
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Shinjiro Hayakawa, Ryo Kato, Hideyuki KatsumataArticle type: Call for Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 357
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (29K)
-
Tomoyuki YASUKAWAArticle type: Highlights
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 359-360
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Toshiyuki OSAKAIArticle type: Reviews
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 361-366
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 04, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMany studies have been conducted by using the oil (O) | water (W) interface as a simple model for understanding ion transfer (IT) or electron transfer (ET) across biomembranes. In this review, we revisit the usability of the O | W interface as a biomembrane model. For understanding biomembrane IT, the O | W interface is the simplest and best suited model. For example, the standard Gibbs transfer energy of drug ions at the O | W interface is a useful measure for evaluating their membrane permeability in a conventional in vitro assay, called PAMPA. However, the O | W interface is not necessarily a good model for understanding biomembrane ET. This is because no net current can be observed with the O | W interface, owing to the ET-coupled proton transfer. In such a case, the self-assembled monolayer (SAM) formed on a metal electrode serves as a better model for understanding biomembrane ET.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (603K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (603K)
-
Dongri LIU, Xiaoyi PAN, Wei MU, Chao LI, Xiaojun HANArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 367-370
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 30, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTetracycline (Tc), a widely used antibiotic, is one of the major pollutants in water. Herein, glutathione (GSH)-protected Au nanoclusters (GSH-AuNCs) were prepared to detect Tc. The fluorescence quenching ratio of GSH-AuNCs shows an excellent linear response against tetracycline in the concentration range of 50 μg/L – 50 mg/L with the detection limit of 5.31 μg/L. For the test paper prepared by GSH-AuNCs, 1 mg/L Tc caused a significant difference that could be recognized by the naked eye. The method exhibited good selectivity and excellent recovery when applied to a tap water sample. The method has the potential for Tc detection in real samples.
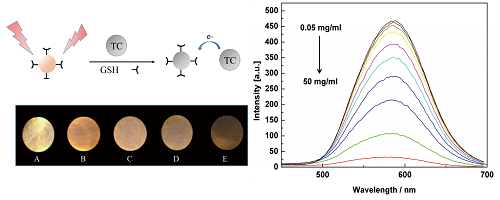 View full abstractDownload PDF (597K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (597K) -
Kosin TEEPARUKSAPUN, Nicha PRASONGCHAN, Auttachai THAWONSUWANArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 371-377
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 30, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA facile, low cost, rapid and easy-to-use colorimetric sensor for the detection of Cu2+ ion is described using alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) functionalized AgNPs. The prepared ALA-AgNPs are yellow, and spherical with an average particle size of 9.23 ± 3.36 nm. The addition of Cu2+ ion resulted in the aggregation of ALA-AgNP solution and caused a visible color change from yellow to orange-brown, which could be detected by the naked eye and UV-vis spectrophotometer. Parameters affecting the sensitivity of the sensor were investigated, including ALA concentrations, reaction times, reaction volumes and pH. Under optimal conditions, the colorimetric sensor could detect Cu2+ ion in the range of 0.625 × 10−5 to 10 × 10−5 M with a linear coefficient (r) of 0.9978. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were 0.43 × 10−5 M (4.3 μM) and 1.45 × 10−5 M (14.5 μM), respectively, which is lower than the limit set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This proposed method showed good selectivity and could detect Cu2+ within 5 min. Finally, the proposed method could be successfully applied for the analysis of Cu2+ ion in tap water samples.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4725K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4725K) -
Grenalynn ILACAS, Frank A. GOMEZArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 379-384
