
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Tsutomu FUJIMURAArticle type: Highlights
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1059-1060
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Ayumu MATSUMOTO, Tetsuo SAKKAArticle type: Reviews
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1061-1072
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 18, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFundamentals to applications of underwater laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) of submerged solid targets are reviewed. Since the deformation of spectral lines caused by plasma confinement has been the most serious problem in underwater LIBS, the methods developed to overcome this effect are overviewed. Deep-sea LIBS, which is the most successful application of underwater LIBS, is described in some detail as well as the hydrostatic pressure effects. Since the downsizing of underwater LIBS instrument is an important task for the applications to on-site measurements, studies on non-gated LIBS are covered. In the subsequent section, the methods for the quantitative analysis of the underwater LIBS signal are reviewed. The basics of the plasma parameters used in quantitative analysis are explained, and various methods of quantitative analysis applicable to underwater LIBS are described.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1431K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1431K)
-
Yanjie ZHENG, Tianhua ZHONG, Yichun XU, Li CHEN, Xinyang YIN, Fei LIN, ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1073-1079
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: November 20, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis paper presents a novel voltametric procedure for 7-hydroxycoumarin determination by using a nanogold/poly-thionine modified electrode. The characterization of nanomaterials has been conducted by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electrochemical methods. The electrochemical sensing of 7-hydroxycoumarin was investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). By combining the excellent electrocatalytic property of nanogold and polymer materials, this sensor shows an improved electrochemical response for 7-hydroxycoumarin detection with a good linear relationship in the range of 5.0 × 10−6 – 3.0 × 10−5 mol L−1; the detection limit was 1.0 × 10−6 mol L−1. This method solves the problem that 7-hydroxycoumarin cannot be accurately quantified on a bare glassy carbon electrode, and also improves the detection sensitivity. This is expected to play a huge potential in the quantitative analysis of quality control, plasma concentration monitoring and mechanism research in vivo of this drug.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1545K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1545K) -
Yang SUN, Minghao LI, Yang JIAO, Chunying DUANArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1081-1085
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSimple, accurate and real-time analytical methods are required for the detection of metal ions in a complex environment. In the present work, a fluorescent probe CPB based on coumarin was designed for recognizing Cu2+ ions. The fluorescence of CPB gradually quenched with increasing concentration of Cu2+ ions, due to the interactions between CPB and Cu2+ ions. With the addition of Cu2+ ions, the emission changes of CPB exhibited a good liner relationship toward the Cu2+ ions content in solution. Additionally, CPB could highly selective recognize Cu2+ ions among other metal ions in solution. Bearing the selectivity and fluorescence property toward Cu2+ ions, CPB was successfully applied to monitoring Cu2+ ions in Hela cells and zebrafish.
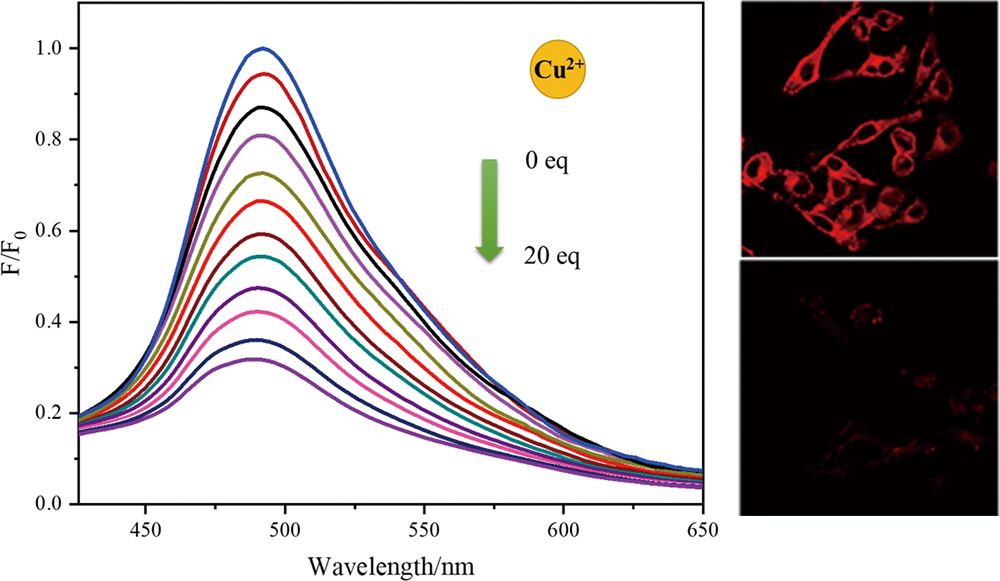 View full abstractDownload PDF (815K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (815K) -
Gang YI, Qiuyue DUAN, Qi YAN, Yuqi HUANG, Wenxiu ZHANG, Shuhui ZHAOArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1087-1093
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 11, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe proposed a dual-template, multi-cycle DNA nanomachine driven by polymerase and a nicking enzyme with high efficiency. The reaction system simply consists of two templates (T1, T2) and two enzymes (KF polymerase, Nb.BbvCI). The two templates are similar in structure (X-X′-Y, Y-Y′-C) with a primer recognition region, a primer analogue generation region, an output region (3′-5′), and two nicking sites. The output strand of T1 is the primer of T2, and the G-rich fragment (G3) is designed as the final product. In the presence of HIV-1, numerous G3 were generated through the multi-cycle amplification strategy and formed a G-triplex/ThT complex after the addition of thioflavin T (ThT), which greatly enhanced the fluorescence intensity as a signal reporter in the label-free sensing strategy. A dynamic response range of 50 fM – 2 nM for HIV-1 gene detection can be achieved through this multi-cycle G-triplex machine, and benefiting from the high efficiency amplification strategy, the enzymatic reaction can be completed within 45 min and followed by fluorescence measurements. In addition, the analysis of other targets can be achieved by replacing the template sequence. Thus, there is a certain application potential of this strategy for trace biomarker analysis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (880K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (880K) -
