All issues

Volume 30, Issue 3
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 317
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (328K)
Rapid Communications
-
Takamasa KINOSHITA, Hiroya MURAKAMI, Yusuke MURANAKA, Yojiro YAMAMOTO, ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 319-322
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA single-step strategy has been developed toward the synthesis of micrometer-sized, tadpole-like structures comprising a repeating sequence of a three-dimensional gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-aniline polymer-AuNP arrangement. The size and shape of the microstructure strongly depends on the concentration of aniline in the reaction solution. Herein, we describe the formation mechanism of the microstructure by focusing on the surface morphology. View full abstractDownload PDF (1219K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1219K) -
Hiroyuki OKAMURA, Hitomi TAKAGI, Taku ISOMURA, Kotaro MORITA, Hirohisa ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 323-325
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSelective synergism for the extraction of lanthanoids(III) (Ln) with β-diketones such as 2-thenoyltrifluoroacetone, 2-naphthoyltrifluoroacetone, and benzoylacetone has been investigated in the presence of trioctylphosphine oxide as a hydrophobic neutral ligand in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as an ionic liquid. The extractability of heavier Ln was remarkably enhanced, resulting in a significant improvement in the separation of Ln. It was found that the present synergism is ascribed to the formation of cationic ternary complexes, followed by ion exchange into the ionic liquid. View full abstractDownload PDF (486K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (486K)
Special Reviews
-
Keitaro UMEZAWA, Daniel CITTERIO, Koji SUZUKIArticle type: Special Reviews
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 327-349
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis review summarizes progress in the field of near-infrared (NIR) fluorophores achieved during the last decade from the viewpoint of chemistry. Those compounds are of wide interest in bioanalysis and bioimaging, such as in vivo fluorescence imaging. Particular focus is placed on the recent developments of BODIPY and rhodamine derivatives, which belong to the most evolved NIR fluorophores. The data compiled in this review, including the chemical structures and optical properties of all compounds introduced, provide readers of this article with an overview of the field of NIR fluorophores.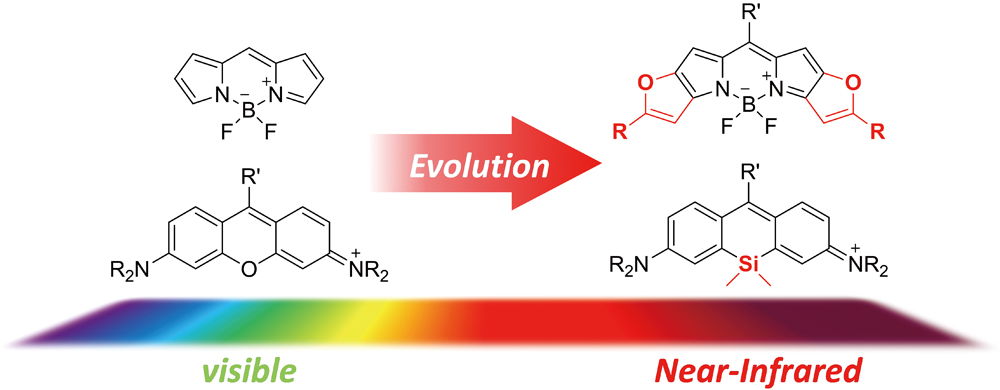 View full abstractDownload PDF (5660K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5660K) -
Yumi YOSHIDA, Junya UCHIDA, Shotaro NAKAMURA, Satoshi YAMAGUCHI, Kohji ...Article type: Special Reviews
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 351-357
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis article reviews the development of a thin-layer electrolysis cell with both a thin aqueous phase and a thin organic phase for ion transfer at the liquid|liquid interface for the absolute determination of a redox-inactive ion. In particular, an improvement of the cell performance by using a conducting polymer-coated electrode in the organic phase is discussed. The applicability of the thin-layer electrolysis cell to the absolute determination of redox-inactive ions using the flow-injection method or stripping method is also described. View full abstractDownload PDF (1358K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1358K)
Original Papers
-
Yiyang DONG, Yan XU, Zaixin LIU, Yuanfang FU, Toshinori OHASHI, Kazuma ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 359-363
