All issues

Volume 30, Issue 5
Displaying 1-15 of 15 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Special Reviews
-
Munetaka OYAMA, Xiaomei CHEN, Xi CHENArticle type: Special Reviews
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 529-538
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWhile increasing attention has been devoted to the use of carbon-based nanomaterials or metal nanoparticles (MNPs) as electrode modifiers for electroanalysis, there is a noticeable development in studies using MNP-graphene nanocomposites or nanohybrids in very recent years. In this review, first, very recent nanoarchitectures in MNP-graphene nanocomposites for modifying electrodes (mainly in 2013) are summarized together with the targets and achievements of electroanalysis. The variety of nanoarchitectures comes from the fact that graphene oxide and metal precursor ions can be reduced chemically or electrochemically, and concurrently or stepwisely. By browsing various preparation methods of the modified electrodes, some characteristic and interesting features of the preparations of MNP-graphene nanocomposites are described together with the possibilities and prospects as electrode modifiers for electroanalysis. View full abstractDownload PDF (5007K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5007K) -
Mitsuru HATTORI, Takeaki OZAWAArticle type: Special Reviews
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 539-544
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSBioluminescent proteins such as luciferases are unique analytical tools with high sensitivity and wide dynamic ranges. However, applicability of the proteins has remained limited to reporter gene analysis. Split luciferase complementation technique is a new powerful strategy to detect protein–protein interactions and their related intracellular signaling in living cells. This review presents a summary of recent topics for the analysis of biological events using split luciferase complementation techniques. Different applications such as G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) screening, monitoring phosphorylations, protein–protein interactions, and pH differences in living tissues are described. View full abstractDownload PDF (8182K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (8182K)
Original Papers
-
Tomokazu KURABAYASHI, Nayuta FUNAKI, Takeshi FUKUDA, Shinnosuke AKIYAM ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 545-550
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDual pH-dependent fluorescence peaks from a semiconductor quantum dot (QD) and a pH-dependent fluorescent dye can be measured by irradiating with a single wavelength light, and the pH can be estimated from the ratio of the fluorescent intensity of the two peaks. In this work, ratiometric pH sensing was achieved in an aqueous environment by a fluorescent CdSe/ZnS QD appended with a pH-sensitive organic dye, based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). By functionalizing the CdSe/ZnS QD with 5-(and 6)-carboxynaphthofluorescein succinimidyl ester as a pH-dependent fluorescent dye, we succeeded in fabricating sensitive nanocomplexes with a linear response to a broad range of physiological pH levels (7.5 – 9.5) when excited at 450 nm. We found that a purification process is important for increasing the high-fluorescence intensity ratio of a ratiometric fluorescence pH-sensor, and the fluorescence intensity ratio was improved up to 1.0 at pH 8.0 after the purification process to remove unreacted CdSe/ZnS QDs even though the fluorescence of the dye could not be observed without the purification process. The fluorescence intensity ratio corresponds to the fluorescence intensity of the dye, and this fluorescent dye exhibited pH-dependent fluorescence intensity changes. These facts indicate that the fluorescence intensity ratio linearly increased with increasing pH value of the buffer solution containing the QD and the dye. The FRET efficiencies changed from 0.3 (pH 7.5) to 6.2 (pH 9.5). View full abstractDownload PDF (2302K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2302K) -
Yoshinari SUZUKI, Ayumi NOBUSAWA, Naoki FURUTAArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 551-559
