All issues

Volume 33, Issue 9
Displaying 1-19 of 19 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Hideya KAWASAKIArticle type: Highlights
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 987-988
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (375K)
Rapid Communications
-
Yuki SAKAGUCHI, Tomoka MINAMIKAWA, Mayuko YAMAMURO, Tadayuki TSUJITA, ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 989-991
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLuminescent europium-doped layered titanates (Eu-TiOx) were synthesized and complexed with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and glucose oxidase (GOx). The emission of a resultant Eu-TiOx/HRP/GOx complex decreased upon the addition of glucose in the presence of guaiacol. The emission decrease was dependent on the concentrations of glucose, and the detection limit for glucose was 3.1 μM. The proposed system would be promising as a new detection method for glucose.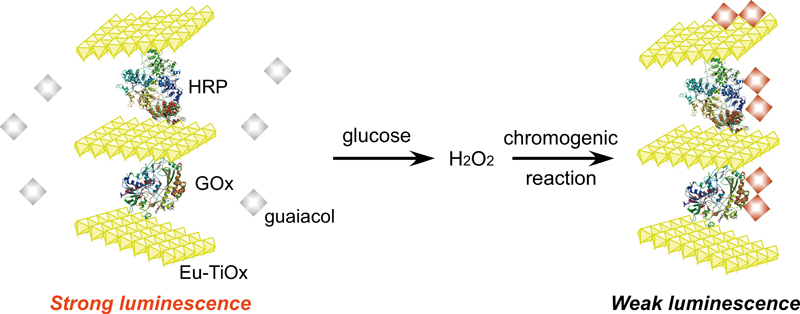 View full abstractDownload PDF (732K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (732K)
Original Papers
-
Yanfang GENG, Euna KO, Van-Khue TRAN, Woo Sung CHUNG, Chan Ho PARK, Mi ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 993-998
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the present study, we developed an electrochemical sensor for highly sensitive detection of hydroxylamine using Au-Pt alloy nanoparticles. Au-Pt alloy nanoparticles were electrochemically deposited on a working electrode made of single-walled carbon nanotubes. The framework composition in the Au-Pt alloy nanoparticle was easily controlled by adjusting the Au3+:Pt4+ composition ratio in the precursor solution. Morphological and chemical characterizations of the resulting Au-Pt alloy nanoparticles were performed using field emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and energy dispersion X-ray spectroscopy. When the Au3+:Pt4+ ratio in the precursor solution was 1:5, the ratio of Au:Pt atom in alloy nanoparticle was about 6:4. Au60Pt40 alloy nanoparticles were found to have the optimum synthetic ratio for hydroxylamine detection. The electrocatalytic performance of Au-Pt alloy nanoparticles in the presence of hydroxylamine was also characterized using cyclic voltammetry, differential pulse voltammetry, and chronoamperometry. In the chronoamperometric detection of hydroxylamine, the sensor exhibited a detection limit of 0.80 μM (S/N = 3) and a high sensitivity of 184 μA mM−1 cm−2. Moreover, the amperometric response of the sensor in 1 mM hydroxylamine was stable for a long time (450 s). Long-term stability tests showed that the current responses to hydroxylamine were 96, 91 and 85% of the initial signal value after storage for 5, 10, and 20 days, respectively. View full abstractDownload PDF (1050K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1050K) -
Jiangbo XI, Juan ZHANG, Haiyan ZHAOArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 999-1005
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel magnetic absorbent based on Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres was developed for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) extraction. Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres were prepared by a one-pot facile solvothermal method and its structural properties were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and analyzer transmission electron microscopy (TEM). It was the first time to use hollow nanospheres which possess high special surface area for magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE). The extraction condition of Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres and its performance for PAHs was systematically investigated. Besides, its extraction performance also compared with bare Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The results indicated the structure with hollow and spherical Fe3O4 perform better enrichment ability than that with solid and amorphous ones. The developed MSPE coupled with HPLC method shows good linearity (0.1 – 5 ng/mL) and low detection limits (2.5 – 10 pg/mL) for six PAHs. It also has been executed for the analysis of environmental samples, with recoveries in the range of 84.6 – 97.8%. View full abstractDownload PDF (1281K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1281K) -
Fumiyuki TAKASAKI, Kazuhiko FUJIWARA, Tomomi KIKUCHI, Takenori TANNO, ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1007-1012
