
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 605-606
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (468K)
-
Hirotsugu MINAMIArticle type: Highlights
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 607-608
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Xiaowen OU, Peng CHEN, Bi-Feng LIUArticle type: Reviews
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 609-618
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 08, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA microfluidic device as a pivotal research tool in chemistry and life science is now widely recognized. Indeed, microfluidic techniques have made significant advancements in fundamental research, such as the inherent heterogeneity of single-cells studies in cell populations, which would be helpful in understanding cellular molecular mechanisms and clinical diagnosis of major diseases. Single-cell analyses on microdevices have shown great potential for precise fluid control, cell manipulation, and signal output with rapid and high throughput. Moreover, miniaturized devices also have open functions such as integrating with traditional detection methods, for example, optical, electrochemical or mass spectrometry for single-cell analysis. In this review, we summarized recent advances of single-cell analysis based on various microfluidic approaches from different dimensions, such as in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo analysis of single cells.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1274K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1274K)
-
Hirokazu SETO, Atsushi SAIKI, Seiji KAMBA, Takashi KONDO, Makoto HASEG ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 619-623
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 01, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTwo types of metal mesh devices with hole diameters of 1.7 and 0.3 μm were prepared by an electroforming method. The metal mesh devices with hole diameters of 1.7 and 0.3 μm transmitted electromagnetic waves with frequencies of approximately 100 and 285 THz, respectively. These spectral frequencies shifted depending on the adsorption amount of protein. The slope in the linear relationship between the adsorption amount and spectral shift (i.e. sensitivity) of the metal mesh device with a hole diameter of 0.3 μm was seven times as great as that of the device with a hole diameter of 1.7 μm. These results agreed with the theoretical concept of the sensitivity for the metal mesh device sensor being proportional to the square of the transmittance frequency. As biosensors, the structurally refined metal mesh devices amplified the output signals.
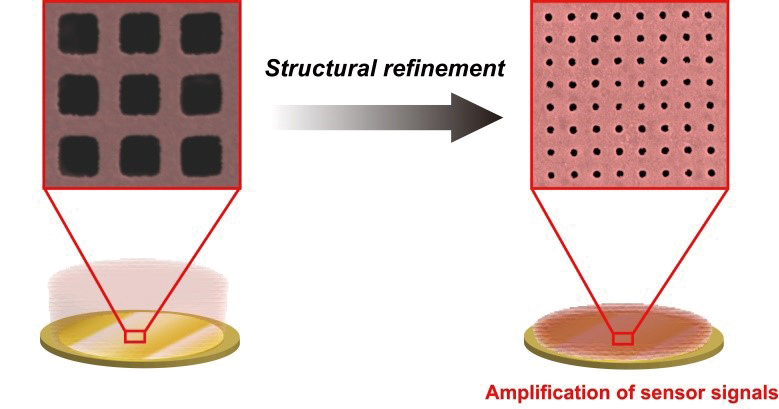 View full abstractDownload PDF (564K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (564K) -
Mingming GUAN, Chunling XU, Jiahua MA, Ting YANG, Jilin LIU, Guodong F ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 625-630
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 01, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA novel “on-off-on” super-sensitive conjugated polymer fluorescence sensor (PPE-DPA) was developed and it was applied to realize the continuous recognition of Cu2+ and pyrophosphate (PPi). The fluorescence intensity decreased linearly with the change of Cu2+ from 0.05 to 5.0 μmol L−1 and the limit of detection was 24 nmol L−1. The fluorescence intensity was linearly enhanced with the increase of PPi from 0.5 to 12.0 μmol L−1 and the limit of detection was 230 nmol L−1. In addition, this method was applied to detect PPi in the blood serum and synovial fluid of patients with arthritis and satisfactory results were obtained. Thus, the PPE-DPA is not only an effective tool for detecting Cu2+ and PPi in samples, but also presents a potential way to diagnose arthritis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (608K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (608K) -
Saima Ameen GHOTO, Muhammad Yar KHUHAWAR, Taj Muhammad JAHANGIRArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 631-637
