All issues

Volume 31, Issue 2
Displaying 1-12 of 12 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Papers
-
Shigetomo MATSUYAMA, Yukari ORIHARA, Shinichi KINUGASA, Hajime OHTANIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 61-65
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDependence of the response of a corona-charged aerosol detector (corona CAD) on the concentration and densities of brominated flame retardants and some related substrates was studied. The calibration curves of the substrates did not show linearity and the substrate with a lower density exhibited the stronger response. Regardless of the solvents (chloroform or toluene), and the injected volume of the substrate solution, the signal intensity of the substrate observed by a corona CAD was substantially proportional to 2/3 power law of concentration and proportional to (−2/3) power law of the density of the substrates. These results suggest that the responses should be proportional to the surface area of the particles generated through the drying process in corona CAD. Contrary to the former reports that the detector response of a corona CAD was independent of chemical species, it was proved that the response varies with the density of a substrate. View full abstractDownload PDF (503K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (503K) -
Yo TANAKA, Yoshihiro SHIMIZUArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 67-71
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRecently, a cell-free protein synthesis system reconstituted solely from essential elements of the Escherichia coli translation system, termed protein synthesis using recombinant elements (PURE), has been widely used in synthetic biology to analyze fundamental life systems. Here, the system was integrated on a glass microchip system to construct a simple protein synthesis system. GFP template DNAs were immobilized on Sepharose microbeads by streptavidin–biotin binding. The beads were introduced into a Y-shaped microchannel in a glass microchip with a 10-μm height dam structure, and a PURE system reaction mixture was flowed through the microchannel. The recovered solutions had a higher fluorescent intensity than that of the reaction mixture before its introduction into the microchannel, thus verifying that GFP synthesis had been achieved. The microchip with DNA immobilized microbeads is reusable. This is advantageous over a conventional in vitro protein synthesis protocol requiring the preparation and addition of template DNA or mRNA into the reaction mixtures in aspect of simpleness and rapidness.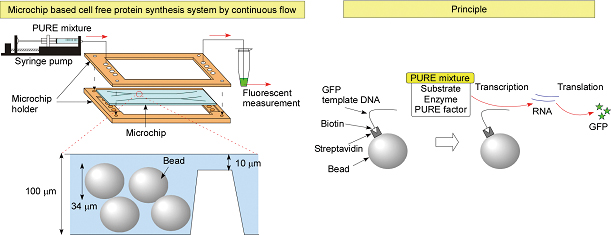 View full abstractDownload PDF (1216K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1216K) -
Yulin ZHANG, Rongmei CHEN, Lu XU, Yong NING, Shenggao XIE, Guo-Jun ZHA ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 73-78
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSilicon nanowire (SiNW) field-effect transistor (FET) biosensors have already been used as powerful sensors for the direct detection of disease-related biomarkers. However, the multiplexed detection of biomarkers in real samples is still challenging. Interleukin 8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) are two typical biomarkers of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). In this study, we developed a multiplexed detection methodology for IL-8 and TNF-α detection in saliva using SiNW FET biosensors. We fabricated the SiNW FET sensors using a top-down lithography fabrication technique. Subsequently, we achieved the multiplexed detection of two biomarkers in saliva by specific recognition of the two biomarkers with their corresponding antibodies, which were modified on the SiNW. The established method was found to have a limit of detection as low as 10 fg/mL in 1 × PBS as well as 100 fg/mL in artificial saliva. Because of its advantages, including label-free and multiplexed detection, non-invasive analysis, highly sensitive and specific determination, the proposed method is expected to be widely used for the early diagnosis of OSCC.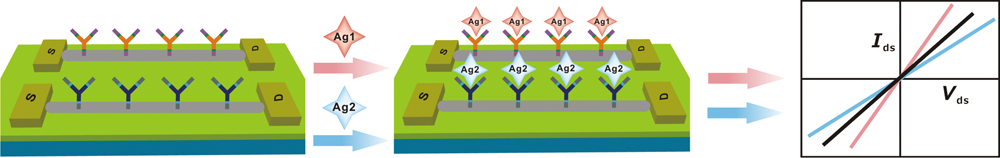 View full abstractDownload PDF (989K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (989K) -