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialLigand exchange reactions of a monomeric zirconium carbonate complex with carboxylic acids were studied by means of extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS), UV absorption spectrophotometry and Raman spectrometry. Three carboxylic acids, gluconic acid, and L-tartaric acid and citric acid, which are mono-, di- and tri-carboxylic acids, respectively, were employed in this study. These three carboxylic acids gave different spectral signatures and concentration dependences, respectively. In the gluconic acid system, the peaks on Fourier transform of EXAFS spectrum and Raman spectrum caused by carbonate ion coordinating to zirconium atom were obviously decreased with increasing gluconic acid concentration compared to the other two carboxylic acid systems. This indicates the high association ability of gluconic acid to zirconium, which was revealed by UV spectrophotometric analysis. View full abstractDownload PDF (1180K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1180K) -
Masuro FUNAKI, Masayori SUWA, Hitoshi WATARAIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1013-1019
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe electromagnetophoretic behavior of organic droplets in an electrolyte solution was investigated in a silica capillary cell using a superconducting bulk magnet (3.5 T) and a magnetic circuit (2.7 T). The initially dispersed emulsion droplets of dodecane migrated to the wall of the capillary, responding to the direction of an electric current, and coalesced to form smaller and larger droplets after some repeated migrations. When the electric current was applied continuously, the larger droplets became arranged with regular intervals on the wall, and smaller droplets rotated around the larger droplets. These interesting behaviors were analyzed while taking into account the local electric current density determined by the flow velocity of the ionic current around a droplet, which was lowest on the electrode sides of the droplet. The difference in the local electric current density generated the Lorentz-force difference in the medium, which lead to local micro-convection around the droplet, and also the alignment of larger droplets by a repelling effect between the adjacent micro-convections.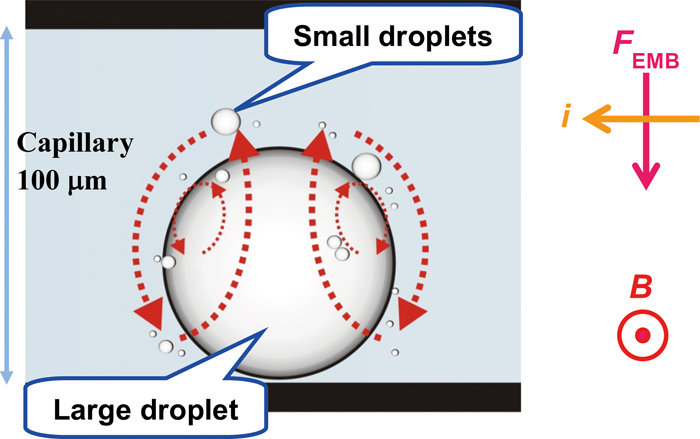 View full abstractDownload PDF (5780K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5780K) -
Geun Wan KIM, Ji Won HAArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1021-1025
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe characterized the optical properties of single platinum-coated core-shell gold nanorods (Pt-AuNRs) under dark-field (DF) and differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy. Furthermore, we examined their potential use as multifunctional orientation probes. Longitudinal surface plasmon resonance damping was observed for single Pt-AuNRs due to Pt metals coated on the AuNR surface under single-particle scattering spectroscopy. Despite the strong plasmon damping with a much-decreased scattering intensity, DIC microscopy allowed us to detect single Pt-AuNRs with much higher sensitivity. We found polarization-dependent DIC images and intensities of single Pt-AuNRs, which allowed us to determine their orientation angle under DIC microscopy. Therefore, we report that single Pt-AuNRs can be used to develop multifunctional orientation probes under DIC microscopy. View full abstractDownload PDF (864K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (864K) -
Ting-Ting HU, Chun-Mei LU, Han LI, Zai-Xiao ZHANG, Yun-Hui ZHAO, Juan ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1027-1032
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe overuse of organophosphorus pesticides on cotton production is a big concern in China today. Therefore, developing methods for the rapid screening and confirming of pesticide residues in textiles has become a top public health security priority. Here, a method was established for the rapid screening and quantifying of 11 kinds of organophosphorus pesticides (ethoprophos, coumaphos, profenofos, diazinon, ethion, parathion, phosalone, quinalphos, dicrotophos, azinphos methyl, and tribuphos) in textiles by high-performance liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry (HPLC-HRMS). Rapid screening and quantifying could be completed by using software of Peakview and MultiQuant. Samples were extracted by the method of modified QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged and Safe) and analyzed in the positive mode with MS detection. The results showed that the limits of detection were between 0.1 and 5.0 ng g−1, with correlation coefficients above 0.9990. The recoveries were in the range of 70.3 – 109.8%, with relative standard deviations from 5.1 to 16.4%. This method is accurate and simple, which can be used in the rapid screening and quantitative analysis of 11 kinds of organophosphorus pesticides in textiles.