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe development of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) detection methods is crucial for animal food security, tackling regional FMDV epidemic, and global FMDV prognostic control. For these purposes, a fast and sensitive analysis method is required. In this study, we developed a microchip-based ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), micro-ELISA, to realize FMDV detection. Nickel(II) chelating chemistry was utilized to immobilize recombinant protein (antigen) on polystyrene micro-beads in order to determine FMDV antibodies in cattle serum samples. In addition, reaction protocol and conditions were investigated. As a result, the FMDV detection was successfully demonstrated with only a 10-μL sample volume in 25-minute assay time. Analytical sensitivity was evaluated by a maximum nominal positiveness percentage value (NPPV) of 303 and a dilution factor of 32×. The method’s inter-run and intra-run CV (coefficients of variance) values were 15.5 and 17.1%, respectively, which were fully compatible with the OIE (World Organization for Animal Health) principle of validation of diagnosis assays for infectious diseases. The developed method should become a powerful tool for determining other animal contagious diseases and/or zoonosis. View full abstractDownload PDF (954K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (954K) -
Xiao Qing YAN, Hui WANG, Wei Di CHEN, Wei Jun JINArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 365-370
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIt is proposed that molecular iodine as a donor could form halogen bonding complexes with amantadine (AMD) and amantadine hydrochloride (AMD-HCl) in chloroform and the resultant charge transfer bands (CT band) would be located at 259 and 253 nm, respectively. The halogen bonding interaction was explored by UV absorption, Raman and X-ray crystallography, and a new bonding model named N+···Nlep bond in crystal was observed. The halogen bonding complexes were utilized in the development of simple and accurate spectrophotometry for the analysis of AMD/AMD-HCl. Compared with the traditional method based on the absorption of I3− at 290 and 365 nm, the new proposed spectrometry based on the CT band of halogen bonding complex was more sensitive and selective for the detection of AMD/AMD-HCl. Linear relationships with good correlation coefficients (>0.9994) were obtained between the absorbance and the AMD/AMD-HCl concentration in the range of 10 – 180 μg mL−1 for AMD-HCl and 0.2 – 13 μg mL−1 for AMD. The limit of detection (LOD) was 2.23 μg mL−1 and limit of quantification (LOQ) was 7.45 μg mL−1 for AMD-HCl. And because of the stronger bond constant between AMD and iodine than AMD-HCl, the method is more sensitive for AMD; the LOD was 0.02 μg mL−1 and LOQ was 0.08 μg mL−1 which was 100 times lower than that of AMD-HCl. View full abstractDownload PDF (2702K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2702K) -
Kenta TAKANASHI, Teru KATOArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 371-376
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialMethylated DNA plays an important role in epigenetic gene regulation, and could therefore serve as a potentially promising biomarker for the diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Therefore, the development of a simple method for analyzing cytosine methylation in a target gene is required. Here, we report on a new method for the sequence-selective chemical modification of a single cytosine in single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). This method is based on the formation of a DNA three-way junction of the ssDNA and two ssDNA probes, and was successfully applied for a simple polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assay for ‘pinpoint’ methylation analysis. View full abstractDownload PDF (776K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (776K) -
Koki HARIGAYA, Hiroyuki YAMADA, Koji YAKU, Hiroyuki NISHI, Jun HAGINAK ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 377-382