Tianci ZHANG, Yazhou SHUANG, Hui ZHONG, Liang LI, Laisheng LIArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1095-1103
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 18, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new β-cyclodextrin-bonded chiral stationary phase (TCDP) with a thiocarbamated benzamide spacer was prepared and evaluated on HPLC by separating a series of chiral pesticides and drugs. TCDP resolved all 24 analytes (11 triazoles, 8 flavanones and 5 β-blockers), and 18 of them were completely separated. The enantioresolution ranges were 1.45 – 3.33 for triazoles, 0.35 – 2.45 for flavanones and 1.26 – 1.58 for β-blockers. Among them the best resolution of tebuconazole was up to 3.33 within 13 min. Bitertanol (two chiral centers) and triticonazole with cis/trans isomers were separated into four peaks, respectively. TCDP could also completely resolve myclobutanil (Rs = 1.68), which was difficult to be separated on other CD-CSPs. Common CDSP only resolved a few analytes. The results showed that the thiocarbamated benzamide spacer of TCDP may provide a synergistic effect of hydrogen bonding and coordination. The spacer deserved full utilization, by which may avoid troublesome derivatization at low cost.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2665K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2665K) -
Bo Kyung KIM, Mi-Ri GWON, Woo Youl KANG, In-Kyu LEE, Hae Won LEE, Sook ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1105-1110
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 25, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA rapid analytical method developed for the analysis of β-lapachone in in vitro samples could not be directly applied to the analysis of clinical samples because of interference from unknown substances. Here, we developed and validated a rapid interference-free analytical method to accurately determine β-lapachone levels in human plasma using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. First, we achieved the baseline-separation of β-lapachone from any interfering substances within a total run time of 4 min by adjusting the eluent strength of the mobile phase. Second, precursor-ion scanning revealed the identity of the interfering substances. Sulfonate- or glucuronide-conjugated metabolites were converted to β-lapachone in an electrospray ion source, causing interference. In a method validation study, calibration curves for β-lapachone in human plasma were linear over a concentration range from 0.5 to 200 ng/mL (r > 0.999), and the lower limit of quantification was 0.5 ng/mL. The other validation parameters, including intra- and interday accuracy and precision, were acceptable with a coefficient of variation less than 10% (n = 5). The validated analytical method was successfully applied to a pharmacokinetic study of a single, oral dose of 100 mg MB12066 (a clinical form of β-lapachone) in healthy volunteers.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3670K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3670K) -
Buddhadev KANRAR, S. Sanjay KUMAR, S. MONDAL, N. L. MISHRA, Sangita DH ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1111-1115
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 01, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA method has been developed for direct non-destructive energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) determination of sulfur in solid uranium ores and intermediates, obtained from the alkaline recovery process for uranium from its ores. The method involves thorough grinding of a few mg of solid powder samples to fine particle size and mixing the fine powder thus obtained with a few drops of 10% collodion solution in amyl acetate to make a paste. A very small amount of this paste was transferred with the help of the pestle tip, spread uniformly in the form of thin slurry on Mylar films, and dried to make very thin sample specimens on thin Mylar film supports. These specimens were presented for EDXRF measurements. A calibration plot was made by plotting the intensity ratios of S Kα and Rayliegh scattered peak of the excitation source (Ge Kα) against sulphur percent in the certified reference materials (CRMs). It was found that the precision obtained using this methodology was within 5% (±1σ) and the deviation of the EDXRF analytical results from the expected values of CRM was within 7%. The developed method was successfully applied for the determination of sulfur in the samples obtained from the different stages of the uranium ore processing using alkaline based leaching method.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (231K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (231K) -
Luca CHIARI, Chihiro OHNUKI, Masanori FUJINAMIArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1117-1122