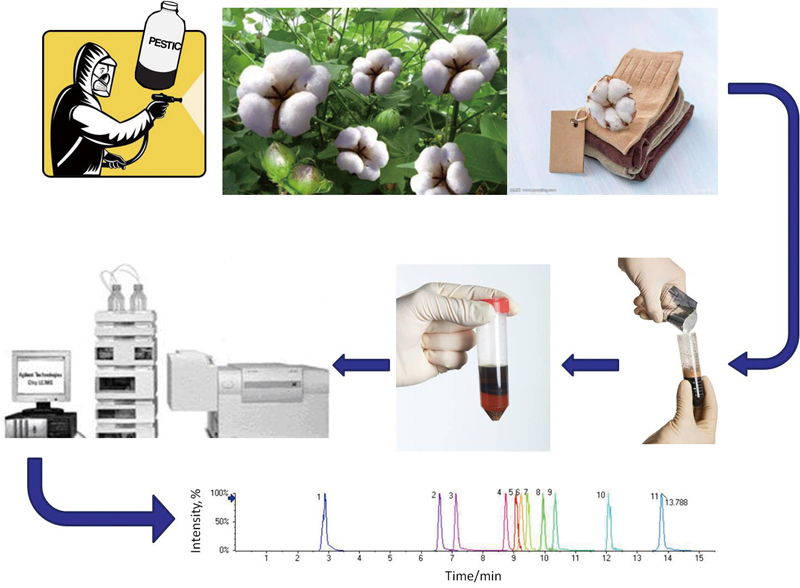 View full abstractDownload PDF (918K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (918K) -
Seiji KAMBA, Hirokazu SETO, Takashi KONDO, Yoshiko MIURAArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1033-1039
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialBiosensing of protein adsorption with metal mesh device (MMD) was investigated by computational calculations and experiments. Electromagnetic field computation was carried out with a single unit cell of MMD. Equivalent circuit model of MMD on the single unit cell was assumed, and the biosensing with MMD was analyzed in detail by computational calculation and experimental measurements. The dip frequency of MMD was shifted by adsorption of protein on MMD. The shift of dip frequency of MMD was proportional to the amount of protein adsorption. The sensitivity of MMD biosensing was dependent on the microstructure of MMD, and proportional to the square of the dip frequency. The refinement of MMD structure can improve the sensitivity of protein detection. View full abstractDownload PDF (1160K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1160K) -
Miki YAMAGUCHI, Taisei NISIMURA, Woon Yong SOHN, Qing SHEN, Shota KUWA ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1041-1046
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe effects of various sample parameters for solid-state dye sensitized solar cells were studied with carrier dynamics measurements and electrochemical measurements. Although many parameters and processes have been decided based on the experience of researchers, the chemical and physical reasons for the selections have not been clarified. We studied the effect of the generally utilized materials and processing such as the blocking layer, titanium oxide thickness, surface treatment, and the selection of dyes and hole transfer materials. Based on our findings, we were able to rationally optimize the structure of the solid-state dye sensitized solar cells in terms of cell performance or the lifetime of charge carriers. View full abstractDownload PDF (2525K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2525K) -
Sijie LIU, Yongning WU, Chiguang FANG, Yong CUI, Nan JIANG, Hui WANGArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1047-1052
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, a highly sensitive and fast method of QuEChERS (acronym of quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, safe) combined with isotope dilution–ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry was developed for the simultaneous determination of 19 plant growth regulators in plant-originated foods. The samples were initially extracted with acetonitrile containing 1% acetic acid and then the QuEChERS method was applied after the pH value was adjusted to 5.5 – 6.0, using 3-indolepropionic-d2 acid and forchlorfenuron-d5 as internal standard. The targeted 19 plant growth regulators were separated on an HSS T3 column using acetonitrile: 5 mmol/L ammonium acetate as the mobile phase. Quantitative results were based on multiple reaction monitoring mode after ionization in positive and negative electrospray ionization mode. Good linearity was achieved within a wide range and all the correlation coefficients were greater than 0.997. The limit of quantification was 0.060 – 6.0 μg/kg. Rate of recovery and relative standard deviation were 72.3 – 115.8 and 1.78 – 5.32%, respectively. The method was successfully applied to measure 19 plant growth regulator residues in 280 plant-originated commercial foods collected from local supermarkets in China. Twelve plant growth regulators were found in some of the analyzed samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (912K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (912K) -
