
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hotaka KAIArticle type: Highlights
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 551-552
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Pawanpreet KAUR, Raghubir SINGH, Varinder KAUR, Dinesh TALWARArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 553-560
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: September 18, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe exploration of an anthranilic acid based Schiff base SB as a “Turn-ON” fluorescent probe for the detection of highly toxic selenite (SeIV) and arsenite (AsIII) species in an aqueous medium is described. The selectivity of SB towards SeIV and AsIII in the presence of other ions was investigated by some spectrofluorimetric and 1H NMR spectroscopic experiments. The studies revealed the interaction between SB and AsIII via the deprotonation of phenolic –OH, which enhanced the conjugation in phenolate ion and in turn enhanced the emission response. The SB has analytical prospects for the quantification of AsIII and SeIV with good sensitivity (LODs; 5.15 ppb for SeIV and 3.12 ppb for AsIII calculated by S/N = 3σ/K). Furthermore, it can be used to evaluate real and synthetic samples for the presence of SeIV and AsIII species as well as the fabrication of on-spot recognition devices (in the form of silica gels SB@SiO2 and silica coated TLC aluminium strips SB@SiO2@Al).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5108K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5108K) -
Tansu GÖLCEZ, Volkan KILIÇ, MUSTAFA SENArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 561-567
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 02, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, a microfluidic paper-based analytical device (μPAD) was integrated with a smartphone app capable of offline (without internet access) image processing and analysis for the rapid colorimetric detection of glucose. A self-inking stamp was used to form hydrophobic channels on a piece of paper-towel due to its superior water absorption efficiency. As demonstrated, the developed sensor was employed for the colorimetric detection of glucose in artificial saliva in the linear scope of 0 – 1 mM with a calculated detection limit of 29.65 μM. The experimental results show that the quantitative analysis of glucose with the proposed smartphone platform could be completed in less than one minute. The app developed for the smartphone platform is capable of extracting the color-changing area with an embedded image processing tool which could address the problem of color uniformity in the detection zones of μPAD. The integrated platform has great potential to be used for non-invasive measurements of glucose in body fluids, like tears, sweat and saliva.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (602K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (602K) -
Dingwen ZHONG, Ran GAO, Hai HUANG, Dayong FAN, Jiefeng HAI, Zhenhuan L ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 569-573
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 02, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe chemical-industrial production of organic semiconductors urgently needs a cheap and fast approach to determine the components’ proportion of the reaction system. In the present work, the Gaussian peak fitting method was applied to process monobromo and dibromo-substituted perylene diimide mixed solutions’ ultraviolet-visible absorption curves. The functional relationship formula between the peak-intensity ratio and the component ratio is then concluded. Finally, field experiments of the perylene imide brominating reaction can be used to confirm that such a formula is able to accurately calculate the proportion of ingredients in the synthesis reaction solution system.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1307K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1307K) -
Huiming YE, Liang SONG, Fuhui ZHANG, Juan LI, Zhiying SU, Yun ZHANGArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 575-580
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 02, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAs a nutrient in body functions, folic acid (FA) plays a very important role for human health, and thus developing a highly sensitive method for its determination is of great significance. In the present work, carbon hollow nanospheres decorated with molybdenum disulfide nanosheets (CHN@MoS2) nanomaterials were produced through a simple method and adopted to modify a glassy carbon electrode for assembling a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor of FA. After characterizing the prepared nanomaterials using scanning-/transmission-electron microscopy and Raman spectra, as well as optimizing various testing conditions, including the pH value of the buffer solution, the accumulation time and amount of nanomaterials on electrode surface, and the electrochemical determination of FA was carried out using a CHN@MoS2 electrode. Owing to the coordinative advantages from CHN and MoS2, the results show that CHN@MoS2 exhibits excellent sensing responses for FA, and it has a wide linear range from 0.08 to 10.0 μM coupled with a low detection limit of 0.02 μM. Finally, the proposed method for FA detection was successfully applied in human urine analysis. The obtained results are satisfactory, revealing that the developed method based on CHN@MoS2 nanomaterials has important applications for FA determination.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (908K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (908K) -
Krishnan SURESH BABU, Deivanayagam PARADESIArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 581-584