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 08, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe chemical state of the active sites in the pores of zeolites is known to greatly affect their chemical and catalytic properties, e.g. the presence of Brønsted acid sites enhances their action as polar adsorbents. Ortho-positronium diffusion in the pore network has been widely used to clarify the zeolite structure, but its interaction with acid centers under different environments remains unclear. Here, a systematic study on Y-zeolites over a wide range of Si/Al ratios in the absence and presence of water in the framework was carried out using positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy. The acidity of the pores was found to significantly inhibit positronium formation and annihilation within the crystalline micropore network in the dehydrated condition, highlighting a strong positronium oxidizing action of the acid centers. Upon water adsorption, the interaction of the acid sites with the water molecules enabled the recovery of positronium formation in the hydrophilic low-silica samples.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (558K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (558K) -
Hikari TAKAHARA, Wataru MATSUDA, Yasushi KUSAKABE, Satoshi IKEDA, Masa ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1123-1129
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 15, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTotal reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) spectrometry was applied to a forensic discrimination of single polyester fibers. In a non-destructive direct measurement of 5 mm long single fibers used for forensic references, trace metallic elements such as Ti, Sb, Ge, Mn, and Co, found in additives and catalyst residues, were detected using a benchtop TXRF spectrometer. The individual elemental compositions of the fibers were identified, and correlations between the compositions and manufacturers were established using principal component analysis (PCA). Black polyester fibers sampled from the car trunk mats were also analyzed. Several fibers were found to contain both Sb and Ge, elements that characterize different polymerization catalysts; this indicates that the fibers were composed of recycled materials. The TXRF and SR-μXRF spectra showed similar patterns for the fiber samples that were analyzed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2187K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2187K) -
Hiroki ISHIDA, Shinya AZUMA, Naoki YAMASAKI, Hitomi KURITA, Takuya HAS ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1131-1137
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 22, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe selection of an appropriate solvent is essential for achieving high yields and selectivity in chemical reactions. The chemical and physical parameters of organic solvents have been classified into several groups, and solvents can be compared with each other with respect to these properties. The acceptor number (AN), donor number (DN) and polarity (ETN) have been widely accepted and used for theoretically and quantitatively evaluating the properties of organic solvents. In a similar manner, the AN, DN and ETN of room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) have been estimated from spectral changes in solvatochromic compounds. In this paper, the AN and ETN of eight types of imidazolium-based RTILs were estimated from the relationship between the AN and ETN values and the first redox potential obtained from the voltammograms of polyoxometalates (POMs) in various organic solvents. The obtained parameters were compared with those estimated by spectrophotometric methods reported previously by several groups. This new method for estimating the AN and ETN of RTILs using the voltammetric behaviour of POMs with low charge density and high symmetry could provide the other path to obtain more reliable AN and ETN of RTILs.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1997K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1997K) -
Marina MUSA, Takao YASUI, Zetao ZHU, Kazuki NAGASHIMA, Miki ONO, Quanl ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1139-1145
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 22, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSince DNA analysis is the fundamental process for most applications in biomedical fields, capturing DNAs with high efficiency is important. Here, we used several oxide nanowire microfluidic devices to capture CpG-rich single-stranded DNAs (ssDNAs) in different pH solutions. All the oxide nanowires exhibited the highest capture efficiency around pH 7 with good capture efficiency shown by each metal oxide; ZnO/ZnO core/shell NWs (71.6%), ZnO/Al2O3 core/shell NWs (86.3%) and ZnO/SiO2 core/shell NWs (86.7%). ZnO/Al2O3 core/shell NWs showed the best performance for capturing ssDNAs under varying pH, which suggests its suitability for application in diverse biological fluids. The capturing efficiencies were attributed to the interactions from phosphate backbones and nucleobases of ssDNAs to each nanowire surface. This finding provides a useful platform for highly efficient capture of the target ssDNAs, and these results can be extended for future studies of cancer-related genes in complex biological fluids.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1253K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1253K) -