Siti BAIDURAH, Yasuko KUBO, Mitsuhiro KUNO, Kazuho KODERA, Yasuyuki IS ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 79-83
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThermally assisted hydrolysis and methylation–gas chromatography (THM-GC) in the presence of an organic alkali was applied to the direct analysis of copolymer composition for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) [P(3HB-co-3HV)] accumulated in whole bacterial cells. Cupriavidus necator was grown on a liquid medium with different molar ratios of valeric acid (V) to glucose (G) in order to control the compositions of P(3HB-co-3HV) produced in the cells. Trace amounts (0.03 mg) of dried Cupriavidus necator cells were directly subjected to THM-GC in the presence of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) at 400°C. The obtained chromatograms clearly showed nine characteristic peaks, attributed to the THM products from 3HB and 3HV units in the polymer chains, without any appreciable interference by the bacterial matrix components. Based on these peak intensities, the copolymer compositions were determined rapidly without using any cumbersome sample pretreatment. Moreover, the compositions thus obtained were in good agreement with those obtained by the conventional technique. View full abstractDownload PDF (722K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (722K) -
Hajime KATANO, Nobuhiro OKAMOTO, Masahiro TAKAKUWA, Shu TAIRA, Taiho K ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 85-89
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple method to separate soyasaponin Bb from a soy extract is presented. This method is based on the difference in the solubility of soyasaponin Bb and Ba and other components into 3:7 and 1:1 (v/v) acetone–water mixed solvents. The crude soyasaponin consisting of soyasaponins Aa, Ab, Ba, and Bb at the 10 wt% level and other components was examined as the soy extract. A 10 mg quantity of the crude soyasaponin was mixed with 1 mL of the 3:7 acetone–water containing 0.1 mol/L HCl, and the supernatant was removed to obtain a precipitate, which was found to contain mainly soyasaponins Bb and Ba. The precipitate was mixed with 0.4 mL of the 1:1 acetone–water containing 0.1 mol/L HCl; the supernatant was transferred, and was mixed with 0.6 mL of water to obtain a precipitate, which was found to contain mainly soyasaponin Bb. The yield was ca. 30%, which may be much higher than that by the conventional preparative chromatographic approach. The separation method is rapid and easy to carry out, and is useful for the preparation of a soyasaponin Bb sample. View full abstractDownload PDF (606K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (606K) -
Hiroshi SAKAMAKI, Takeharu UCHIDA, Lee Wah LIM, Toyohide TAKEUCHIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 91-97
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSColumns made of three different materials were evaluated with regard to the carryover of phosphorylated peptides and fumonisins in liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). In order to eliminate carryover caused by the injection operation in the autosampler, the column carryover was calculated using the duplicated solvent gradient method. A column made of a glass-lined stainless-steel tube and polyethylene frits (GL-PE column) yielded the most significant improvements in the peak shape and the carryover as compared to the other columns. The carryover of fumonisin B1 (FB1) and HLADLSpK (T19p) in the GL-PE column could be reduced; the lower limit of quantitation of T19p, and the range of the calibration curve were also improved. Since carryover peaks with the GL-PE column were symmetrical peaks of the samples, carryover in the column did not occur. The carryover calculated by the duplicated solvent gradient method corresponded to those in the flow path from the injection port to the inlet frit of the column. The carryover value of FB1 in the column with a stainless-steel tube and stainless-steel frits (S-S column) was 1.70%, and that of the flow path was 0.23%. We found that the majority of the carryover in our system occurred in the S-S column. View full abstractDownload PDF (686K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (686K) -
