
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Nobuhiko IKIArticle type: Highlights
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1223-1224
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Min ZHAO, Jianwei ZHAO, Lirong QIN, Zhengyan JIANG, Hongliang JIAArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1225-1230
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA hierarchical CuO array film was fabricated by electrochemical deposition with the aid of a colloidal monolayer as a template, followed by oxidation at high temperature. The prepared CuO film with a granular structure was arranged with ordered, hexagonal close-packed, and bowl-like pores. Combined with a gold layer sputtered on a glass substrate, this CuO array film was used as an electrochemical electrode in the amperometric detection of l-ascorbic acid. The array film exhibited a high sensitivity of 3484 μA mM−1 cm−2, a wide linear range from 1 μM to 7 mM, and a detection limit of 0.2 μM. Excellent stability was also achieved. The results demonstrate that the hierarchical CuO bowl-like array film is a promising new platform for the construction of non-enzymatic ascorbic acid sensors.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2290K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2290K) -
Sheng-Yao CHANG, Ming-Yuan LEE, Ching-Chou WUArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1231-1236
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA microchip electrophoresis (ME) device with off-channel contact conductivity detection (C2D) was constructed using top–bottom antiparallel indium tin oxide (ITO) electrodes and a cross-type microchannel. The 500-m wide top–bottom antiparallel decouplers were found to effectively decrease the interference of the electrophoretic current. The cross-type microchannel was formed by bonding the patterned negative photoresist microstructures and the two top–bottom opposed ITO-deposited glass substrates. Five seconds of 150 V/cm injection field and the 100 V/cm separation field equipped with the C2D of AC 200 mV excitation voltage provided adequate ME operational parameters to obtain the K+ and Na+ peaks separation. The ME devices obtained good coefficients in a range of 11000 μM for the K+ and Na+ detection. The calculated limit of detection was 1 μM. This design for off-channel and top–bottom antiparallel electrodes shows that C2D ME devices have great potential for the measurement of inorganic ions.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (353K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (353K) -
Tomonori NOMOTO, Masahiro TAKAHASHI, Takuya FUJII, Luca CHIARI, Taro T ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1237-1242
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: June 29, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAlthough the mechanical properties and compositions of lipid bilayer membranes can change upon deformation, the fundamental relations between the composition, membrane tension and fluidity of membranes with little curvature have not yet been studied. In the current study, the membrane tension and the diffusion coefficients of free-standing black lipid membranes (BLMs), based on 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC), were observed by systematic control of the cholesterol concentration and the osmotic pressure with the laser-induced surface deformation (LISD) and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) techniques. When the osmotic pressure was raised