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe sulfur (S) concentrations of three peptides were determined by using nano HPLC-ICPMS under a flow of O2 in an octapole reaction cell, and the determined values showed a good agreement with theoretical values. This method was then applied to trypsin-digested peptides from human albumin for protein quantification. Assigning of the number of S atoms in each peptide/peak and the tryptic digestion efficiency were important for protein quantification. The number of S atoms in each peptide/peak was assigned by using verification scores that gave the lowest standard deviation of the peptide S concentration and the highest S recovery. The peptide concentrations were calculated as the ratio of the S concentration/the number of S atoms in the peptide/peak. The tryptic digestion efficiency was calculated as the sum of the S concentration in the mono-peptides divided by the total S concentration in a native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) band before tryptic digestion. Our result indicates that a protein can be quantified through peptide quantification, after taking into account the tryptic digestion efficiency, via S quantification using ICPMS. View full abstractDownload PDF (1114K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1114K) -
Yingya KAN, Cheng JIANG, Qiang XI, Xiangyu WANG, Lei PENG, Jianhui JIA ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 561-568
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe screening of potential drugs specifically binding to polydeoxyadenosine (poly(dA)) has been of great interest in recent studies. We have developed a simple colorimetric strategy through the mechanism of target induced split G-quadruplex formation for detecting coralyne, a poly(dA)-binding drug with noticeable antitumor activity. Two DNA oligonucleotides containing a split G-quadruplex sequence and an adenine-rich sequence are used in our strategy. In the presence of coralyne, the adenine-rich sequences of two oligonucleotides are drawn into close proximity, resulting in the formation of a split G-quadruplex DNAzyme that catalyzes the generation of a colored product. The DNAzyme-based colorimetric assay for coralyne has a linear range of from 0.033 to 1.667 μM with a low detection limit of 16 nM. The developed method is simple, cost-effective and visible; it holds great potential for applications in drug screening.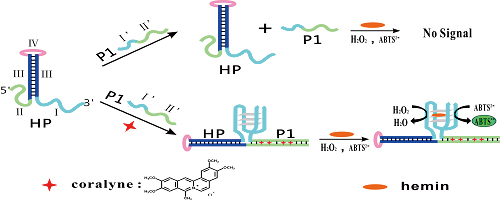 View full abstractDownload PDF (3988K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3988K) -
Shunsuke FURUTANI, Nahoko NARUISHI, Masato SAITO, Eiichi TAMIYA, Yusuk ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 569-574
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialOn-site detection by flow-through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) microfluidic systems for rapid and highly sensitive analysis, are significantly desired for bioanalytical and medical research. The conventional continuous-flow PCR chips realized rapid detection, but their sensitivity was very low (106 to 108 copies μL−1). We improved this drawback by coating the chip with a PCR reagents mixture, and succeed to obtain a rapid and highly sensitive detection by using a segment-flow PCR system. In the present work, we developed a portable segment-flow PCR system for practical use. PCR was performed for the uid A gene in E. coli. By real-time segment-flow PCR using coated chips, we realized rapid detection in 8 min and a high sensitivity of 4 cells μL−1. The sensitivity by the segment-flow PCR chip was the same as that of a conventional thermal cycler. Moreover, the detection speed of our segment-flow PCR chip was 15-times as rapid as that of the conventional thermal cycler. View full abstractDownload PDF (906K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (906K) -
Daisuke YAMASHITA, Atsushi ISHIZAKI, Tomoyuki YAMAMOTOArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 575-579
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe investigated the desorption of water from a TiO2 surface under a dry atmosphere by collecting the photoemission yield spectra with an open counter. For this purpose, a new attachment for the photoemission yield measurement was prepared. This apparatus is capable of detecting, in the open air, low-energy electrons excited by photons under dried atmospheres; the dew point is below −35°C. A significant change in the photoemission yield spectra due to exposure to a dry atmosphere was observed. To gain a better understanding of these results, observations of the change in the photoemission yield spectra caused by the thermal desorption of adsorbed water were also carried out. The results are consistent with those obtained by exposure to a dry atmosphere. Based on the relationship between the photoemission yield and the thickness of the water layer, the time dependence of the change in the thickness was explained by the second-order reaction rate equation.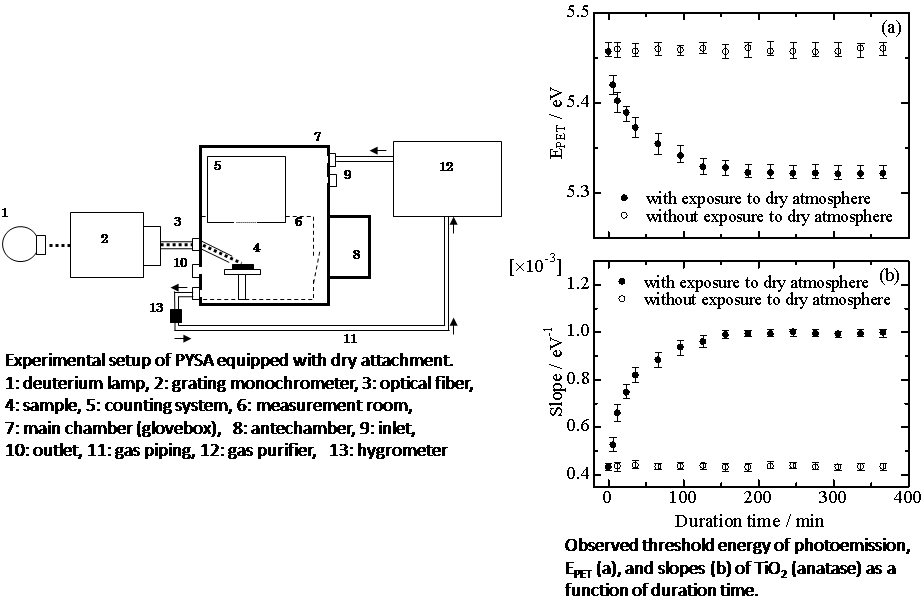 View full abstractDownload PDF (673K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (673K) -
Minh-Phuong N. BUI, Seong S. SEOArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 581-587
