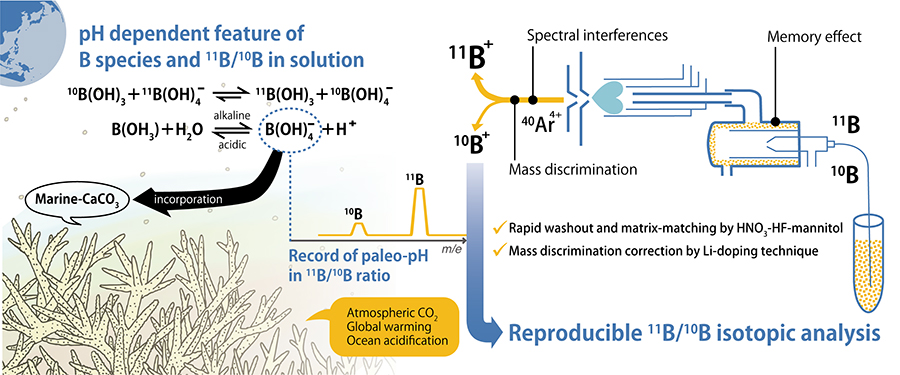
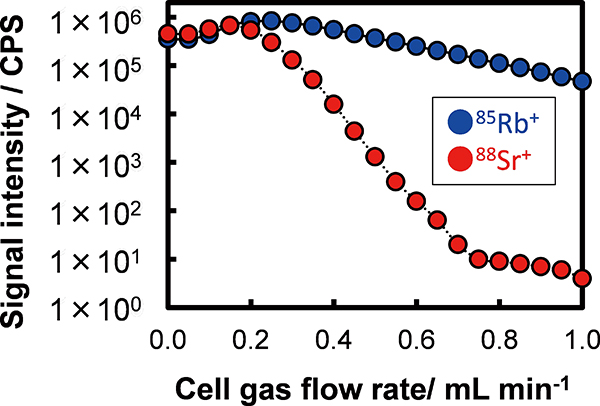
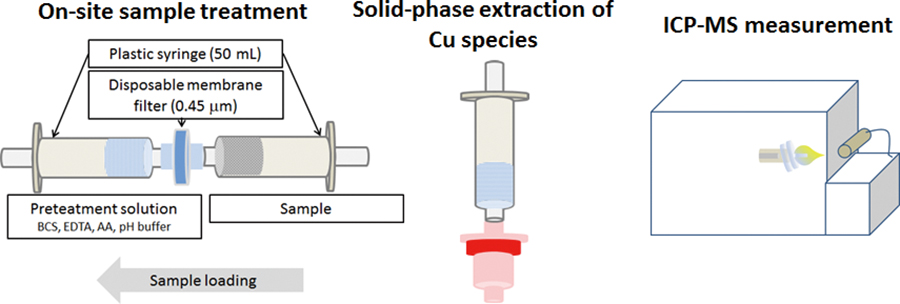
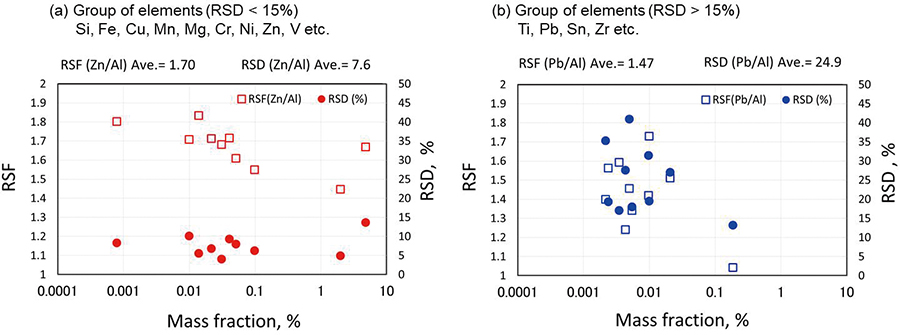
Volume 34, Issue 6
Displaying 1-19 of 19 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 637-638
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (527K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 639-641
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (672K)
Guest Editorial
-
Article type: Guest Editorial
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 643
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (22K)
Reviews
-
Stable Isotope Composition of Metal Elements in Biological Samples as Tracers for Element MetabolismArticle type: Reviews
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 645-655
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (2003K) -
Article type: Reviews
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 657-666
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (2980K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 667-674
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (810K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 675-679
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (1741K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 681-685
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (183K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 687-691
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (66K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 693-699
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (428K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 701-710
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (214K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 711-717
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (2989K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 719-724
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (253K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 725-728
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (178K) -
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 729-733
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (468K) -
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 735-738
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (195K) -
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 739-742
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (1076K) -
Article type: Notes
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 743-746
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (240K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2018Volume 34Issue 6 Pages 747
Published: June 10, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2018
Download PDF (1059K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|