and, therefore, the curvature became larger, both the membrane tension and the diffusion coefficients increased as well. On the other hand, when the cholesterol concentration was raised, the membrane tension increased whereas the diffusion coefficient decreased. The importance of the present results goes beyond this quantitative evaluation of the relation between the membrane tension and the fluidity, as it clarifies the changes in the fundamental properties of lipid bilayers upon natural fluctuations and perturbative deformation that were hitherto unknown.
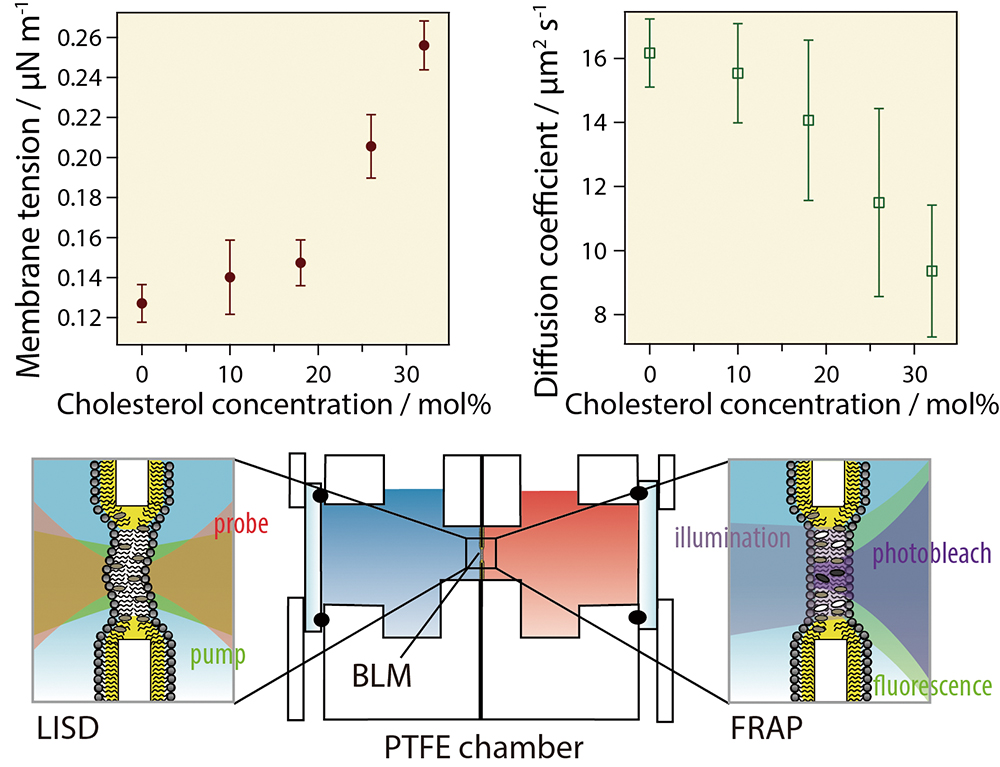 View full abstractDownload PDF (493K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (493K) -
Khadijah ZAI, Kazuki YUZURIHA, Akihiro KISHIMURA, Takeshi MORI, Yoshik ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1243-1248
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: June 29, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe induction of antigen-specific immunotolerance has been gathering attention concerning the therapy of allergy and autoimmune diseases. Tolerogenic dendritic cells (tDCs) play crucial roles in immunotolerance therapy because they induce anergic responses for auto-reactive helper T cells, and also enhance differentiation to regulatory T cells to maintain tolerance against auto-antigens. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is one of the representative molecules used to induce tDCs. We have proposed a simple formulation of ovalbumin nanoparticles complexed with ATRA (OVA/RA NPs). OVA/RA NPs were taken up by DCs and successfully induced phenotypes of tDCs.
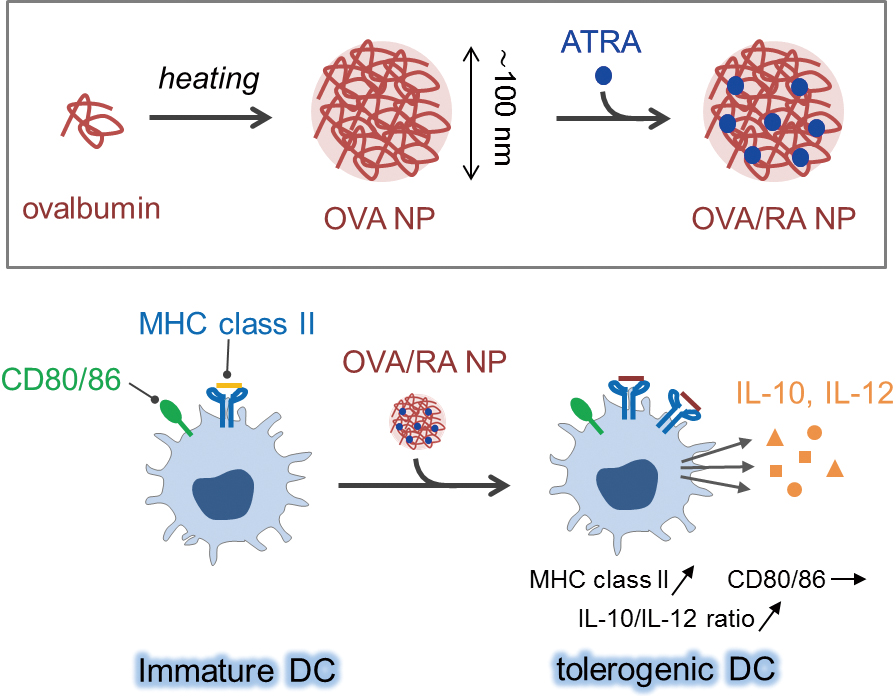 View full abstractDownload PDF (687K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (687K) -
Chen ZHANG, Si-qin-gao-wa HAN, Hang ZHAO, Shuang LIN, Wu-Li-Ji HASIArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1249-1255
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: July 06, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this investigation, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) technology was performed to detect bucinnazine hydrochloride (BH) injection in water and urine. The theoretical Raman spectrum of BH with characteristic peaks was calculated and identified by density functional theory (DFT). Employing an improved silver sol as a SERS active substrate, the SERS spectra of a BH solution with different concentrations were acquired with a 0.5 mol/L KI solution as an aggregation agent. It was determined that the limit of detection (LOD) was low, to 0.01 μg/mL. A good linear relationship of BH between the Raman intensity and the concentrations was obtained in water at a concentration range from 0.5 to 6 μg/mL (R2 = 0.9914), which laid a favorable foundation for quantitative analysis. In addition, the recovery rate of spiked samples from 95.13 to 120.54% were calculated. Finally, the detection of BH injection in artificial urine was completed and the detection limit could reach 0.5 μg/mL, which met the requirements of a rapid on-site detection of drugs in urine. As a result, it indicates that the inspection of BH by the SERS method is with simplicity and high sensitivity, having a great potential for real-time detection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3126K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3126K) -
Azureen MOHAMAD, Natasha Ann KEASBERRY, Minhaz Uddin AHMEDArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1257-1263