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 07, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis paper describes the design and development of miniaturized microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) for biological assays and enzyme storage instruments. Here, a glucose assay utilizing glucose oxidase (GOx), horseradish peroxidase (HRP), and potassium iodide (KI) is used as the model system. The efficacy of the miniaturized devices is further examined by assessing the activity of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Two types of μPADs were developed: one, “strip” chips of detection zones of area 0.5, 0.1 cm2 and, two, “grid” chips of detection zone 0.05 cm2. The devices are easily fabricated via a wax printing process whereby lines of wax are deposited onto chromatographic paper and heated to create rows of hydrophobic barriers. The “strip” chips were subjected to three different temperature environments (–20, 0, and 20°C) over 30 days and glucose assays conducted at intermittent times yielding a correlation between corrected average inverse yellow intensity, days, and glucose concentration. Calculated and experimentally derived color intensity values for 1, 4, and 9 mM glucose concentrations after a 7-day storage study showed a good correlation (0.89 – 15.76% error). Both types of μPADs are effective platforms as potential point-of-care (POC) diagnostic devices and display minimal enzyme denaturation. μPADs of this size show promise as alternative devices for resource-limited regions and especially those areas where materials and instrumentation are not always available.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2594K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2594K) -
Ashraf YOUSEFZADEH, Jafar ABOLHASANI, Javad HASSANZADEH, Mohammad Hoss ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 385-391
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialHerein, an efficient chemiluminescence (CL) reaction with a high emission intensity is reported based on a synergistic improving effect of silver nanoclusters (AgNCs) and graphene quantum dots (GQDs). First, the syntheses of AgNCs and GQDs were simply performed by the chemical reducing of AgNO3 and a thermal treatment of glucose, respectively. After the characterization steps, the beneficial behavior of the prepared nanomaterial was investigated in CL systems. The oxidation reaction of KMnO4-rhodamine B produced weak CL emission. However, the presence of AgNCs and GQDs led to a synergetic enhancing effect, and thus higher emission was obtained. A possible mechanism was investigated for this effect using absorption and fluorescence experiments. Furthermore, rabeprazole showed a relatively selective enhancing impact on the CL emission. The CL intensity was linearly increased in the rabeprazole concentration range of 4 – 133 ng mL−1 with a detection limit (3Sb/m) of 1.1 ng mL−1. The developed CL method was utilized for the measurement of Rbp in biological samples with acceptable precision and accuracy.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1806K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1806K) -
Quoc Trung HUA, Hiroyuki SHIBATA, Yuki HIRUTA, Daniel CITTERIOArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 393-399
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 07, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialFlow control-based paper devices have recently shown great potential for point-of-need analysis, since they allow for the easy operation of multi-step assays by minimizing user operation. In this work, a wax printing method was evaluated as a means to control liquid flow in 3D microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs). The resulting flow control-based 3D μPADs were applied to determine paraoxon-ethyl as a typical organophosphate pesticide model system. The analytical procedure is as simple as applying a 200-μL sample solution, resulting in reproducible (relative standard deviation of colorimetric signals from 6 independently fabricated devices, 2.63%) colorimetric signals within 1 h of the assay time with the limit of detection (LOD) reaching 25.0 μg/L. Finally, results obtained for pesticide-spiked water samples analyzed by flow control-based 3D μPADs showed good agreement with those from a conventional HPLC analysis with UV detection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3228K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3228K) -
Wenzhi TANG, Jingxian YANG, Fei WANG, Zhonghong LIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 401-406
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 14, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and inexpensive strategy is reported to facilitate the detection of an organophosphorus pesticide by acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Pullulan is able to preserve AChE at room temperature, but the activity of conserved AChE varies significantly depending on the time, stir and volume of solution to dissolve it. The reason is that AChE entrapped in pullulan tablet remains in an inactive state to avoid denaturalization and deactivation. There is a reactivation process to gradually recover the enzyme activity during dissolution of the tablet. Stirring would interrupt this procedure and lead to a loss of enzyme activity. Dissolution of the tablet for 5 min with a volume of 15 μL could facilitate full recovery of AChE activity. The feasibility of activated AChE for organophosphorus pesticide detection was evaluated using malaoxon. These results contribute to the understanding of preservation mechanism by pullulan and the development of easy-to-use enzyme assays.
