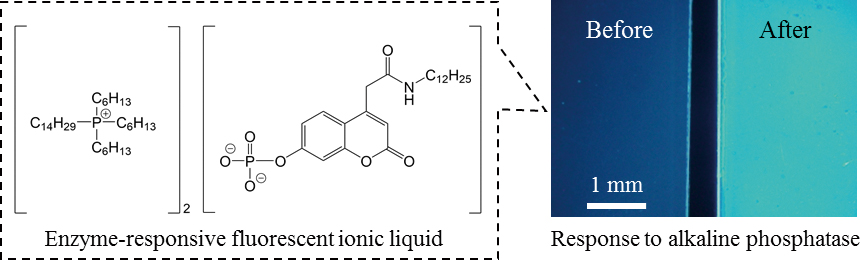
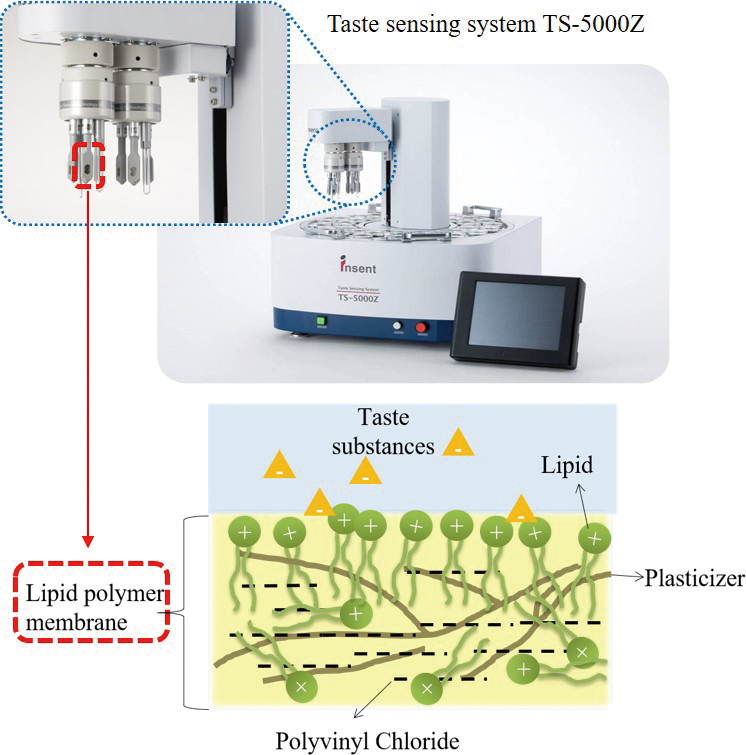
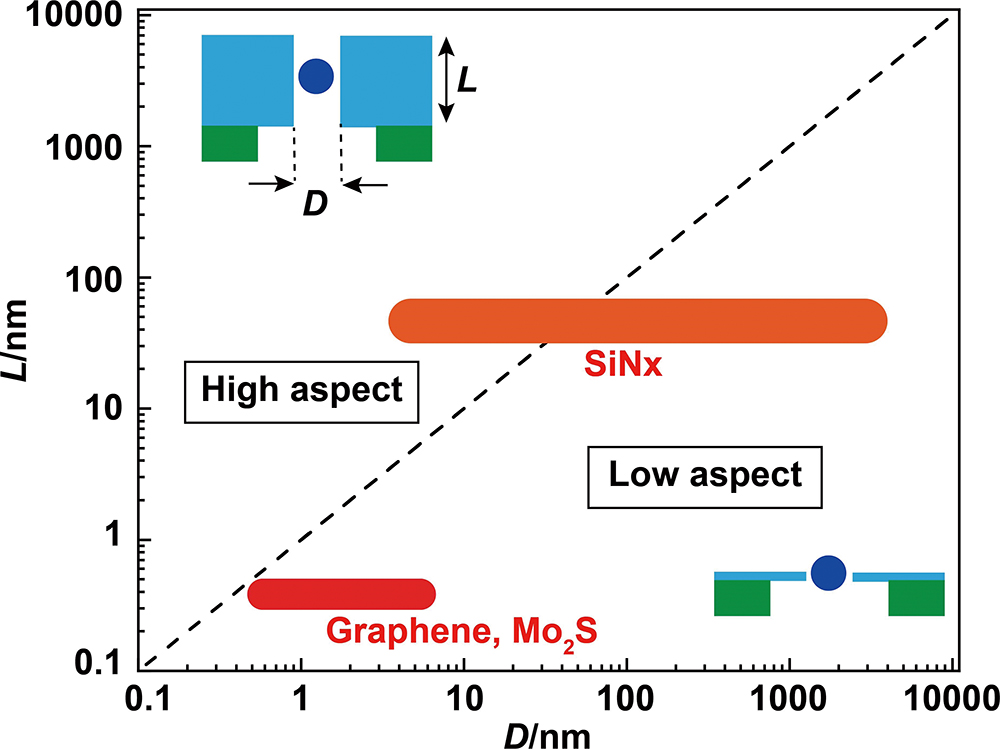
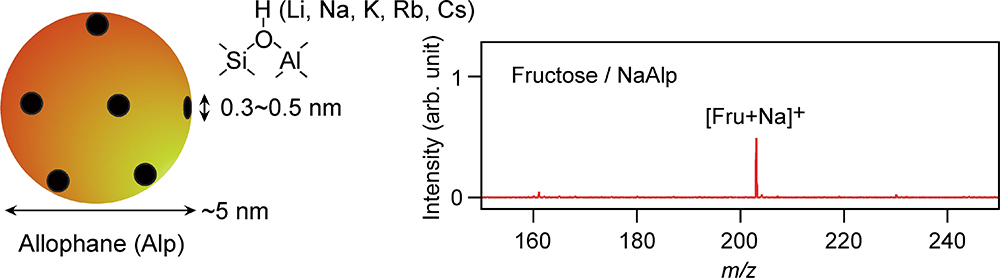
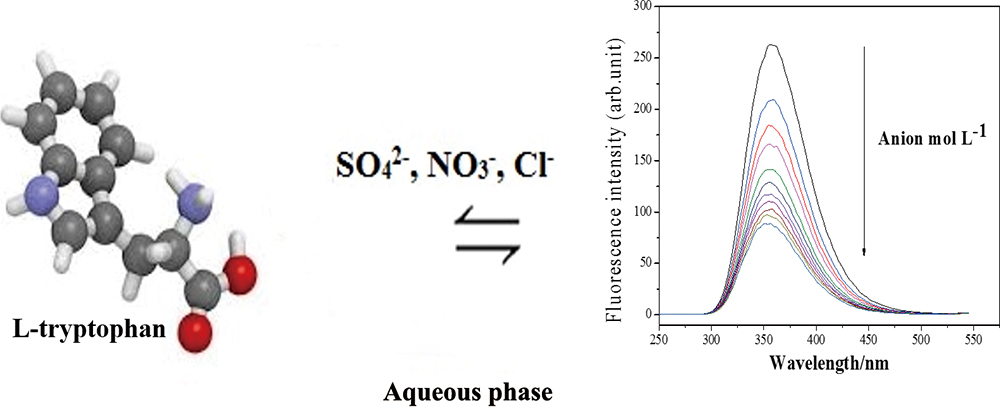
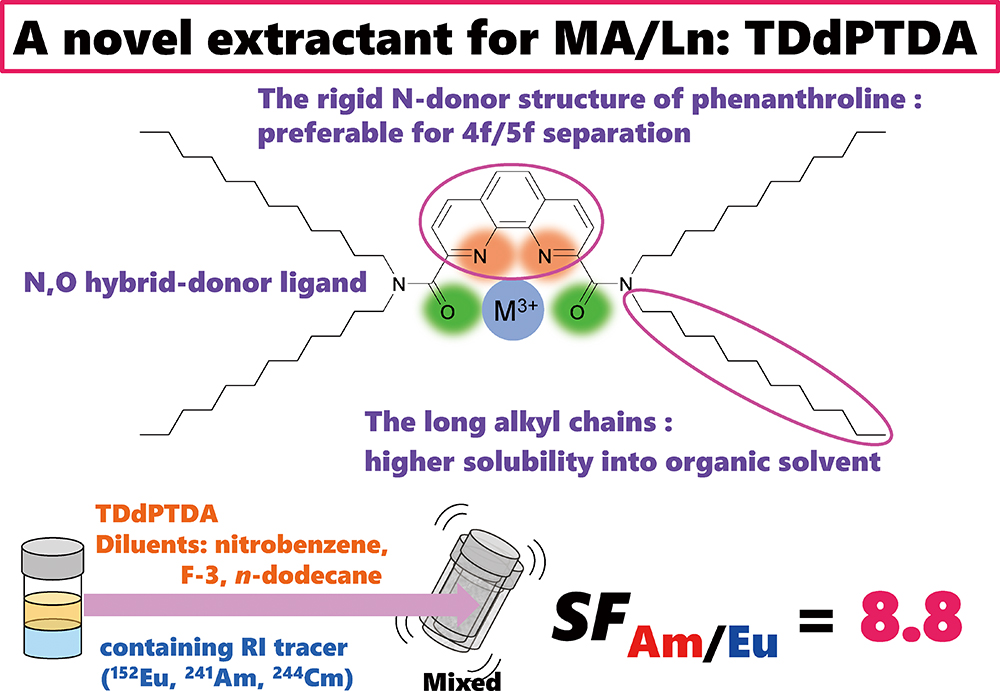
Volume 36, Issue 2
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2019Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 141-142
Published: February 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Download PDF (194K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 143-145
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 24, 2020Download PDF (218K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 147-159
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: November 29, 2019Download PDF (2034K) -
Article type: Rapid Communications
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 161-175
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: December 06, 2019Download PDF (3985K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 177-181
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: August 30, 2019Download PDF (575K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 183-185
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 27, 2019Download PDF (1421K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 187-191
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 06, 2019Download PDF (503K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 193-199
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 06, 2019Download PDF (635K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 201-206
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 13, 2019Download PDF (662K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 207-212
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 13, 2019Download PDF (159K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 213-219
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 20, 2019Download PDF (3570K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 221-226
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 20, 2019Download PDF (634K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 227-232
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 27, 2019Download PDF (1510K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 233-239
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Download PDF (171K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 241-246
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 27, 2019Download PDF (2236K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 247-253
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 27, 2019Download PDF (551K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 255-262
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 04, 2019Download PDF (2474K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 263-268
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 04, 2019Download PDF (1635K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 269-276
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 11, 2019Download PDF (5846K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 277-281
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 11, 2019Download PDF (213K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2020Volume 36Issue 2 Pages 283
Published: February 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: February 10, 2020
Download PDF (47K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|