Yuki YOKOTA, Makoto GEMMEI-IDE, Yoshinori INOUE, Shigehiro KAGAYAArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1147-1156
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 29, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialInternal standardization was applied to the solid-phase extraction of trace elements using the following commercially available aminocarboxylic acid-type chelating resins: InertSep ME-2, NOBIAS Chelate PA-1, and Presep PolyChelate. The concentration of the trace elements in initial sample solution can be calculated by using the ratio of the added amount of the internal standard element, Y, in the initial sample solution to that in the final solution after the solid-phase extraction, which is proportional to the volume of the sample solution passed through the cartridge, and the ratio of the volume of the initial sample solution to that of a blank solution for preparing the calibration curve. In this solid-phase extraction, strict control of the volumes of the sample solution passed through the cartridge and the final solution after the solid-phase extraction is not needed because these are not used in the calculation of the trace element concentration. The solid-phase extraction with the internal standardization using Y could be applied to the separation and preconcentration of some trace elements, namely Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Ni, Pb, Ti, and Zn in an artificial seawater spiked with the elements and some certified reference materials, EnviroMAT ES-L-1 Ground Water and EU-L-3 Waste Water, without any interference.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5117K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5117K) -
Claudio A. G. A. VIEIRA, Breno PUPIN, Tanmoy T. BHATTACHARJEE, Kumiko ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1157-1163
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 29, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study aims to explore biochemical changes in saliva during cardiorespiratory exercise using attenuated-total-reflectance–Fourier-transform-infrared-spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR). Saliva and blood samples were obtained from six athletes at rest, and after running at speeds of 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, and 20 kilometers-per-hour (km/h) on a treadmill (maximal stress test). Saliva ATR-FTIR spectra were analyzed using deconvolution and multivariate analysis. Area-under-the-curve calculations suggest differential changes in glucose, lactate, protein, lipids, carbohydrate and phosphate content in saliva during the test. Increases in glucose and lactate levels with increasing speeds were verified by simultaneous measurement of blood glucose and lactate levels using standard equipment (Roche®). Multivariate principal-component-analysis (PCA) showed discrete clusters for low (rest-14 km/h) and high (15 – 20 km/h) speeds, and PCA–linear-discriminant-analysis showed 100% classification of 18 – 20 km/h as high speed. Overall, results suggest the possibility of using this non-invasive saliva-based ATR-FTIR method for biochemical assessment during sports exercise and stress tests.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (667K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (667K) -
Shin KOIKE, Yusuke MIYAJI, Hinako SANO, Natsuki AIKAWA, Masayuki KAI, ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1165-1170
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 29, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, we developed an analytical method using LC-MS/MS for the simultaneous determination of five bile acids (BAs) that have been recently reported as candidate diagnostic biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) or AD related factors in the brain. The measurement of BAs in the brains of healthy mice led to the determination of candidate diagnostic markers for AD, such as cholic acid and deoxycholic acid, and other bile acids, such as chenodeoxycholic acid noted for the ameliorating effect on the symptoms of AD. Significant positive correlations were observed between the brain and plasma concentrations of four BAs in healthy young mice. These results indicate that the BA level in the brain may be estimated by the corresponding BA level in the plasma. Thus, our study suggested that the proposed method for the analysis of the five bile acids would aid in the diagnosis of AD or in studies that use AD model mice.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (597K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (597K) -
Yutaka MATSUDA, Monica LEUNG, Zhala TAWFIQ, Tomohiro FUJII, Brian A. M ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1171-1176