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAn alkylating agent, 4-chloro-1-butanol, is a genotoxic impurity (GTI); it may be generated during the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). For the trace-level detection of GTIs in APIs, usually, gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is employed. In this study, a novel LC-inductively coupled plasma (ICP)-MS method was developed and validated. Linearity was observed over the 0.5 – 50 ppm (μg/g API) range, with an R2 value of 0.9994. The detection limit (DL) and quantitation limit (QL) were 0.2 and 0.5 ppm, respectively. The DL and QL values are well over the thresholds specified in the guidelines. The accuracy was 95.1 – 114.7% for concentrations of 1 – 50 ppm, and the relative standard deviation of the spiked recovery test’s repeatability was 6.2%. In addition, six lots of an API were analyzed, and all results were lower than the reported threshold (1 ppm). View full abstractDownload PDF (679K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (679K) -
Ruge CAO, Fusae KOMURA, Airi NONAKA, Takeshi KATO, Junji FUKUMASHI, To ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 383-388
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis study works on D-(+)-glucose quantitative analysis using diffusion ordered-quantitative 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (DOSY-qNMR), by which an analyte could be distinguished from interferences based upon a characteristic diffusion coefficient (D) in gradient magnetic fields. The D value of D-(+)-glucose in deuterium oxide at 30°C was 5.6 × 10−10 m2/s at a field gradient pulse of between 5.0 × 10−2 and 3.0 × 10−1 T/m, distinguished from fructose, sucrose and starch. Good linearity (r2 = 0.9998) was obtained between D-(+)-glucose (0.5 – 20.0 g/L) and the ratio of the resonance area of α-C1 proton (5.21 ppm) in D-(+)-glucose to that of the β-C1 proton (5.25 ppm) in D-glucuronic acid (50.0 g/L) as an internal standard. The DOSY-qNMR method was successfully applied to quantify D-(+)-glucose in orange juice (18.3 ± 1.0 g/L), apple juice (26.3 ± 0.4 g/L) and grape juice (45.6 ± 0.6 g/L); the values agreed well with a conventional F-kit glucose method. View full abstractDownload PDF (780K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (780K) -
Jitwilai WALUVANARUK, Wanlapa AEUNGMAITREPIROM, Thawatchai TUNTULANI, ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 389-395
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe silica gel modified with benzothiazole calix[4]arene (APS-L1) via Schiff’s base reaction was applied as a sorbent in an online system for preconcentration and determination of silver ion by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). APS-L1 was used as an effective sorbent for solid phase extraction (SPE) of silver(I) ion in both batch and column methods. The optimum experimental parameters such as pH, eluent type, sample flow rate, eluent volume and eluent flow rate including the effect of interfering ions were investigated. Silver(I) ion was determined at pH 6 – 7. The capacity of APS-L1 sorbent was found to be 12.2 mg/g of sorbent. The high affinity was obtained without interference from the interfering ions. The optimum conditions of the online flow injection preconcentration coupled with the FAAS (FI-FAAS system) were evaluated. The sample flow rate was 3.0 mL min−1 using sample volume of 5 – 10 mL. Elution was performed with 250 μL of 0.1 mol L−1 thiosulfate at the flow rate of 1.5 mL min−1. The analytical characteristics and performance of the FI-FAAS system were studied under optimum conditions using a solution spiked with standard silver(I) ion at 20 and 50 μg L−1. The detection limit of 0.44 μg L−1 was obtained. The accuracy of the proposed method was evaluated and percentages of recovery at 20 and 50 μg L−1 were 100.2 and 99.5%, respectively. The percent relative standard deviations (%RSD) at 20 and 50 μg L−1 were 6.1 and 3.3%, respectively. The developed method was successfully applied to determine trace silver(I) ion in drinking and tap water samples.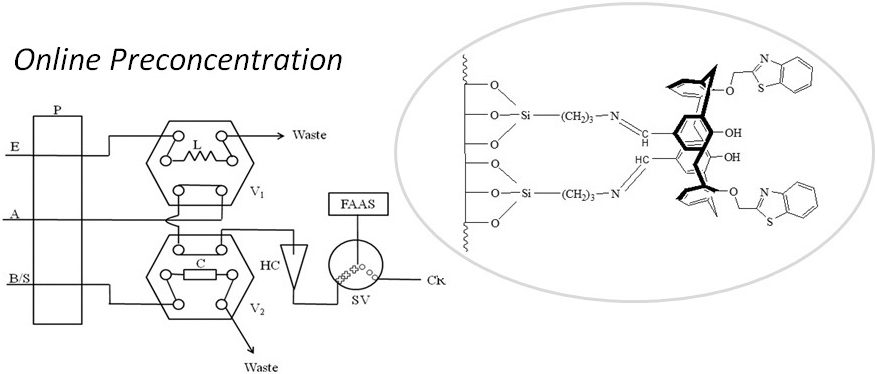 View full abstractDownload PDF (751K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (751K) -