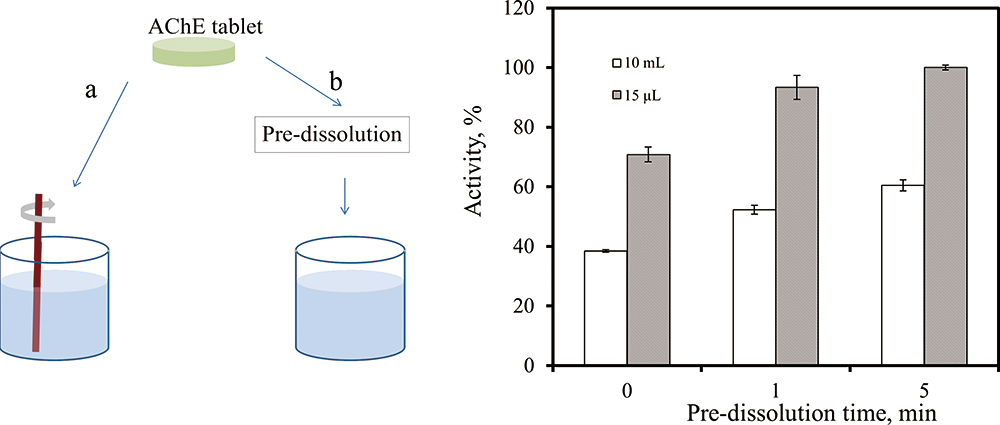 View full abstractDownload PDF (873K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (873K) -
Sohei TANAKA, Misaki SEKIGUCHI, Atsushi YAMAMOTO, Sen-ichi AIZAWA, Kan ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 407-412
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 14, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRacemic synephrine, which was transformed into diastereomers by derivatization with 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-β-D-glucopyranosil isothiocyanate, was resolved by a reversed phase HPLC with UV detection at 254 nm. The total contents of synephrine enantiomers in citrus fruit samples were exocarp > mesocarp > endocarp > sarcocarp, suggesting that synephrine content of outer side of citrus fruits was higher than that of the inner side. (R)-Synephrine was detected in exocarp of eleven fresh citrus fruits, except for lemon, lime, and grapefruit samples. (S)-Synephrine was determined in the exocarp of four citrus fruits (mikan, orange, bitter orange, and ponkan samples) and the ratio of (S)-synephrine to total synephrine was 0.5 – 0.9%. The racemization of (R)-synephrine in aqueous solution during heating at 100°C was also examined. An increase in the heating time brought about an increase in the (S)-synephrine content in a linear fashion. The racemization was found to be significantly reduced by the addition of D-fructose, D-maltose, D-glucose, D-mannose or D-galactose, but not D-sucrose or D-mannitol. It is suggested that the reducibility of sugars may result in the inhibition of racemization.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (280K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (280K) -
Shigehiro KAGAYA, Ryo IKEDA, Takehiro KAJIWARA, Makoto GEMMEI-IDE, Yos ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 413-419
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialChelating resins immobilizing phosphomethylated polyethyleneimine (PM-PEI) with different phosphomethylation (PM) rates were prepared by using different amounts of both phosphonic acid and paraformaldehyde in the phosphomethylation of PEI immobilized on a methacrylate resin as a base resin. The extraction of many elements improved with increasing PM rate; REEs, Be, Fe, Mo, Ti, and V were quantitatively extracted at pH 2. The elution of the elements tended to become difficult with increasing PM rate. When a PM-PEI resin with a PM rate of 0.26 was used, REEs and Be could be eluted using 0.2 mol L−1 EDTA solution adjusted to a pH of 7 and 3 mol L−1 nitric acid, respectively, although the elution of Fe, Mo, Ti, and V was insufficient. The PM-PEI resin could be reused at least 10 times to recover REEs and Be without the influence of any other elements. The PM-PEI resin could be applied to a recovery test using artificial seawater spiked with REEs, except for Sc, Tm, Yb, and Lu, and the separation of the REEs in NIST SRM 1515 Apple Leaves.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1218K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1218K) -
Pheeraya JAIKANG, Sununta WANGKARN, Pathinan PAENGNAKORN, Kate GRUDPANArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 421-425
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe propose a simple greener colorimetric method for the determination of nitrate-nitrogen by operating on a 96-well microplate and using a smartphone camera as a simple detector. A slurry containing 0.3 mg zinc was used for reduction of nitrate to nitrite, the reduction solution was transferred to a 96-well microplate to react with Griess reagent to form a pink azo dye product. The color product image was captured and processed by a smartphone camera and ImageJ software, respectively. The limit of detection and limit of quantitation were 0.04 and 0.10 mg/L nitrate-nitrogen, respectively, for the smartphone camera. Application to real samples was demonstrated. The proposed method results showed no significant difference (at 95% confidence) with the hydrazine reduction method. The proposed method could be used as an alternative method for on-site analysis due to the advantages of portability and rapidity; duplicate run of 20 samples could be carried out simultaneously in 12 min.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (519K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (519K) -
Yukiko HORIE, Ayaka GOTO, Sumi TSUBUKU, Mari ITOH, Shigeo IKEGAWA, Sho ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 427-432
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialMany studies have demonstrated that the dietary supplementation of polyamines, especially spermidine (SPD), prevents age-related diseases. Rice bran is rich in polyamines and their amounts could be increased by fermentation with Aspergillus oryzae (A. oryzae). In this study, we developed a method for the determination of putrescine (PUT), SPD and spermine (SPM) in rice bran samples by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-MS/MS) after derivatization with 4-(N,N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-7-fluoro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (DBD-F). The derivatization improved the LC retention and ESI-MS/MS detectability of the polyamines, and consequently enabled precise and accurate quantification. Using this method, we found that the SPD content increased to 158% due to fermentation with A. oryzae, while the content of PUT and SPM decreased. SPD is known as the polyamine playing a central role in cell proliferation and growth, and therefore has health benefits. The fermented rice bran might be a good material for functional foods aimed at SPD supplementation.