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 29, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe field of oncology has recently seen an exponential growth in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) as a biopharmaceutical class with seven ADCs being launched onto the market in the last ten years. Despite the increase in the industrial research and development of these compounds, their structural complexity and heterogeneity continue to present various challenges regarding their analysis including reaction monitoring. Robust and simple reaction monitoring analysis are in demand in the view of at-line in-process monitoring, and can instill control, confidence and reliability in the ADC manufacturing process. Aiming at providing chromatographic methods for conjugation monitoring, we evaluated herein the potential of utilizing reverse phase HPLC analysis, without sample pretreatment, for characterization of traditional cysteine-based ADCs. This analysis can be used for estimation of drug antibody ratio (DAR), which has shown the same trends and results as other well-established HPLC techniques. This methodology was also applied to three ADCs derived from three different antibodies. Additionally, we analyzed unpurified ADC samples existing in a complex reaction matrix and separated ADC species and payload compounds. This investigation was conducted using three different ADCs based on different payloads. The results described herein indicate the potential application of this RP-HPLC methodology in reaction monitoring studies.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (765K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (765K)
-
Ndeye A. DIOP, Jean-Pierre BAKHOUM, Pape A. DIAW, Olivier M. A. MBAYE, ...Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1177-1180
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 01, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe photo-induced fluorescence method is often applied to determine non-native fluorescent compounds. It typically uses UV irradiation from a high pressure mercury vapor discharge lamp to create photo-induced fluorescent compounds, which are then quantified by fluorescence spectroscopy. However, these mercury lamps require a high-voltage power supply and may accidentally induce electric shocks and the release of mercury vapors. As an alternative, we have evaluated in this technical note new UV-C germicidal lamps. These lamps exhibit a higher power at 254 nm and allowed us to obtain a far greater amount of photo-induced compounds in a shorter time. For the first time, this new irradiation system has been applied for the determination of pesticides in water and has shown a significant increase in the method sensitivity. These good results allowed us to conclude that the new UV-C lamps are a relevant alternative to high pressure mercury vapor discharge lamps for use with photo induced fluorescent methods.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1819K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1819K) -
Chunhai YUArticle type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1181-1184
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: January 15, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study demonstrated the signal enhancement interference from soluble iron (Fe) during mercury (Hg) determination in water by cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry (CV-AAS) using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as reductant. In the presence of 50 mg L−1 soluble Fe, Hg values will be overestimated by around 25%. The reason for the Hg signal enhancement is still unclear, but it is speculated to be attributable to the catalyst function for the equilibrium reduction reaction between Hg2+ and BH4− from the atomic Fe formed at the same time. Using the matrix matching calibration standards prepared in 50 mg L−1 Fe solution, the problem of Hg overestimation could be minimized. This study also indicated that stannous chloride (SnCl2), another common reductant for Hg analysis, does not suffer from the overestimation problem from soluble Fe in the presence of NaBH4.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (141K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (141K) -
Yuko KITAMAKI, Naoki SAITO, Nanako SASAKI, Mariko MORITA, Tomohiro SAS ...Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1185-1188
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
Advance online publication: February 05, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe built a heating furnace using stainless-steel instead of aluminum in gas chromatography combined with an oxidation/reduction system; it increased the oxidation temperature to 650°C. At 600°C, it completely oxidized five organochlorine compounds. This system was applied to a standard solution of 23 volatile organic compounds. The analytical results of 20 hydrocarbon and organochlorine compounds showed good agreement with the expanded uncertainty (k = 2) of the reference values. Three organobromine compounds obtained values higher than the reference; this was investigated further.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (113K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (113K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2021 Volume 37 Issue 8 Pages 1189
Published: August 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (71K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