Moe TANAKA, Kumi NAGAMATSU, Hiroyuki NISHIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 397-406
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe enantiomer separation of five nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, ketoprofen (KP) and naproxen (NX), which are included in The Japanese Pharmacopoeia 16th edition (JP16), was investigated by employing four kinds of 3 μm reversed-phase chiral columns (AD-3R, AS-3R, OD-3R and OJ-3R). Except for KP, the enantiomers of four NSAIDs were successfully separated by one of the four columns. Among five NSAIDs, only NX has been used as a single enantiomer (S-form, active form) in the clinical field (JP16); therefore, optical purity testing method of NX is required for its quality evaluation. Among four CSPs, the method was developed by using an AS-3R column, which showed good enantioselectivity for NX enantiomers. By optimizing the conditions, the resolution (Rs) of 2.55 was obtained for NX enantiomers within approximately 6 min. The minor enantiomer R-form eluted before the main active enantiomer S-form. Finally, the developed method was applied to the optical purity testing of NX active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), and its formulations (tablet and capsule). Other than the minor enantiomer (R-form, inactive form, 0.21 – 0.78%), normal (not chiral) impurities at levels of 0.01 – 0.3% were simultaneously separated and determined by the method, showing an excellent separation capability of the method for those impurities including the minor enantiomer. The content uniformity test of the NX tablet according to JP16 was also successfully performed by the method with the AS-3R column. Normal phase separation with two chiral columns (AD-H and OD-H) and capillary electrophoretic (CE) separation were also investigated for five NSAIDs enantiomers to discuss the enantioselectivity.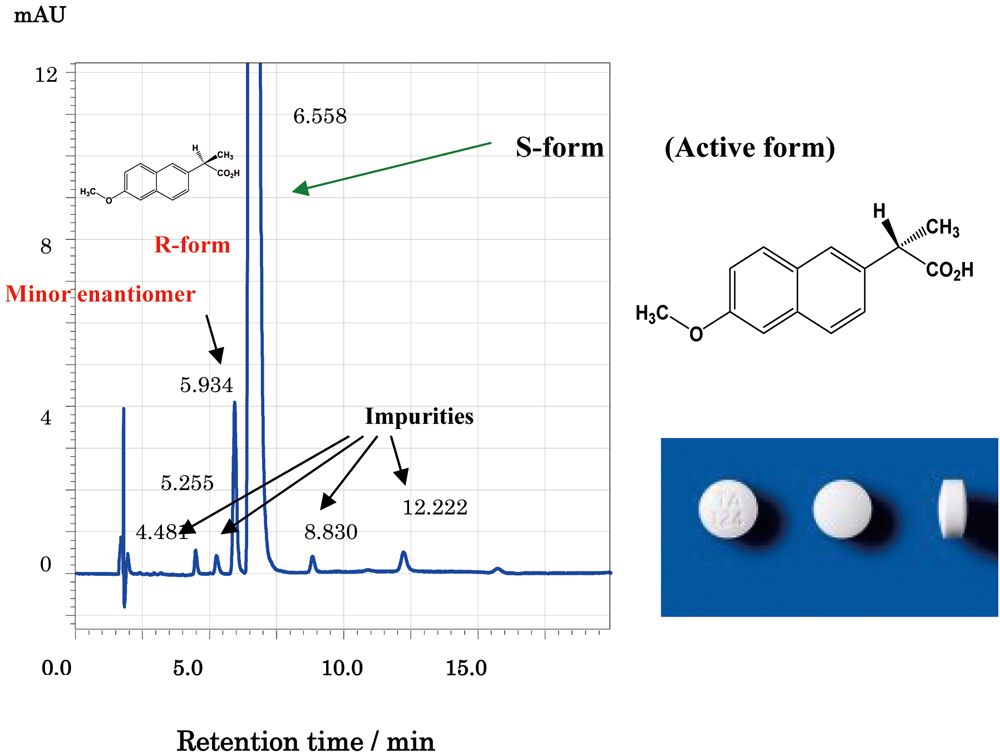 View full abstractDownload PDF (892K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (892K) -
Ikuo UETA, Ayako MIZUGUCHI, Kazue TANI, Susumu KAWAKUBO, Yoshihiro SAI ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 407-412
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel method for evaluating the thermal catalytic decomposition of organic compounds on a solid acid catalyst was developed using a capillary gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (GC-FID) equipped with a packed-capillary column. The thermal catalytic decomposition of various organic compounds was investigated by introducing gaseous or liquid organic compounds into a heated test tube packed with TiO2 particles. The resulting carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) in the test tube were determined in a conventional capillary GC system with a methanizer after separation on a packed-capillary column. In the packed-capillary GC system, several parameters affecting thermal catalytic reactions of various organic compounds were successfully evaluated, such as the type of the catalysts and the effect of catalytic temperatures. Finally, a sequential decomposition of organic compounds was confirmed in the heated reaction tube packed with TiO2 particles. View full abstractDownload PDF (522K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (522K) -
Shingo TERAKADO, Thomas R. GLASS, Kazuhiro SASAKI, Naoya OHMURAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 413-418