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 08, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA rapid and simple colorimetric approach has been developed for sensing dithiocarbamate pesticides (ziram, zineb and maneb) in environmental samples using sodium dodecyl sulfate capped silver nanoparticles (SDS-AgNPs). They were characterized by a UV-vis spectrophotometer, FT-IR, SEM and EDX. Dithiocarbamates on interactions with SDS-AgNPs induce the aggregation of NPs, leading to a color change from yellow to greyish or dark brownish, depending on the concentration of pesticides added. A shift in the wavelength was observed from 400 to 570 nm with the broad band. The absorption ratio, 570/400 nm, was found to be linearly related to the concentration of pesticides in the range of 195.7 – 733.9 ng/mL for ziram, 17.6 – 66.2 ng/mL for zineb and 16.9 – 63.6 ng/mL for maneb with the detection limits of 149.3, 4.0 and 9.1 ng/mL for ziram, zineb and maneb, respectively. The method was successfully applied for the determination of DTCs in environmental samples (tap water, tomato, mango beverage) with percentage recoveries of 94.8 – 108.4% for ziram, 93.7 – 105.4% for zineb and 93.2 – 107.6% for maneb. The procedure was repeatable with inter-day RSD (n = 5) within 3.4, 4.8, 7.6% and intra-day RSD (n = 5) within 1.2, 1.7 and 1.8% for the ziram, zineb and maneb respectively.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (632K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (632K) -
Xueling SHAN, Yuting PAN, Xiaohui CHEN, Wenchang WANG, Zhidong CHENArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 639-644
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 08, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA novel electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensor for detection of brilliant blue FCF (BB) has been developed using Ru@Zn-MOF/nafion modified GCE (glass carbon electrode) in this research. Different from conventional method for usage of Ru(bpy)32+ in solution-phase, Ru(bpy)32+ here was immobilized on a zinc-metal-organic-framework (Zn-MOF). After adding BB, a significant quenching phenomenon of ECL intensity was observed. The behavior of BB on the quenching effect of Ru(bpy)32+/Zn-MOF in different conditions was investigated thoroughly and the detection limit was achieved to 2.5 × 10−8 M in an optimized condition. Furthermore, the interference of some conventional ions and amino acids to the detection of BB was also investigated. Additionally, the composite showed a good effect on the detection of BB in commercial samples. The proposed sensor provided a promising platform for food safety analysis, environmental monitoring and clinical testing.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (469K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (469K) -
Yue ZHAO, Masato MORITA, Tetsuo SAKAMOTOArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 645-649
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialSpiders capture their prey by weaving an “invisible” orb-web that has both adhesive and fixed properties. Different types of silk in the orb-web have different functions, wherein the key to capturing a prey is the ball-like glue (glue ball), which coats the silk strands. This glue ball has highly versatile properties, but the mechanisms leading to its versatility remain unclear. The salts found in the web have been previously suggested to play an important role in terms of viscosity, not water. However, the distribution of salt and water in the glue ball has not yet been directly observed. Here, we mapped the salts in different states using a homemade time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer (TOF-SIMS) with a high lateral resolution. To our surprise, the glue ball was found to contain little water. The functional transformation of the glue ball from a viscous glycoprotein (capturing prey) to a hardened protein (retaining prey) relies solely on the stimulation of mechanical forces. The phosphate is a key factor for its versatility.
