing the hydrophobic area of a pre-designed pattern on filter paper with a simple lab-made pen filled with nail polish as the hydrophobic agent. The stamping and spraying approaches required the use of a designed mask, which was made by laser cutting of the magnet rubber sheet. With laser cutting, two types of templates were made, i.e., positive and negative counterparts. The positive counterpart was the inside pattern and the negative counterpart was the outside pattern of the magnet sheets. For the stamping approach, the negative counterpart of the magnet rubber mask was attached onto a simple rubber stamper that was then stamped onto filter paper after loading with nail polish solution. With the spraying method, the positive counterpart was used to cover the hydrophilic area on the paper. Then, the nail polish solution was used with an air brush and sprayed on the paper covered with the magnet rubber mask. All approaches were cost effective and required neither extra equipment nor any pretreatment step. Among all three methods, however, the spraying method was found most suitable for mass production and provided the best resolution when compared with the other two approaches. With this approach, the actual channel widths obtained were similar to the designed widths, with the narrowest possible channel width of 650 μm. Furthermore, a nail polish-treated PAD was prepared by soaking the paper in the nail polish solution. The ability of the nail polish-treated PAD was examined for its resistance to a strong basic solution and an organic solvent (up to 30% ethanol and dichloromethane). The nail polish-treated paper also showed the potential to be used as an organic-aqueous separator.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1241K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1241K) -
Li CHEN, Xiaodong LV, Jiangdong DAI, Lin SUN, Pengwei HUO, Chunxiang L ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 613-618
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA novel tailored multilayer probe for monitoring potential pyrethroids in the Yangtze River was proposed. The room-temperature phosphorescence method was applied to realize a detection strategy that is superior to the fluorescence method. Efficient Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots with uniform size of 4.6 nm were firstly coated with a mesoporous silica to obtain a suitable intermediate transition layer, then an imprinted layer containing bifenthrin specific recognition sites was anchored. Characterizations verified the multilayer structure convincingly and the detection process relied on the electron transfer-induced fluorescence quenching mechanism. Optional detection time and standard detection curve were obtained within a concentration range from 5.0 to 50 μmol L−1. The stability was verified to be good after 12 replicates. Feasibility of the probe was proved by monitoring water samples from the Zhenjiang reach of the Yangtze River. The probe offers promise for direct bifenthrin detection in unknown environmental water with an accurate and stable phosphorescence analysis strategy.
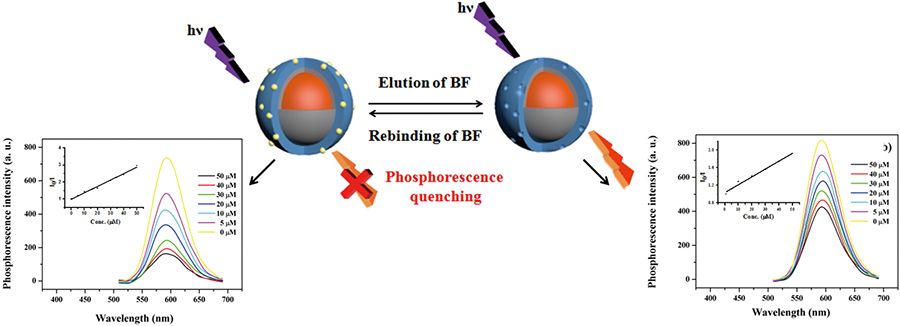 View full abstractDownload PDF (1525K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1525K)
-
Tomás BARRANCO, Jose J. CERÓN, Pía LÓPEZ-JORNET, Josep PASTOR, Jose M. ...Article type: Notes
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 619-622
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe aimed to investigate the impact of saliva collection and processing methods on AST, CK and LDH. Saliva was collected from 17 healthy participants by a passive drool. Each saliva sample was distributed into 3 aliquots: not treated, centrifuged, and passed through cotton. Centrifugation improved the precision of assays and produced lower values of AST and CK. The use of cotton resulted in decreased levels of LDH. This data stress the importance of the standardization of sample processing to measure enzymes in saliva.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (58K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (58K) -
Yura JANG, Jeongae LEE, Hesson CHUNGArticle type: Notes
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 623-626
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe developed a colorimetric method for measuring the amount of oil in mouse stool after co-administering an oil-soluble dye. When the amount of oil in the feces calculated from the amounts of Sudan III and Oil Red O was plotted against the amount of oil detected by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, the graph was linear, showing a one-to-one correlation between two analyses. This method may be utilized to determine the efficacy of lipase inhibitors, or to assess fat malabsorption in vivo.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1570K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1570K) -
Yusuke SATO, Daijiro IWASAWA, Kuo Ping HUI, Rena NAKAGOMI, Seiichi NIS ...Article type: Notes
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 627-630
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHere we examined optimization of the running buffer in boronate affinity electrophoresis for improved separation of PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) with 2′-O-methylated ribose in 3′-terminal nucleotide. The use of Good’s buffer, such as HEPES, significantly increased the separation efficiency for piRNA over normal RNA with free 3′-terminal ribose, and retained an ability to resolve the difference by at least 4-nucleotide lengths in the target piRNAs. We also demonstrated a single-step separation of piRNA from mouse testis total RNA.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (228K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (228K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2018 Volume 34 Issue 5 Pages 631
Published: May 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1091K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|