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe have developed an optical chemical sensor for the detection of organophosphate (OP) compounds using a polymerized crystalline colloidal array (PCCA) thin film composed of a close-packed colloidal array of polystyrene particles. The PCCA thin film was modified with β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) polymer as a capping cavity for the selective detection of paraoxon-ethyl and parathion-ethyl chemical agents. The fabrication of the modified PCCA thin film was optimized and the structure was characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The arrangement of polystyrene particles in the PCCA follows a pattern of the fcc (111) planes with strong diffraction peak in the visible spectral region and pH dependence. The diffraction peak of the β-CD modified PCCA thin film showed a red shift according to the change of paraoxon-ethyl and parathion-ethyl concentrations at a fast response time (10 s) and high sensitivity with detection limits of 2.0 and 3.4 ppb, respectively. Furthermore, the proposed interaction mechanism of β-CD with paraoxon-ethyl and parathion-ethyl in the β-CD modified PCCA thin film were discussed. View full abstractDownload PDF (2396K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2396K) -
Caiyun LIU, Huifang WU, Wen YANG, Xiaoling ZHANGArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 589-593
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple 4-hydroxynaphthalimide-derived colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probe (1) containing a receptor of levulinate moiety was designed and synthesized to monitor sulfite. Probe 1 could quantificationally detect sulfite by a ratiometric fluorescence spectroscopy method with high selectivity and sensitivity. Specially, probe 1 exhibited a 100 nm red-shifted absorption spectrum along with the color changes from colorless to yellow, and 103 nm red-shifted emission spectra upon the addition of sulfite. Thus, 1 can serve as a “naked-eye” probe for sulfite. Further, the recognition mechanism of probe 1 for sulfite was confirmed using nuclear magnetic resonance and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Also, the preliminary practical application demonstrated that our proposed probe provided a promising method for the determination of sulfite.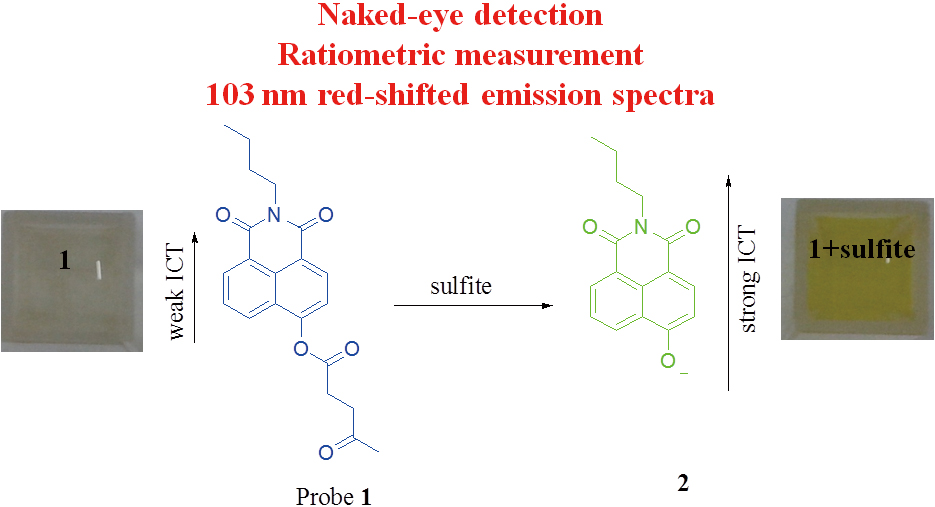 View full abstractDownload PDF (821K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (821K) -
Riho WATANABE, Yui TERAUCHI, Makoto SAKAUE, Teruo HINOUEArticle type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 595-599
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWhen laser light impinges upon a liquid–liquid interface between an optically transparent aqueous and opaque organic phase from the aqueous to organic phase, the temperature at the interface and the interfacial region rises. Using this rise in temperature, we have proposed and developed thermal modulation voltammetry at an interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions (TMV-ITIES) and have determined the standard entropy changes of ion transfer, ΔStr°,O→W. In this work, we have determined ΔStr°,O→W for four 1-alkylpridinium ions, namely 1-methylpyridinium ion (MePy+), 1-ethylpyridinium ion (EtPy+), 1-propylpyridinium ion (PrPy+), and 1-buthylpyridinium ion (BuPy+) by TMV-ITIES. As a result, we obtained the ΔStr°,O→W values of 108.0 ± 0.5 (n = 3), 75.8 ± 4.4, 55.6 ± 1.2, and 42.7 ± 0.9 J K−1 mol−1 for MePy+, EtPy+, PrPy+, and BuPy+, respectively. From these values of ΔStr°,O→W, we have suggested that MePy+, EtPy+, and PrPy+ are classified as water structure-breaking ions and BuPy+ as a weak water structure-making ion. Further, we discuss the relationship between the standard free energy change, ΔGtr°,O→W, and ΔStr°,O→W of ion transfer for 1-alkylpridinium ions and tetraalkylammonium ions. View full abstractDownload PDF (533K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (533K) -
Prabhjot KAUR, Priyanka NARULA, Varinder KAUR, Raghubir SINGH, Sushil ...Article type: Original Papers
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 601-607
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new molecularly imprinted mesoporous material (MIM) containing specific pockets for the extraction of diethyl phthalate (DEP) as copper complex has been prepared for the first time. The mesoporous material was developed by utilizing copper-phthalate complex (Cu-DEP) as the template molecule, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APS) as a functional monomer and tetraethoxyorthosilicate (TEOS) as the silica source for polymer network formation. The mesoporous material showed fast uptake kinetics, and equilibrium was obtained within 30 min due to the introduction of copper, which provides an additional site for interaction with the functional monomer. Synthesized polymer was well characterized using UV-Vis spectrophotometry, IR spectroscopy, TGA studies, and TEM. To achieve efficient extraction of the template molecule, various factors including sorption kinetics, quantity of MIM, time required for equilibrium set-up, sorption isotherm and reuse of MIM were optimized. The extracted DEP samples were analyzed quantitatively at 310 nm using an HPLC-DA system. The prepared material is robust and can be reused. In addition, it was found to be selective for DEP as compared to other phthalates. View full abstractDownload PDF (4972K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4972K)