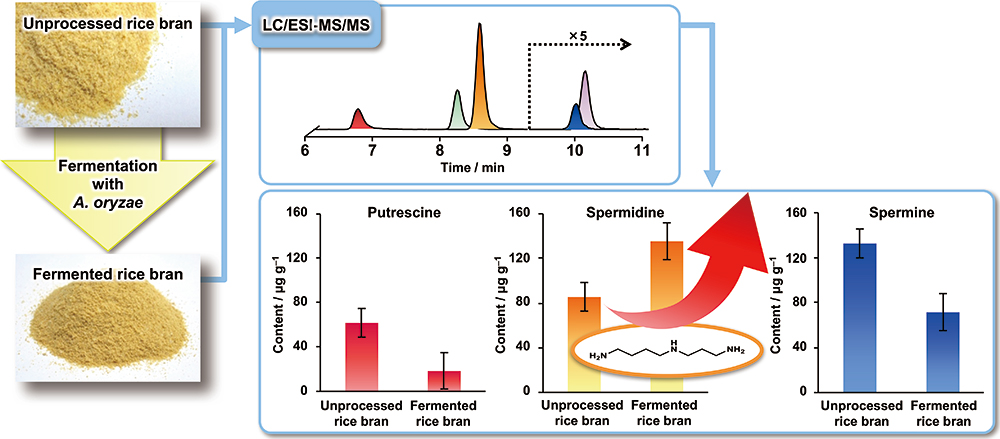 View full abstractDownload PDF (279K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (279K) -
Hsuan CHUNG, Satoshi TAJIRI, Mai HYOGUCHI, Riho KOYANAGI, Akihiro SHIM ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 433-439
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this study, a simultaneous assay for catecholamines and their metabolites in the brain was established using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS). To achieve complete separation, a cation-exchange/reversed-phase mixed-mode copolymer resin column containing 0.81 wt% sulfo groups was used for the simultaneous LC-MS assay. The analyzed catecholamines were dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), and epinephrine (E), while the metabolites lacking amino groups were 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), homovanillic acid (HVA), and 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG). The metabolites were separated and detected using LC-MS, on columns with and without sulfo groups. However, we could not achieve adequate separation of catecholamines on both columns using a gradient elution of 0 – 50 (v/v)% methanol containing 0.1 (v/v)% formic acid (FA). When volatile ion-pairing reagents were added to the mobile phase, they improved the retention and detection of catecholamines on the sulfonated mixed-mode column. Under optimized elution conditions, which involved a linear gradient elution of water containing 0.1 (v/v)% FA to 50 (v/v)% acetonitrile in 50 mM ammonium formate at 40°C and a 0.20 mL/min rate, all six target molecules were simultaneously detected within 25 min, when using negative mode LC-MS on a sulfonated mixed-mode column. The limits of detection (LODs) for DA, NE, E, DOPCA, HVA, and MHPG were determined to be 20.7, 12.6, 74.6, 1110, 18.7, and 3196 nM, respectively. Moreover, the established LC-MS assay allowed the detection of endogenous DA, NE, and HVA, in normal mouse brain samples at concentrations higher than 20, 9, and 4 pmol/mg, respectively.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (196K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (196K) -
Xiaojing WANG, Mei YANG, Qingyan LIU, Siyi YANG, Xintong GENG, Yixia Y ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 441-448
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 28, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this paper, an ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor based on carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotube/molybdenum disulfide composites (MWCNTs-COOH/MoS2) for the detection of KRAS gene is described. An easy, low-cost method, named one-step hydrothermal, was used for the synthesize of MWCNTs-COOH/MoS2 nanocomposites, and scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were used for characterizing the prepared composites. Furthermore, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) were employed for an electrochemical performance study of this biosensor. Under optimal conditions, the detection limit of target DNA achieved down to 3 fM (S/N = 3) with high sensitivity; the linear range with the logarithm of the concentrations of target DNA varied from 1.0 × 10−14 to 1.0 × 10−7 M. Finally, the practicality of our proposed sensor was verified by a determination of the KRAS gene in human serum samples with good accuracy and high precision due to the excellent conductivity and large active surface area of the MWCNTs-COOH/MoS2 nanocomposites. This proposed biosensor thus provides a practical method for the rapid and sensitive analysis of gene detection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1979K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1979K) -