Ikuo UETA, Suguru MOCHIZUKI, Susumu KAWAKUBO, Tetsuo KUWABARA, Yoshihi ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 99-103
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel analytical method for determining formaldehyde (FA) in aqueous samples was developed with a miniaturized extraction capillary in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The extraction capillary was prepared by packing silica gel particles in a stainless steel capillary of 0.8 mm i.d. and 1.6 mm o.d. A derivatization reagent of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) was impregnated on the silica gel particles by pumping a solution of DNPH to the capillary. Two extraction methods; dynamic extraction and purge-and-trap (PT) methods, were investigated for derivatizing and extracting FA from water samples onto the silica gel in the extraction capillary. The extraction capillary was directly connected to a six-port valve, and then desorption of the derivative from the capillary and injection to conventional HPLC system were simultaneously achieved with a flow of acetonitrile through the capillary. In the dynamic extraction, FA was determined with a simple sample preparation procedure, and the limit of detection (LOD) was 18 μg L−1 at a sample volume of 20 mL, while several limitations were found in the method, such as bleeding of the derivatization reagent and the corresponding derivatized FA from the capillary during the sample load/extraction process. The sensitivity was significantly improved by introducing a PT technique, where the LOD was 6.9 μg L−1 at a sample volume of 20 mL with a sampling time of approximately 20 min. With the PT method, successful recoveries of FA were confirmed for spiked tap water, river water and fruit juice samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (465K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (465K) -
Masaki OHATA, Satoru KUROSAWA, Isao SHINODUKA, Yuichi TAKAKU, Yoko KIS ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 105-111
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSpectroscopic characteristics of a spiral flow inductively coupled plasma (ICP), which could be sustained stably at 9 L min−1 of Ar plasma gas flow rate with 1.5 kW RF forward power, were studied for axially viewing ICPOES. The emission intensity profile, excitation temperature and plasma robustness were evaluated, and were similar to those of the standard ICP. The background and emission intensities of elements as well as the excitation behavior for both atom and ion lines were also examined and compared to those of the standard ICP. Since the spectroscopic characteristics of the spiral flow ICP were similar to those of the standard ICP, it could be used as a new low gas flow ICP in axially viewing ICPOES. View full abstractDownload PDF (1224K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1224K) -
Guoyan LIU, Huipeng REN, Yuyu GUAN, Ronghua DAI, Chunyan CHAIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 113-118