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: July 06, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNanoparticles have been widely developed and shown to have intrinsic enzymatic ability, and are used in biosensors. Compared to biological enzymes used in biosensors, which are expensive and tedious to harvest, enzyme-mimic nanoparticles or nanozymes are both more stable and sensitive. An important area in this work is the development of a simple detection principle of immunosensor based on the one-step synthesis of silver nanoparticle seeded onto a gold core. The gold-silver core-shell nanoparticle acts as a peroxidase mimic, which enables them to oxidise 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) with H2O2, giving a colourimetric response. Herein, the analytical performance of the nanozyme is exploited to detect haptoglobin as a model analyte in a 96-well plate and measured the colourimetric product using spectrophotometer. The sensitivity of the immunosensor was as low as 100 pg mL−1. The viability of our immunosensor was shown to have good selectivity and satisfactory recovery in real serum samples.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (541K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (541K) -
Tetsuo SAKAMOTO, Masato MORITA, Keita KANENARI, Hideki TOMITA, Volker ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1265-1270
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: July 06, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe characterization of radionuclides in Fukushima is important to determine their origins and current state in the environment. Radionuclides exist as fine particles and are mixed with other constituents. A measurement method with both micro-imaging capability and highly selective element detection is necessary to analyze these particles. We developed such an imaging technique using a time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry and wavelength-tunable Ti:Sapphire lasers for the resonance ionization of target elements without mass interference. This is called resonant laser ionization sputtered neutral mass spectrometry. The instrument has a high lateral resolution and a higher ionization selectivity using two-step resonance excitation of Cs with two lasers at different wavelengths. Optimization of the wavelength for resonance ionization using a Cs compound was performed, and a real environmental particle containing radioactive Cs was analyzed. Isotope images of three kinds of Cs were successfully obtained without interfere from Ba isotopes for the first time.
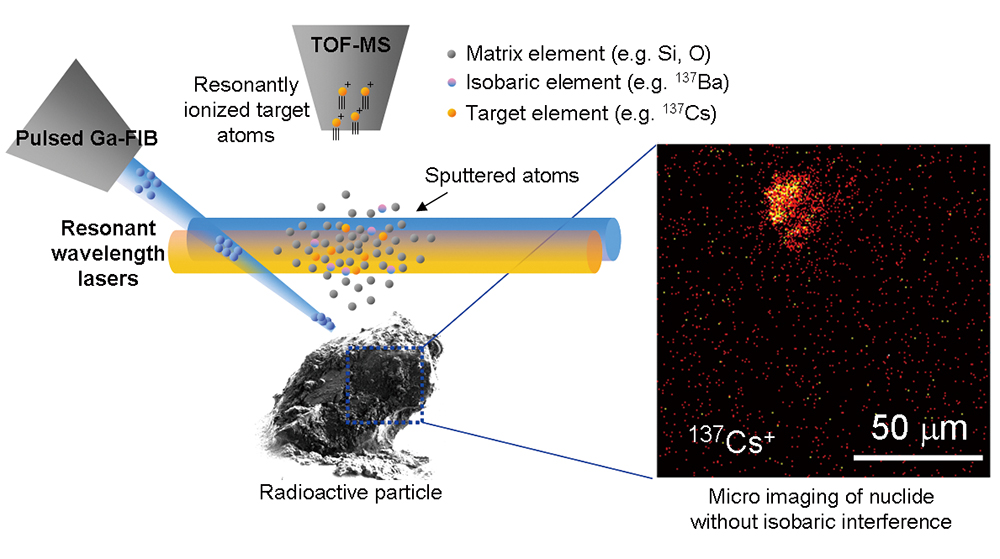 View full abstractDownload PDF (3459K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3459K) -
Eun-Sook PAIK, Yang-Rae KIM, Hun-Gi HONGArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1271-1276
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe developed an amperometric glucose biosensor based on glucose oxidase (GOx) embedded in zinc oxide (ZnO)-chitosan (CS) hybrid composite films on electrodeposited Pt-Fe(III). This sensor exhibited a fast amperometric response (less than 10 s) to glucose, linearity from 10 μM to 11.0 mM of glucose with a detection limit of 1.0 μM (S/N = 3) and sensitivity of 30.70 μA mM−1 cm−2. An apparent Michaelis–Menten constant of 5.19 mM indicated high affinity between glucose and GOx immobilized in the ZnO-CS films. The effect of interferences such as uric acid, ascorbic acid, and acetaminophen on the performance of this sensor was negligible. In addition, this sensor retained 87% of its initial performance after two weeks of storage at 4°C, indicating that the hybrid composite films allowed successful immobilization of GOx with its high enzymatic activity.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1206K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1206K) -