Motohiro BANNO, Hotaka TAKAKUWA, Hiroharu YUIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1053-1058
Published: September 30, 2006
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWhen high voltage is applied to a gap between electrodes in aqueous solution, a discharge plasma is generated that connects the edges of the facing electrodes. When the width of the gap between the electrodes is extended to more than several millimeters, the plasma is separated into two and they are localized at the vicinities of the edges of the anode (+plasma) and cathode (–plasma). Although they are expected to supply characteristic reaction fields, the properties of the plasmas, such as electron number density and temperatures of transient species, have not yet been clarified. In the present study, a time- and space-resolved emission spectrometer with a discharge cell was developed for optical diagnostics of the +plasma and –plasma separately. The electron number density for the +plasma was obviously lower than that for the –plasma. The difference in the electron number density should result from the difference in the ionization energy of the cathode materials. From the temporal evolutions of the emissions from the components, the emissions from the –plasma were sustained for about 0.5 μs after the decay of the applied voltage, probably due to the large number of free electrons in the –plasma. It is also clarified that hydroxyl radicals are effectively generated by the collisions between cations deriving from water and low-energy free electrons in the +plasma. The wide-gap in-solution discharge supplies two plasmas simultaneously with different properties. For plasma reactions, one plasma with suitable properties can be selected. View full abstractDownload PDF (864K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (864K) -
Nobuhiro MATSUMOTO, Takuya SHIMOSAKAArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1059-1065
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe purities of two high-purity organic compounds with a nitroxyl radical moiety were quantified based on their free-radical content using the effective magnetic-moment method. Magnetic moments were measured and X-band electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra were obtained using a superconducting quantum interference device and X-band EPR spectrometer, respectively, over a wide temperature range of near-room temperature to near-liquid-helium temperature. Concerning measurements of effective g-values using an EPR spectrometer, both the sweep direction and sweep speed were taken into account to obtain accurate g-values. The purities of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl (TEMPO) and 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl benzoate (4-hydroxy-TEMPO benzoate) were close to 1 kg kg−1 with relative uncertainties of 1%, which represented improved values compared to those obtained by us previously. These results show a possibility for both compounds to act as reference materials in providing reliable quantification of free radicals per unit mass using this analytical method.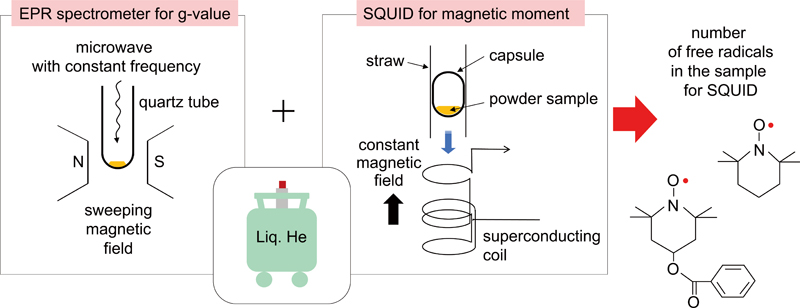 View full abstractDownload PDF (1091K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1091K) -
Hirofumi FUKAYA, Tomohiro UCHIMURAArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1067-1070
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe first quantitative analysis of an oil component in an emulsion was achieved by multiphoton ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MPI-TOFMS). An oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion was prepared. Styrene (0 – 5000 ng μL−1) and Triton X-100 were used as the oil phase and the disperser, respectively. Toluene was employed as an internal standard. We obtained a series of mass spectra, and then constructed the time profiles for styrene and toluene. As a result, we found several spikes from both time profiles when measuring emulsions with higher concentrations of styrene. Moreover, the timing of spikes for toluene coincided with that of styrene. These results suggested the movement of toluene into styrene droplets in the prepared emulsion. Furthermore, we constructed calibration curves of styrene using both the absolute calibration curve method and an internal standard method. Linear calibration curves were obtained in the concentration range investigated in the present study; the coefficients of determination obtained by both methods were 0.9956 and 0.9986, respectively. View full abstractDownload PDF (615K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (615K) -