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 09, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA new reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) method has been developed for the separation and identification of impurities present in metadoxine. Herein, we report that one of the impurities eluted from the metadoxine sample is 4-deoxypyridoxine hydrochloride (4-DPH). In HPLC analysis, the retention time (RT) of 4-DPH was observed to be at 13.5 min in both the reference and metadoxine samples and the relative retention time (RRT) was 1.71. The presence of 4-DPH in a metadoxine sample was also confirmed by a chromatogram obtained by spiking the 4-DPH standard into the sample. Furthermore, the elution and mass of impurity 4-DPH in metadoxine was proven by LC-mass spectroscopy studies. This method highlights the presence of another unknown impurity that has so far not been observed in earlier methods of metadoxine evaluation. Hence, the developed method achieved superior resolution between metadoxine and impurities and thereby facilitates the production of a purer metadoxine drug.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (253K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (253K) -
Abdellah MUHAMMED, Ahmed HUSSEN, Mesfin REDI, Takashi KANETAArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 585-592
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 09, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMicrofluidic paper-based analytical devices (μ-PADs) fabricated in Japan were employed for the determination of total chromium (Cr) in water, soil, and lettuce irrigated with wastewater in Ethiopia. The μ-PADs, which were printed by wax printing in Japan, were transported to Ethiopia and prepared for the determination of total Cr by adding appropriate reagents to the pretreatment and detection zones. Soil and lettuce samples were determined by the μ-PADs and a UV-Vis spectrophotometer in Ethiopia. A paired t-test showed that the mean total Cr concentrations determined in the soil and lettuce samples were not significantly different between μ-PADs and UV-Vis spectrophotometric analysis at the 5% level of significance. This implies that the μ-PADs have good accuracy and reliability, and could be employed to monitor Cr in environmental samples. We found that the total Cr concentrations in all soil and lettuce samples were above the permissible limit. Moreover, evaluating Cr contamination level using the geo-accumulation index indicated that the soils were contaminated with Cr moderately to heavily. Thus, the present work successfully demonstrated the potential of remote investigations of pollution in a less-equipped laboratory by transporting the μ-PADs fabricated in another laboratory.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (590K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (590K) -
Kanji MIYABEArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 593-598
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 09, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
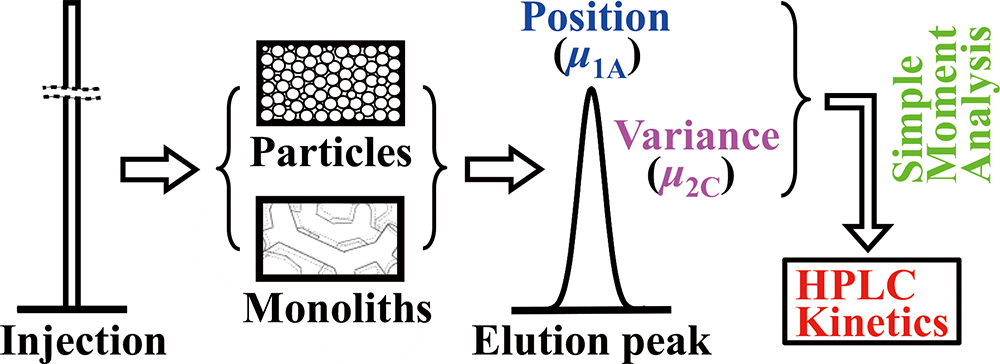
Supplementary materialA simple procedure of moment analysis was proposed for a kinetic study of the rate processes in the columns packed with full-porous spherical particles and silica monoliths. Previous chromatographic data measured in reversed-phase HPLC systems using Mightysil and Chromolith columns were analyzed by a simple moment analysis. The surface of the packing materials is chemically modified with octadecyl alkyl ligands. A mixture of methanol and water (80/20, v/v) and alkylbenzene homologous series (C6H5CnH2n+1, n = 0 – 7) were used as the mobile-phase solvent and sample probes, respectively. More detailed information about the experimental conditions is provided in Supporting Information. The values of the intra-stationary phase diffusivity (De) and the surface diffusion coefficient (Ds), derived by the simple moment analysis, were almost the same as those by the conventional moment analysis. The simple moment analysis is effective for quantitative studies of mass transfer in chromatographic systems. The previous chromatographic data were also analyzed by assuming external porosity (εe) as typical values, i.e., 0.40 for spherical particles and 0.70 for silica monoliths. The resulting values of De and Ds were of the same order of magnitude as those derived by using εe experimentally measured. Even if εe is assumed to be typical values, the simple moment analysis is effective for preliminary studies of the mass-transfer kinetics in the columns.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (281K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (281K) -
Sonia SAM, Sanu K. ANAND, Manna Rachel MATHEW, Krishnapillai Girish KU ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 599-603
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 16, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFor the first time, we report on a copper nanoclusters based fluorescence sensor for hemoglobin (Hgb). The aggregation-induced quenching of tannic acid capped copper nanoclusters’ (TACuNCs) fluorescence by a Hgb-H2O2 mixture that mimics the Fenton’s reagent is used here for the selective determination of Hgb. It is possible to effectively determine Hgb using this sensitive and cost-effective sensor in the linear range of 5.0 × 10−8 to 4.0 × 10−9 M with a detection limit of 5.6 × 10−10 M. The practical utility of the sensor is evident from the good recovery values obtained from Hgb spiked with artificial blood serum.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5376K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5376K) -
Lijun SUN, Lili LIU, Xiangyun LIN, Zhiyi XIA, Jingli CAO, Shaofu XU, H ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 605-611