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA fast and simple mercury detection kit was developed based on melamine-functionalized gold nanoparticles (GNPs). The detection kit contained reagent 1 (GNPs), reagent 2 (melanine), a reaction cuvette with four separated cells, a colorimetric card and a plastic pipette. The GNPs were prepared by a citrate reduction of HAuCl4. A proper amount of melamine was applied to functionalize the GNPs. The complex reaction took place in the present of Hg2+ in the test samples, leading to the combination of Hg2+ with the C=N group of melamine located on the surface of the GNPs. This reaction resulted in damage to the stability of colloid gold, and the aggregation of GNPs occurred. Different color changes (from claret-red to lilac, purple and plum) were displayed with different concentrations of Hg2+ in the test samples. It was very easy and convenient to determine the amount of mercury ion by the naked eye. The advantages of this methodology are listed as follows: a short detecting time (within 10 min), a high specificity (no significant interference was indicated upon adding a certain amount of Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Mg2+, Cd2+ and Fe2+), high sensitivity with a detection limit of 0.01 mg L−1 , easy operation and practical on-site use.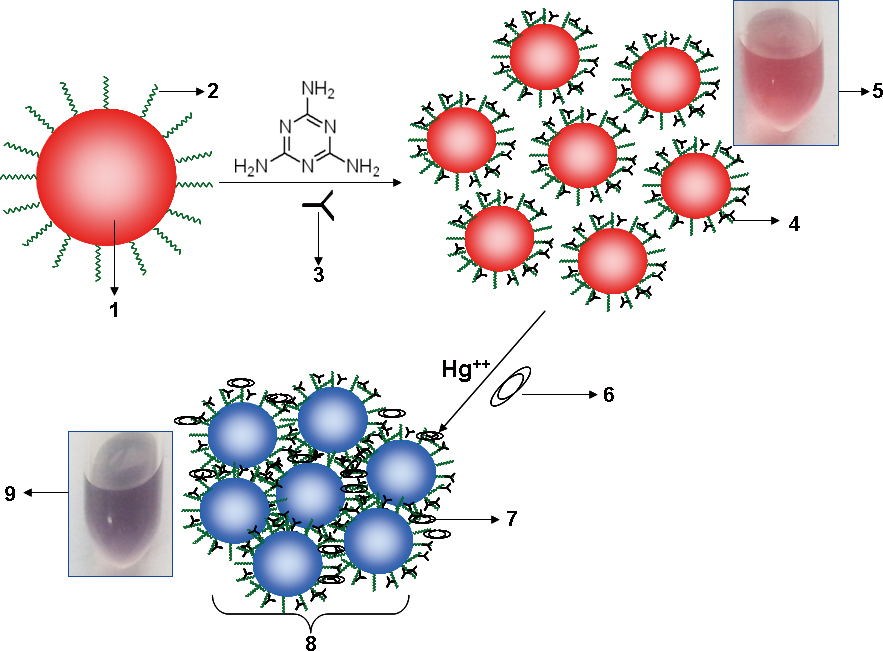 View full abstractDownload PDF (1052K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1052K) -
Elham RAGHEB, Payman HASHEMI, Kamal ALIZADEH, Mohammad Reza GANJALIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 119-124
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method based on solidification of floating organic drop (DLLME-SFO) was developed for the preconcentration of ultratrace amounts of palladium (Pd)(II) before its determination by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Diphenyl ether (m.p. 26°C) was used for the first time as a heavier than water organic solvent in the developed method. Pd was complexed by N,N′-bis(thiophen-2-ylmethylene)ethane-1,2-diamine to be extracted into the dispersed diphenyl ether phase using acetonitril as the disperser solvent. Upon cooling and centrifugation, the organic solvent was sedimented at the bottomn and the aqueous phase was easily decantated. Some factors influencing the extraction efficiency of Pd(II) and its subsequent determination, including extraction and dispersive solvent type and volume, pH of sample solution, concentration of the chelating agent and salting out effect, were studied and optimized both with univariate and multivariate methods. Under the optimized conditions, the calibration graph exhibited linearity over a range of 10 – 120 μg L−1. The enrichment factor was 83.3, the detection limit for Pd (3σ) was 47 ng L−1 and the relative standard deviation was 3.2% (n = 10, 1 ng mL−1). The method was successfully applied to the determination of trace amounts of Pd(II) in water samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (837K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (837K) -
Alexander TÖRPE, Daniel J. BELTONArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 125-130
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFullerenes are among a number of recently discovered carbon allotropes that exhibit unique and versatile properties. The analysis of these materials is of great importance and interest. We present previously unreported spectroscopic data for C60 and C70 fullerenes in high-solubility solvents, including error bounds, so as to allow reliable colorimetric analysis of these materials. The Beer–Lambert–Bouguer law is found to be valid at all wavelengths. The measured data were highly reproducible, and yielded high-precision molar absorbance coefficients for C60 and C70 in o-xylene and o-dichlorobenzene, which both exhibit a high solubility for these fullerenes, and offer the prospect of improved extraction efficiency. A photometric method for a C60/C70 mixture analysis was validated with standard mixtures, and subsequently improved for real samples by correcting for light scattering, using a power-law fit. The method was successfully applied to the analysis of C60/C70 mixtures extracted from fullerene soot. View full abstractDownload PDF (603K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (603K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2015 Volume 31 Issue 2 Pages 131
Published: February 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2619K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|