Mitsuyuki KONNO, Yoshitaka TAKAGAIArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1277-1283
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: July 20, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA radiometric quantitative methodology of 90Sr in seawater was developed using a measurement of the 90Y decay time following iron-barium co-precipitation. With calculations of its decay time, the radioactivity of 90Sr can be indirectly determined under conditional environmental samples. In addition, to avoid the interference of other radionuclide, the prepared samples were measured using a germanium semi-conductivity detector; then, the deposited radioactivity was subtracted from the actual measurement values of beta-ray counting. In this paper, the seawater samples were collected within 2 km around Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants during the term from October 2011 to March 2012. This method showed good linearity between the 90Sr concentration and the total beta counting following the proposed method, with a correlation coefficient of 0.99 in seawater sample analysis. No interference that was caused by other radionuclides, such as radioactive cesium, was not observed in the quantification of 90Sr. The whole process requires 12 h to quantify 90Sr; this time is 1/40 shorter than traditional milking-low background gas-flow counting method. The lower limit of detection (average value n = 60) of the 90Sr radioactivity was shown to be 0.03 Bq/L (uncertainty 4.2%).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (491K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (491K) -
Mingpeng YANG, Zhe HUANG, Jianguo CHANG, Hui YOUArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1285-1290
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel solution-auto-introduction electrophoresis microchip based on capillary force aimed at improving portability is proposed in this paper. Two kinds of materials with micropores, poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA)-sponge and nano-sponge, were employed as suction pumps that realized the introduction of a running buffer into the reservoirs. The surfaces of the microchannels in the microchips were modified by PVA to improve the moving velocity of the running buffer and the detection performance of the microchip. The introduction velocity of a running buffer in the PVA-coated microchannels was increased by two times compared with that in the native microchannels. The electrophoresis detection performance of several microchips composed of different microchannels and suction materials were evaluated comparatively. The results indicated that the surface coating of PVA can significantly improve the repeatability of the detection results by 20 – 40%, and the noise of the detected signals in the PVA-coated microchips is much lower than that in the native microchips. The proposed solution-auto-introduction electrophoresis microchip is a successful attempt that completely avoids the external connectors to accomplish the auto-introduction of running buffer. The solution-auto-introduction method provides a new train of thought for portable detection instruments with electrophoresis microchips in the future.