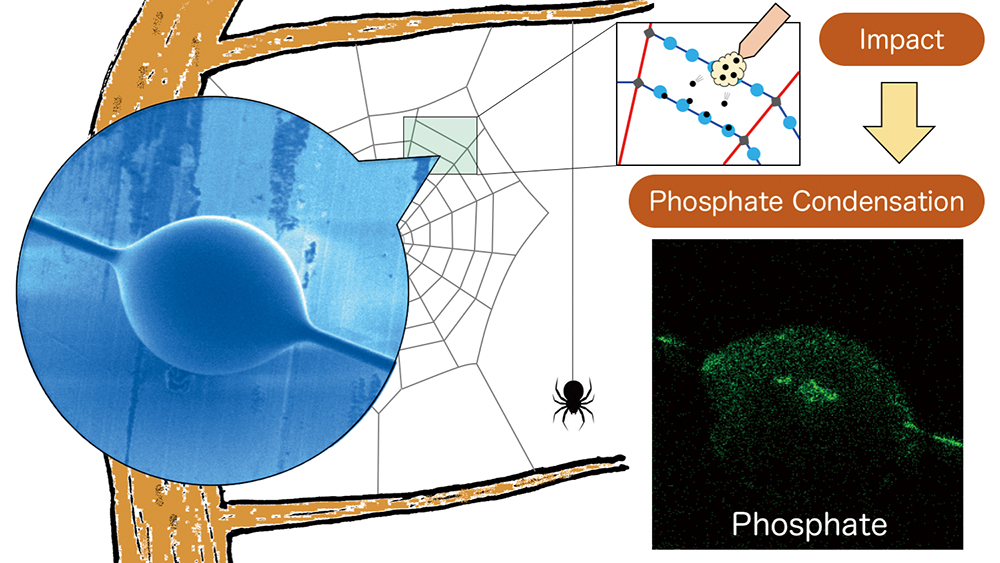 View full abstractDownload PDF (2696K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2696K) -
Hisashi HAYASHI, Mao TAKAISHIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 651-357
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLow-cost tube-type sample cells for X-ray spectroscopy of solutions, sols, and gels were made from plastic straws. Energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence (XRF) experiments showed that the X-ray transparency of the straw cells is ∼50% superior to that of quartz capillary cells for 6 – 7 keV XRF and is almost uniform over the entire range, allowing its use for position-dependent measurements. Wavelength-dispersive XRF experiments showed that the difference in the surface curvature between the straw cells and pellet samples leads to an apparent ∼1.5 eV shift of the Fe Kβ1,3 peak; however, chemical effects of Fe Kβ1,3 spectra can be studied if all the samples (including standards) are evenly set in the straw cells. Additionally, the application of the straw cell in studying precipitation band formation in gels was shown on two gel samples containing 0.004 M [Fe(CN)6]3−/[Fe(CN)6]2− in 2 mass% κ-carrageenan and 0.040 M Fe2+/Fe3+ in 1 mass% agarose, respectively.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2772K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2772K) -
Kanae NISHIMURA, Jun HAGINAKAArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 659-664
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMolecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) for promazine (PZ) and chlorpromazine (CPZ), MIPPZ and MIPCPZ, were prepared by multi-step swelling and polymerization using methacrylic acid as a functional monomer and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as a crosslinker. The retention and molecular-recognition properties of MIPPZ and MIPCPZ were evaluated using a mixture of potassium phosphate buffer and acetonitrile, or a mixture of ammonium formate and acetonitrile as the mobile phase in LC. PZ and CPZ gave the maximal retentions on MIPPZ and MIPCPZ at an apparent pH 8.2 using a mixture of potassium phosphate buffer and acetonitrile as the mobile phase. The retentions of PZ and CPZ decreased with an increase of acetonitrile contents from 70 to 90 vol% using a mixture of ammonium formate and acetonitrile as the mobile phase. The template molecules (PZ and CPZ, respectively) were recognized the most on the respective MIPs, and the imprinting factor of PZ was higher on MIPCPZ than on MIPPZ. These results indicate that in addition to shape recognition, ionic and hydrophobic interactions seem to work for the retention and molecular-recognition of PZ and CPZ on the MIPs. MIPCPZ was successfully utilized for the selective extraction of PZ in rat-serum samples in column-switching LC with fluorescence detection.