Caiyan LIU, Zengjuan HU, Xiong WANG, Yilong GENG, Cuiping MA, Zonghua ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 449-453
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 04, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialBursaphelenchus xylophilus (B. xylophilus) is one of the most important causal agents of infectious diseases in forest pathology. Obviously, the rapid detection of B. xylophilus is an urgent need for its prevention and cure. We have developed a detection method of B. xylophilus by strand exchange amplification (SEA). This method could detect 105 copies of genomic DNA of B. xylophilus, and it was sufficiently sensitive to detect a single nematode as short as 40 min. Moreover, because the amplification result could be visualized by the naked eyes, the only equipment required throughout the process was a simple isothermal block. Therefore, our method would be a potential for developing on-site detection of B. xylophilus to prevent and control its spread.
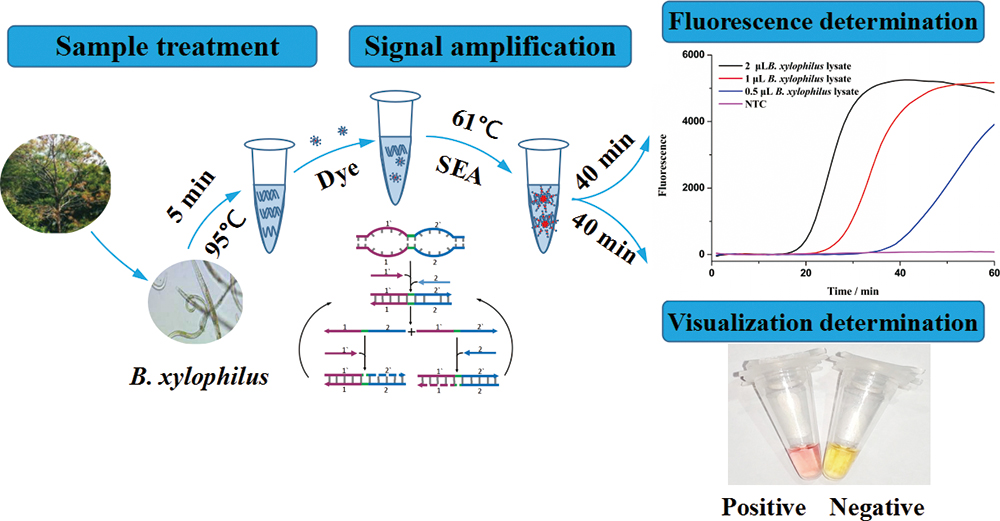 View full abstractDownload PDF (1394K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1394K) -
Yoshinori TSUMURA, Yu TSUSHIMA, Azusa TAMURA, Makiko HASEBE, Tsunefumi ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 455-460
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: January 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA novel ex vivo method to simultaneously evaluate hepatic glucose utilization, uptake, and production was developed in rats. The right lateral lobe of the liver was perfused with Krebs–Henseleit bicarbonate buffer containing 5 mmol/L uniformly labeled 13C-glucose ([U-13C]-glucose). The whole glucose concentration in the perfusate was measured by colorimetric assay, and the concentrations of [U-12C]-glucose (natural isotope) or [U-13C]-glucose were estimated on the basis of the abundance ratio of [U-12C]-glucose or [U-13C]-glucose, which were measured by GC-MS. The difference in whole glucose and [U-13C]-glucose concentrations between the baseline and effluent perfusate represents hepatic glucose utilization and glucose uptake, respectively. The [U-12C]-glucose concentration in the effluent perfusate corresponds to hepatic glucose production. With this method, we clarified the precise mechanism that underlies the hepatic impairment of diabetic animals and pharmacological effects of anti-diabetic agents. Thus, this method is useful for the pathophysiological and pharmacological research of type 2 diabetes.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (404K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (404K)
-
Kaname SAGA, Hideya SUZUKI, Tatsuro MATSUMURA, Takehiko TSUKAHARAArticle type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 461-464
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 07, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe phase transition-based gelification phenomenon of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) [poly(NIPAAm)] has great potential in developing new waste-free extraction processes. In this study, we realized the direct and complete temperature-swing extraction of all trivalent rare-earth (RE) ions from a multi-component nitric acid solution onto a poly(NIPAAm) gel as chelate complexes with hydrophobic diglycolamide-typed ligands. Moreover, we elucidated that the extractabilities are affected by not only the coordination ability of the ligands with RE ions but also by the hydrophobic interaction between the poly(NIPAAm) and the ligands.