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple new model for estimating the screening performance (false positive and false negative rates) of a given test for a specific sample population is presented. The model is shown to give good results on a test population, and is used to estimate the performance on a sampled population. Using the model developed in conjunction with regulatory requirements and the relative costs of the confirmatory and screening tests allows evaluation of the screening test’s utility in terms of cost savings. Testers can use the methods developed to estimate the utility of a screening program using available screening tests with their own sample populations. View full abstractDownload PDF (838K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (838K) -
Mohamed A. F. ELMOSALLAMY, Alaa S. AMINArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 419-425
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNew, simple and convenient potentiometric and spectrophotometric methods are described for the determination of dextromethorphan hydrobromide (DXM) in pharmaceutical preparations. The potentiometric technique is based on developing a potentiometric sensor incorporating the dextromethorphan tetrakis(p-chlorophenyl)borate ion-pair complex as an electroactive species in a plasticized PVC matrix membrane with o-nitophenyl octyl ether or dioctyl phthalate. The sensor shows a rapid near Nernstian response of over 1 × 10−5 – 1 × 10−2 mol L−1 dextromethorphan in the pH range of 3.0 – 9.0. The detection limit is 2 × 10−6 mol L−1 DXM and the response time is instantaneous (2 s). The proposed spectrophotometric technique involves the reaction of DXM with eriochrom black T (EBT) to form an ion-associate complex. Solvent extraction is used to improve the selectivity of the method. The optimal extraction and reaction conditions have been studied, and the analytical characteristics of the method have been obtained. Linearity is obeyed in the range of 7.37 – 73.7 × 10−5 mol L−1 DXM, and the detection limit of the method is 1.29 × 10−5 mol L−1. The relative standard deviation (RSD) and relative error for six replicate measurements of 3.685 × 10−4 mol L−1 are 0.672 and 0.855%, respectively. The interference effect of some excepients has also been tested. The drug contents in pharmaceutical preparations were successfully determined by the proposed methods by applying the standard-addition technique.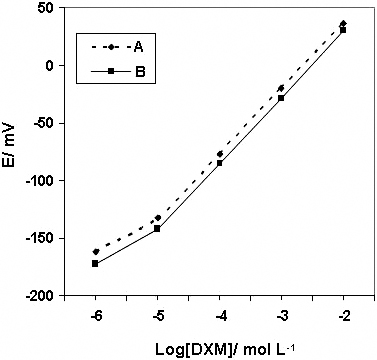 View full abstractDownload PDF (670K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (670K)
Notes
-
Mariko HAYASHIDA, Tomoko OTA, Minori ISHII, Kyoko IWAO-KOIZUMI, Shigen ...Article type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 427-429
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe have developed a new method for directly using unprocessed biological specimens as templates for the TaqMan assay. DNA extraction and purification had been believed to be required for the assay, but our new method could avoid hindering fluorescence detection, even if the templates were used directly. Saliva was needed to be put on water-soluble paper and dried, and hairs were cut to be about 10 mm long. This method could reduce both the time and effort involved, and also the risk of contamination. It should prove to be very valuable for genetic diagnoses in various fields. View full abstractDownload PDF (408K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (408K) -
Shinya KISHIOKAArticle type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 431-434
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new type of optically transparent electrode is fabricated using template-stripped gold film whose surface shows highly oriented, atomically flat terraces and steps. The electrode indicates typical Au(111) electrochemical properties and stability for spectroelectrochemical measurements.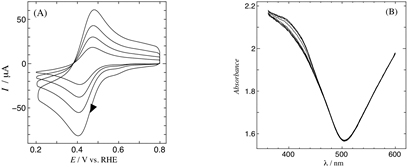 View full abstractDownload PDF (433K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (433K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014 Volume 30 Issue 3 Pages 435
Published: March 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2523K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|