Yong-jin PENG, Yu-ling LIU, Qiang WU, Ping-chuan SUNArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1071-1076
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe change in the infrared spectrum of polymer samples with temperature and their differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) experimental results are analyzed. According to the van’t Hoff equation at constant pressure, the changes in the absorbance ratio corresponding to high and low vibrational states are calculated, and the apparent enthalpy differences of the vibration energy states transformation of the characteristic group can be obtained. From the experimental results, we can find that characteristic vibration modes of a chemical group in a polymer are under the influence of the glass transition process of the polymer with a different extent. The characteristic vibration modes of the same chemical group behave differently due to the influence of the polymer system at which the chemical moiety is situated. View full abstractDownload PDF (1964K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1964K) -
Rima BAO, Zhikui WU, Hao LI, Fang WANG, Xinyang MIAO, Chengjing FENGArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1077-1080
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe study of fluid inclusion is one of the important means to understanding the evolution of mineral crystals, and can therefore provide original information of mineral evolution. In the process of evolution, outside factors such as temperature and pressure, directly affect the number and size of inclusions, and thus are related to the properties of crystals. In this paper, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) was used to detect sodium sulfate crystals with different growth temperatures, and absorption coefficient spectra of the samples were obtained. It is suggested that the evolution of sodium sulfate could be divided into two stages, and 80°C was the turning point. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and polarizing microscopy were used to support this conclusion. The research showed that THz-TDS could characterize the evolution of mineral crystals, and it had a unique advantage in terms of crystal evolution. View full abstractDownload PDF (1185K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1185K)
Notes
-
Kiyoharu NAKATANI, Naoki SAWADA, Tatsumi SATOArticle type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1081-1084
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSUsing a Cd-deposited microelectrode, an electrochemically generated Cd(II) ion in a micro-water phase was reacted with 5-octyloxymethyl-8-quinolinol (HC8Q) in 1,6-dichlorohexane. The fluorescence intensity of Cd(C8Q)2 near the water/oil interface (IF) was analyzed under a confocal fluorescence microscope. The rate of decrease of IF was independent of the HC8Q concentration and pH, but was influenced by the phase-boundary potential between the water and oil phases, suggesting that Cd(II) extraction is governed by Cd(C8Q)+ desorption at the interface. View full abstractDownload PDF (566K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (566K) -
Atsushi WATANABE, Young-Min KIM, Akihiko HOSAKA, Chuichi WATANABE, Nor ...Article type: Notes
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1085-1089
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWhen a GC/MS system is coupled with a pressurized reactor, the separation efficiency and the retention time are directly affected by the reactor pressure. To keep the GC column flow rate constant irrespective of the reaction pressure, a restrictor capillary tube and an open split interface are attached between the GC injection port and the head of a GC separation column. The capability of the attached modules is demonstrated for the on-line GC/MS analysis of catalytic reaction products of a bio-oil model sample (guaiacol), produced under a pressure of 1 to 3 MPa.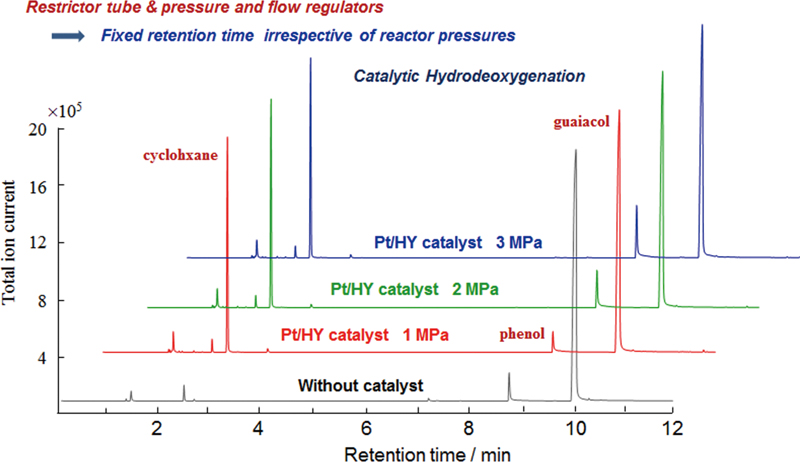 View full abstractDownload PDF (671K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (671K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017 Volume 33 Issue 9 Pages 1091
Published: September 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (3087K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|