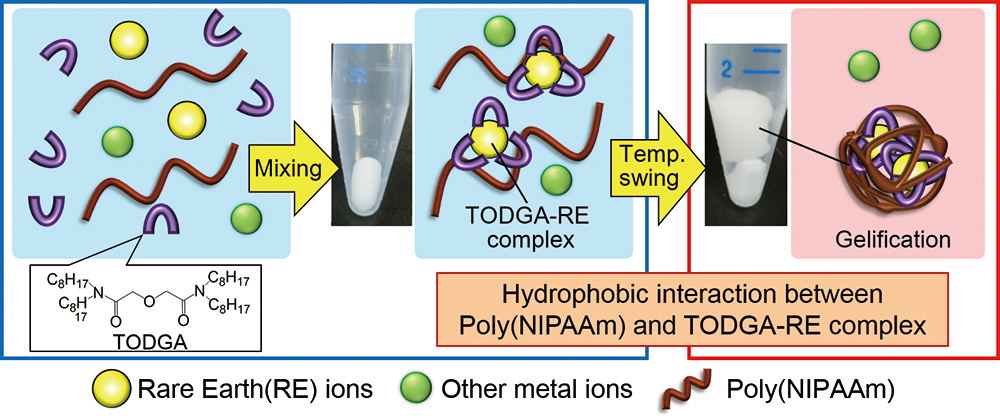 View full abstractDownload PDF (383K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (383K) -
Takuya NISHIWAKI, Kiichi SATO, Kin-ichi TSUNODA, Hiroaki HORIUCHI, Ter ...Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 465-469
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
Advance online publication: December 21, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPolarized visible attenuated total reflection spectrometry with a glass slab optical waveguide revealed that when a hydrophobic dye, curcumin, was adsorbed onto the cetyltrimethylammonium chloride (CTAC) reverse micelles immobilized on a glass surface, in an undissociated form, the curcumin was perpendicular to the surface plane, while in a dissociated form, the curcumin was parallel to the plane. This implies that the former may be located in the CTAC monolayer while the latter may be located in the reverse micellar water phase immobilized on the plane.
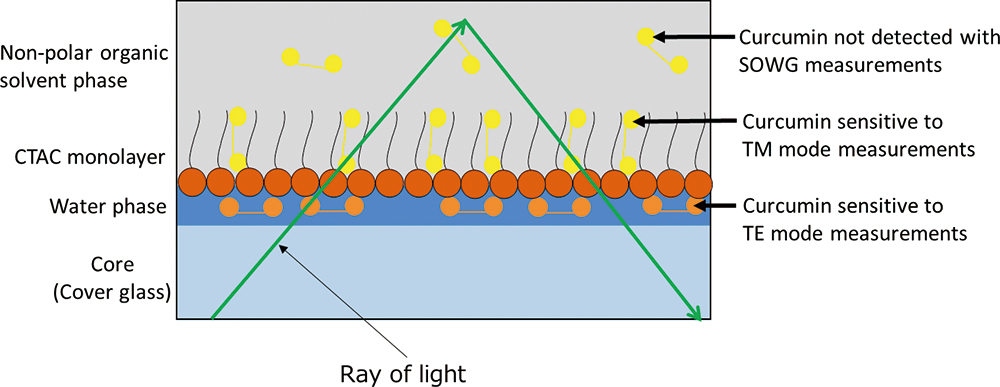 View full abstractDownload PDF (1612K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1612K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2019 Volume 35 Issue 4 Pages 471
Published: April 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: April 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1125K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