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 23, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPlant roots play critical roles in absorbing nutrients for the growth and development of plants as well as adapting different environments. Currently, there is no satisfactory way to track dynamic information when studying roots at the high temporal and spatial resolution. Herein, a simple microfluidic device with crossed microchannels was utilized for a microscopic investigation of Arabidopsis thaliana roots in situ. Our experimental results showed that the microfluidic system combined with a microscope could be conveniently utilized for the quantification of primary roots and root hairs with a change of micrometers within a time of minutes. Using the same approach, the influences of high salinity stress could also be investigated on different parts of roots, including the root cap, meristematic zone, elongation zone, mature zone, and root hairs. More importantly, the growth of roots and root hairs could be quantified and compared in a solution of abscisic acid and indole-3-acetic acid, respectively. Our study suggested that the microfluidic system could become a powerful tool for the quantitative investigation of Arabidopsis thaliana roots.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1009K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1009K) -
Syunichi OSHIMA, Hidekazu OHINATA, Takushi MATSUNO, Kenta TAKASAWA, Yu ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 613-617
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 23, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSurface functionalized mesoporous silicates, MCM-41s, having 3-(2-pyridylmethylideneimino)propyl group (PI-MCM-41) or 3-(2-quinolylmethylideneimino)propyl group (QI-MCM-41) were prepared via Schiff base reaction, and the adsorption behavior of metal ions onto the modified MCM-41s was investigated. The function groups on the modified MCM-41 surface were confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and elemental analysis. The metal ions examined, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+, were quantitatively adsorbed on the PI-MCM-41 and QI-MCM-41, except for Mn2+. In the complexation with these metal ions, it was suggested that imine-N and heterocyclic-N atoms act as donor atoms. In addition, it was considered that the hydrophobicity derived from the organo-functional groups modified on MCM-41 contributed to improving the adsorption ability.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (733K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (733K) -
Kazuya TAMURA, Takurou HASEGAWA, Masato MORITA, Tetsuo SAKAMOTOArticle type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 619-623
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 23, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialCisplatin is one of the most popular and traditional platinum-based anti-cancer drugs. Additionally, it is known for its effect on different types of cancers. To clarify the reaction mechanism of anti-cancer drugs in a cell, the visualization of drugs in a single cell is required. In this study, we investigated a secondary ion species obtained from cisplatin, which was bounded to the nucleus in a cell and its intensity. PtCl2− was mainly detected via SIMS during an analysis of pure cisplatin reagent. In contrast, a high-intensity signal for PtCN− was detected from cultured cells that were administered cisplatin. However, this signal was not detected from cisplatin in the reagent state. Chlorine in the cisplatin structure is replaced with water when it is combined with the cell nucleus. Therefore, PtCN− was mainly detected from the intracellular region because the structure was changed by cisplatin binding to the nucleus and which exhibits anti-cancer activity. The results showed that the cisplatin selectively combined with the nucleus. Through TOF-SIMS, we achieved a visual distribution of the cisplatin intracellular nucleus.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (577K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (577K) -
Kenji MORITA, Kazuhiro MORIOKA, Hizuru NAKAJIMA, Katsumi UCHIYAMA, Aki ...Article type: Original Papers
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 625-631
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: December 18, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn innovative technique is proposed for forming silver thin films of nanometer-order thickness via a silver-mirror reaction. This approach is made possible by the real-time monitoring of the thickness of a silver thin film formed on the edge surface of a fiber core during the silver-mirror reaction using a homemade absorbance measurement system. The monitored absorbance value increases as silver plating progresses, and the relationship between the absorbance values and the thickness of the silver thin film is linear in the thickness range from approximately 30 to 60 nm. This technique was applied to the preparation of a fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance (FO-SPR) sensor. The sensor was successfully used to measure sucrose solutions with concentrations of less than 16% (w/v). The sensitivity of the sensor probe was estimated to be 2205 nm/RIU in the refractive index range of 1.333 – 1.357. The relative standard deviation of the wavelength shift obtained from measurements using different sensor probes was estimated to be less than 3.3%.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (677K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (677K)
-
Ken-ichi OHNO, Katsuhiko SATO, Masayuki KUMANO, Kazuhiro WATANABE, Tsu ...Article type: Notes
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 633-635
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
Advance online publication: October 23, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this paper we propose a novel measurement for NO and ·OH by electrochemical detection using sesamol. Standard samples of the sesamol monomer and dimer were subjected to differential pulse voltammetry, resulting in their peaks being clearly separated and detected. Based on the oxidative dimerization of sesamol, the current simple, sensitive and selective method was successfully applied to preliminary measurements for NO and ·OH, respectively.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (383K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (383K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2021 Volume 37 Issue 4 Pages 637
Published: April 10, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (199K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