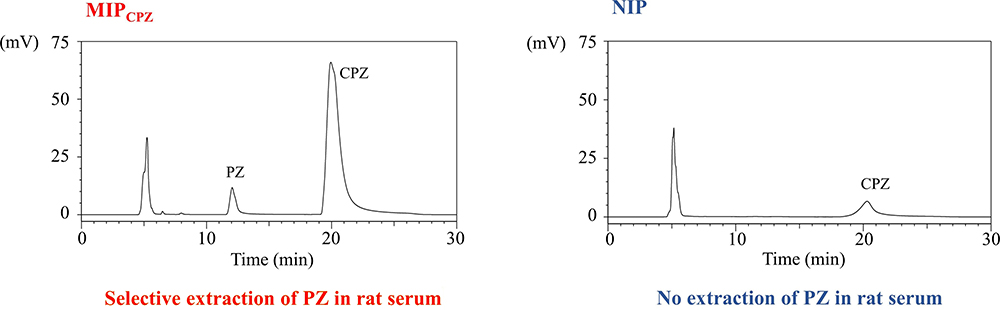 View full abstractDownload PDF (437K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (437K) -
Hisanori IWAI, Mitsuo YAMAMOTOArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 665-670
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSColloidal organic matter is an important factor in our understanding of the transport of trace metals by rivers to coastal areas and the characteristics of organic matter in the sediment, including the effect of humic substances on the transport of such metals. The structural features of humic acids (HAs) derived from surface sediments collected from the mouths of four rivers in northwest Hokkaido, Japan, were evaluated from the perspective of land use in their basins. The sediments in two rivers (referred to as NS and SK) were lacking in HAs, but the sediments of the others (referred to as SM and PO) contained relatively high levels of HAs. UV-vis spectroscopic characteristics suggested that the HAs in SM and PO contained components derived from humified materials. The PO and SM basins contain rice paddy fields, and TMAH-py-GC/MS analysis showed that the pyrograms of paddy soil HA had a similar character to those of PO-HA and SM-HA samples. Thus, the differences of the structural features can be attributed to the land use in river basins. The findings indicate that the properties of organic river sediments are heavily influenced by the type of land use in the river basins.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (851K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (851K) -
Douglas H. READ, Komandoor E. ACHYUTHAN, Cory S. FIX, Ronald P. MANGIN ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 671-677
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe describe for the first time hydrogen bonded acid (HBA) polymer, poly{methyl[3-(2-hydroxyl, 4,6-bistrifluoromethyl)phenyl]propylsiloxane}, (DKAP), as stationary phase for gas chromatography (μGC) of organophosphate (OP), chemical warfare agent (CWA) surrogates, dimethylmethylphosphonate (DMMP), diisopropylmethylphosphonate (DIMP), diethylmethylphosphonate (DEMP), and trimethylphosphate (TMP), with high selectivity. Absorption of OPs to DKAP was one-to-several orders of magnitude higher relative to commercial polar, mid-polar, and nonpolar stationary phases. We also present for the first-time thermodynamic studies on the absorption of OP vapors and quantitative binding energy data for interactions with various stationary phases. These data help to identify the best pair of hetero-polar columns for a two-dimensional GC system, employing a nonpolar stationary phase as GC1 and DKAP as the GC2 stationary phase, for selective and rapid field detection of CWAs.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (289K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (289K) -
Evan L. ANDERSON, Pablo D. SAMANIEGO, Philippe BÜHLMANNArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 679-684
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 22, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialPolyquaternium polymers are polycationic polymers that are contained in many hair shampoos and conditioners and are also often added to water to remove organic and inorganic anions by floc formation. While polyquaternium analysis is not trivial, electroanalytical methods have been proposed for their detection using either irreversible emf responses or reversible potential-driven extraction into and out of polymeric sensing membranes. We present here an alternative technique for the determination of a representative polyquaternium polymer, poly(dimethylamine-co-epichlorohydrin) chloride, by equilibrium binding with a singly charged anionic surfactant, 1-dodecyl sulfate. Binding of an anionic surfactant to the polyquaternium polymer simplifies electrochemical detection as the concentration of unbound surfactant can be monitored using the equilibrium Nernstian emf response of ion-exchanger membranes. The latter can be used to determine the nature of the binding interaction and allows for the straightforward determination of polyquaternium polymer concentrations by titration.