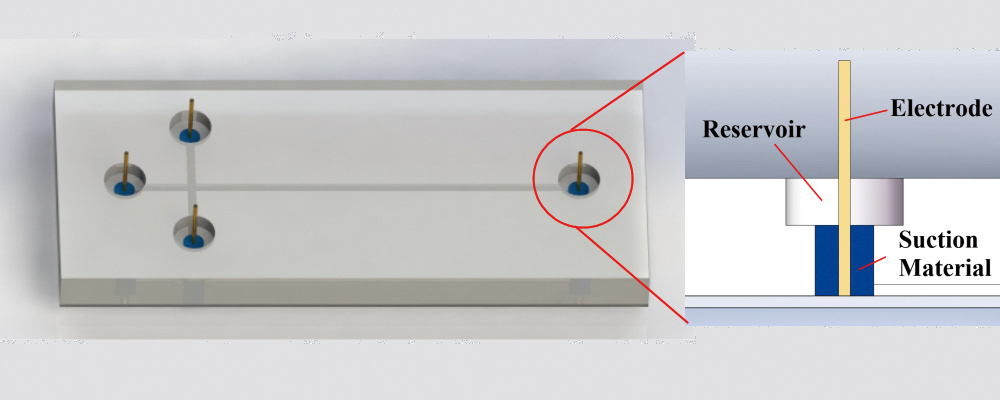 View full abstractDownload PDF (1544K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1544K) -
Feifei YANG, Huaizhong GUO, Lisha ZHANG, Jing SHI, Mengmeng SHEN, Dong ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1291-1296
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPartial degradation products (PDPs) of herbal medicine (HM) polysaccharides with precolumn derivatization using 1-phenyl-3-methy-5-pyrazolone (PMP) were mapped by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and three groups of confusable HMs were differentiated using the PDP fingerprints assisted with cluster analysis (CA). Three variables of HPLC mobile phase, i.e. acetonitrile proportion, buffer concentration and pH value were optimized with PDP of β-cyclodextrin. Radix Glehniae and Radix Adenophorae; Radix Sophorae Tokinensis and Rhizoma Menispermi; Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae and Radix Cyathulae were successfully distinguished by the method, respectively. The results involving mass spectrometry analysis showed that these PDPs primarily included oligosaccharides and a few monosaccharides. The method can be used as an effective approach for the identification and quality control of HMs, and can also facilitate the in-depth study of biological activity and further development of HM polysaccharides to some extent.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (496K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (496K) -
Hao WANG, Xiaoming WU, Feiyan TAO, Shaoxiang YANG, Hongyu TIAN, Yonggu ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1297-1302
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: July 27, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new highly selective and visible colorimetric fluorescent probe (probe 1) was developed to detect hydrazine (N2H4) concentration in real water samples. As different concentrations of N2H4 were added, the color of the probe solution was graded gradually from colorless to pink, which could be observed by the naked eye under UV light at 365 nm. Our research indicates that probe 1 offers a certain practical significance for use as a visible detection agent to detect N2H4 efficiently by distinct color response. Furthermore, our work showed that probe 1 can be successfully applied to detect N2H4 concentrations in real water samples.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1347K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1347K) -
Apichaya ANEKSAMPANT, Atsushi TANAKA, Xuefei TU, Hisanori IWAI, Mitsuo ...Article type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1303-1308
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: August 03, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFertilization with a mixture of steelmaking slag and compost can affect the supply of dissolved iron used to restore seaweed beds, however, the mechanisms of iron elution from the fertilizer are not well understood. In the present study, the microorganism was isolated from Fe-fertilizer incubated in coastal seawater for 6 months, and was identified as Exiguobacterium oxidotolerans by 16S rDNA sequencing. The iron elutability of the bacteria was proved based on the increasing of dissolved iron by incubation with Fe2O3 (hematite) under a seawater-like condition. The value of ORP was changed by inoculated of the bacteria from ca. 0 to ca. –400 mV, which is anticipated concerning to reduction of Fe. The concentration of eluted iron was largely depended on those of organic acids produced by bacteria. From the results, it was proved that E. oxidotolerans is capable of Fe reductive eluting of iron from Fe2O3 into seawater. Anthraquinone-2,7-disulfonate (AQDS), which can play as an electron acceptor/donor between microbe and insoluble Fe2O3 particles, enhanced the effect of iron bio-leaching.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1440K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1440K) -
Kenta HAGIWARA, Yuya KOIKE, Mamoru AIZAWA, Toshihiro NAKAMURAArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1309-1315
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: August 03, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA rapid, simple technique combining disk solid-phase extraction and handheld X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry was developed for the on-site determination of As, Se, and Cr(VI) in drinking water. For the preconcentration of As, Se, and Cr(VI), a 50-mL aqueous sample was adjusted to pH 4, followed by passage through a Ti-loaded anion-exchange disk (Ti-AED). Both sides of the Ti-AED were coated with an adhesive cellophane tape prior to drying using a cordless hair iron, followed by a handheld XRF measurement. The Ti-AED adsorbed As(III), As(V), Se(IV), Se(VI), and Cr(VI) in water without requiring oxidation and reduction. The detection limits of As, Se, and Cr(VI) were all 1.0 μg L−1. Good recoveries were obtained by measuring certified reference materials, and spiking natural mineral water with As, Se, and Cr(VI). As the proposed method does not require a power supply or toxic reagents in any analytical step, it is suitable for the on-site determination of toxic elements in drinking water.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (467K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (467K) -
Kento SAKAI, Yuki KITAZUMI, Osamu SHIRAI, Kenji KANOArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1317-1322