Notes
-
Suppression of the Incoherent Molecular Formation Effect by Oxygen Gas in Arsenic Analysis by ICP-MSTomohiro NARUKAWA, Koichi CHIBAArticle type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 609-612
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe Incoherent Molecular Formation (IMF) effect, which involves the molecular formation of arsenic (As) atoms depends, on its oxidation state in the inductively coupled plasma. This leads to determination errors, when As is measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The sensitivity of As(V) is 4 – 7% higher than that of As(III) at m/z 75, since the final ionization rates of As(V) and As(III) are different from each other due to the IMF effect. A precise measurement of As by ICP-MS is generally very difficult. Recently, the collision/reaction cell is widely used for ICP-MS to eliminate spectral interferences caused by polyatomic molecules. Especially, oxygen gas (O2) is one of the most useful reaction cell gases for As analysis, because As+ is oxygenated into AsO+, which is free from the such interferences as ArCl+. In addition, the use of O2 as a reaction gas is extremely effective for reducing the IMF effect and eliminating the sensitivity difference between As(III) and As(V). View full abstractDownload PDF (445K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (445K) -
Carlos MUÑOZ, M. Inés TORAL, Inés AHUMADA, Pablo ...Article type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 613-617
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study demonstrates the first use of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) immobilized on a rotating disk for the extraction of copper from aqueous matrices and its subsequent direct determination by solid phase UV-Visible spectrophotometry. To accomplish the solid-phase extraction and the direct solvent-free spectrophotometric measurement, sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (NaDDTC) was used as an analytical reagent to form the uncharged chromophore complex Cu(DDTC)2, which absorbs at 432 nm. Different physicochemical conditions (pH, temperature, reagent concentration, chemical modifiers) and hydrodynamic factors (rotation velocity, extraction time, sample volume) were optimized. Under the optimized conditions, extraction equilibrium times of 30, 53 and 90 min were obtained for 100, 500 and 1000 mL of sample, respectively, with preconcentration factors of 286, 712 and 1284, respectively. The methodology was precise (repeatability and reproducibility of 7.2 and 8.4%, respectively, as relative standard deviation) and accurate (recovery of 96.7%) when analyzing a multielement certified reference standard. The latter study also confirmed the high selectivity of the extraction and determination of the copper chromophore over other metal ions. The obtained limits of detection and quantification reached values lower than 12 μg L−1, which can be reduced further by increasing the sample volume. Accuracy was also assessed using both recovery tests on drinking water matrices (95.5% recovery) and comparison with results obtained by an independent method using inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES); no significant differences were observed. View full abstractDownload PDF (2420K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2420K) -
Kento SHIMAOKA, Shota KUWAHARA, Makoto YAMASHITA, Kenji KATAYAMAArticle type: Notes
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 619-621
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialPhotocatalytic organic reactions were performed using automatic photocatalytic microreactor, where several open-end capillaries with photocatalytic materials coated inside were just soaked in a test tube including a reactant solution. Organic reactions of the alkyl radicals generated from carboxylic acids due to the photo-Kolbe reaction was studied, in analogy with the reactions using a photosensitizer. This methodology features the reusability of the reactor and an easy process for analysis due to easy separation of the reactant solution. View full abstractDownload PDF (514K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (514K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014Volume 30Issue 5 Pages 623
Published: May 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2523K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|