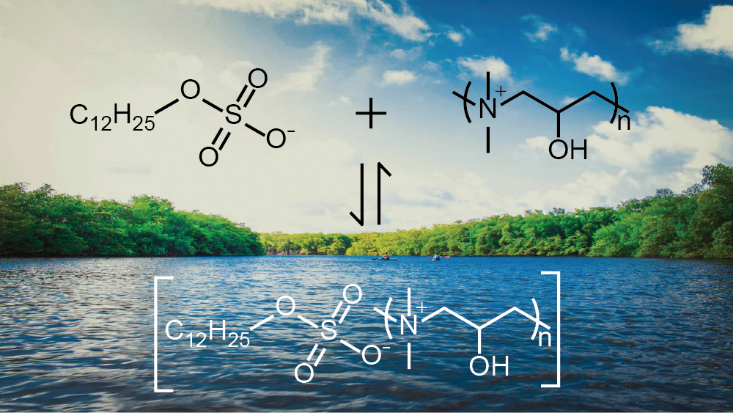 View full abstractDownload PDF (301K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (301K) -
Yuki YANO, Masamichi NISOUGI, Yuki YANO-OZAWA, Tsuyoshi OHGUNI, Atsush ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 685-690
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 01, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSGold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been commonly used in molecular sensing, in the form of observation of the color change from red to blue of the AuNP solution, caused by target-molecule-induced AuNP aggregation. In this work, the changes in absorbance and scattering spectra caused by AuNP aggregation were studied using thrombin-induced AuNP aggregation as a model. We demonstrated for the first time that scattering spectra is more sensitive to the changes owing to AuNP aggregation than absorbance spectra. Moreover, a digital color analysis of darkfield images using dark field microscopy (DFM) facilitated a simple method for detection of AuNPs aggregation without the use of spectroscopic analysis. Furthermore, we demonstrated that DFM is useful for detecting AuNPs aggregation in a colored solution, in which the color change by AuNPs aggregation is not visible.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (15368K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (15368K) -
Yan YANG, Fang TAN, Xiaoxue XIE, Xiumei YANG, Zaichun ZHOU, Keqin DENG ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 691-699
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: March 08, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialPlasmon-enhanced light harvesting has been of great interest to enhance the catalytic efficiency of some composites or hybrids. The enhanced peroxidase-like activity of phosphorylated iron(III) porphyrin (TPPFe(III))-based nanocomposite, induced by localized surface plasmon resonance for a colorimetric assay, was developed in this study. Firstly, a phosphate group modification strategy was adopted to synthesize water-soluble iron(III) porphyrin materials. Then, the as-synthesized TPPFe(III) was covalently attached to core-shell gold nanorods (GNRs), GNR@Au2S/AuAgS, to form TPPFe(III)-GNR@Au2S/AuAgS nanocomposite, which shows greatly enhanced peroxidase-like activity compared to TPPFe(III). A mechanism for the enhanced peroxidase-like activity of TPPFe(III)-GNR@Au2S/AuAgS was proposed, which results from a synergic effect of hot electrons excited by localized surface plasmon resonance and photogenerated electrons of the TPPFe(III), verified by experiments. Furthermore, a fast colorimetric assay for the detection of H2O2 and glucose was established based on the unique property of TPPFe(III)-GNR@Au2S/AuAgS. This colorimetric assay was applied to determine practical human serum samples; satisfactory results demonstrate this method has high accuracy. The present study would not only provide some insights into the mechanism of plasmon-activated enzyme-like reactions, but also offer new strategies for improving the catalytic activity of a mimetic enzyme.