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: August 10, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, nanostructured porous gold electrodes were prepared by the anodization of gold in the presence of oxalic acid or glucose as a reductant, and applied as scaffolds for direct electron transfer (DET)-type bioelectrocatalysis. Gold cations generated in the anodization seem to be reduced by the reductant to construct a porous gold structure. The DET-type performance of the electrode was examined using two DET-type model enzymes, bilirubin oxidase (BOD) and peroxidase (POD), for the four-electron reduction of dioxygen and the two-electron reduction of peroxide, respectively. BOD and POD on the anodized porous gold electrodes exhibited well-defined sigmoidal steady-state waves corresponding to DET-type bioelectrocatalysis. Scanning electron microscopy images revealed sponge-like pores on the electrodes. The anodized porous gold electrodes demonstrate promise as scaffolds for DET-type bioelectrocatalysis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1194K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1194K) -
Yang XIE, Hui YOU, Zhiyuan GAO, Zhe HUANG, Mingpeng YANGArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1323-1327
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: August 10, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWith the development of microfluidic systems for portable devices where the capillary force as the driving force drove the liquid in a microchannel. An effective capillary microvalve based on a micro-hole array is proposed in this paper for the purpose of good performance, and programmable control, and easy-to-fabricate. The Wenzel model was used to slow down the velocity of fluid flow. The microvalve was made by a hot-embossing and hot-bonding process. The valve function was assessed by liquid flowing experiments. The results showed that the valve employs an abruptly changing contact angle to slow down the fluid flow. The controlling time is approximately 177 – 213 s. The best control effect was obtained when the contact angle equaled to 90°. The effect of the roughness of the microvalve was also evaluated. Therefore, this work has a great potential and broad prospect for both research and applications in microfluidic systems, such as the portable devices in the medical testing field.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4815K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4815K) -
Tomohiro NARUKAWA, Takahiro IWAI, Koichi CHIBA, Joerg FELDMANNArticle type: Original Papers
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1329-1334
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: August 17, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new determination method was developed for the measurement of methylmercury (Me-Hg) and inorganic mercury (i-Hg) in biological samples using high-performance liquid chromatography–inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS) following alkaline extraction. Mercury species in biological samples were extracted with 10% (w/w) tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) solution at 80°C for 2 h. Methylmercury was completely separated from i-Hg by adamantyl type and octadecylsilyl type columns within 6 and 4 min using isocratic elution, respectively. The detection limits (3σ) of adamantyl and octadecylsilyl columns using the proposed system were 0.08 and 0.13 ng g−1 (as Hg), respectively. Inorganic Hg completely separates from Me-Hg without tailing. The proposed determination methods were applied to several biological certified reference materials (CRMs). The measurement results of Me-Hg obtained by the present method were in good agreement within the expanded uncertainties (k = 2) with the certified values. The analytical precision (n = 3) of Me-Hg was less than 2%, and the recoveries of Me-Hg and i-Hg were 101 ± 1 and 103 ± 3%, respectively. In addition, this method enables the determination of Me-Hg and i-Hg for 20 samples in 1 h.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (209K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (209K)
-
Xing-Zheng WU, Luowei HUANGArticle type: Notes
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1335-1337
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
Advance online publication: July 20, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAlthough the newly developed beam deflection/fluorescence detection system for real-time in situ simultaneous monitoring of dissolved oxygen (DO) and material movements in the vicinity of aquatic plants was not only much more sensitive but also could be carried out much more closely to real time than conventional analytical methods that monitor the concentration changes at a bulk solution, it could not be applied to the photosynthesis process of aquatic plants. Here, improvements are reported to enable application of the system to the photosynthesis process. A white-light LED, which was used as a light source for photosynthesis in our previous paper, was replaced by a red-blue LED with wavelength of about 660 and 450 nm. Also, an interference filter of 589 ± 25 nm was placed in front of a photomultiplier tube (PMT). Furthermore, the LED and its electric power supply were placed outside of the dark room for preventing great temperature increases in the photosynthetic experiments. Experimental results showed the DO-quenched fluorescence could be sensitively monitored in both the respiration and photosynthesis processes, while only in the respiration process before the improvements. It is successfully demonstrated that the DO change and material movement-induced beam deflection in the vicinity of the plants in both the respiration and photosynthesis processes could be real-time in situ monitored with high sensitivity.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (827K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (827K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2018 Volume 34 Issue 11 Pages 1339
Published: November 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1096K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