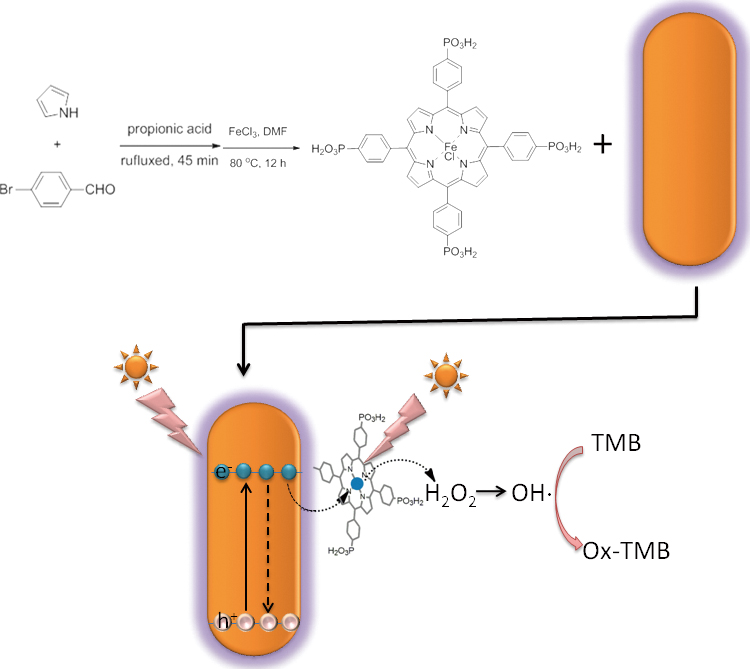 View full abstractDownload PDF (1432K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1432K)
-
Hiroki OKAYAMA, Masahiro TOMITA, Masato SUZUKI, Tomoyuki YASUKAWAArticle type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 701-704
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 15, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe have developed a simple and rapid formation of a cell-based array on microwell array electrodes by an attractive force of positive dielectrophoresis (p-DEP), even after removing an upper disk electrode stick that was used as a counter electrode to the microwell array electrodes. The attractive force of p-DEP generated by the scanning of the disk electrode allows the formation of a cell-based array on all microwell arrays. We demonstrated an exploration of target cells spiked with a low ratio after removing the disk electrode.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (551K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (551K) -
Makoto FUSE, Yasuto FUJIMAKI, Shigeru OHSHIMA, Atsuko NISHIGAKIArticle type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 705-708
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
Advance online publication: February 22, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWhen ethanolic solutions of 1-nitropyrene (1-NP) and 3-nitrobenzanthorone (3-NBA) were irradiated with intense light, which they absorb, for several minutes, the fluorescence characteristics of the solutions were significantly changed. After such preliminary irradiation, the fluorescence intensity of 1-NP increased immediately by a factor of 104 with a blue shift of 100 nm and that of 3-NBA 700 with a red shift of 10 nm. The findings were applied to high performance liquid chromatography with a fluorescence detector so that the two nitroarenes could be quantitatively analyzed by preliminary irradiation of their solutions before measurements. The calibration curves were linearly drawn over the concentration range from 1.0 × 10−9 to 1.0 × 10−7 M for 1-NP and 1.0 × 10−8 to 1.0 × 10−6 M for 3-NBA and the limits of detection were 2.3 pg for 1-NP and 28 pg for 3-NBA. From the results, fluorescence enhancement was found to be very effective for determining nitroarenes, being practically non-fluorescent and very important in environmental health-risk assessment, easily and sensitively. The mechanism of the fluorescence enhancement of 1-NP and 3-NBA was also discussed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (219K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (219K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2019 Volume 35 Issue 6 Pages 709
Published: June 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1179K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
