
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Keitaro YOSHIMOTOArticle type: Highlights
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1063-1064
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
-
Hidenobu NAKAO, Je-Deok KIMArticle type: Rapid Communications
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1065-1067
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 06, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
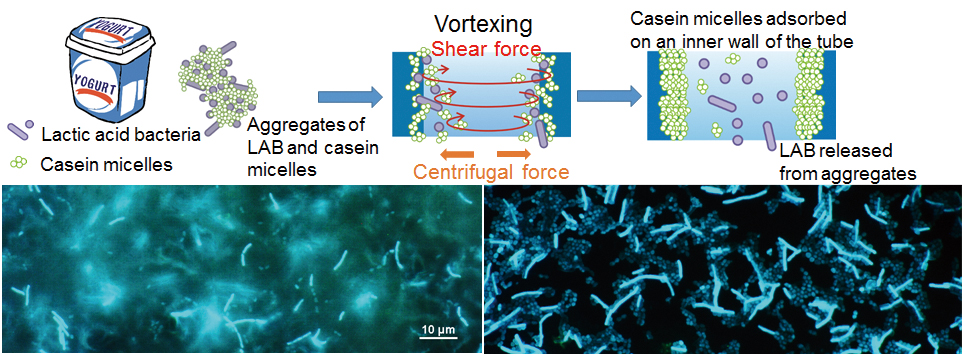
Supplementary materialWe have reported a simple method for separating lactic acid bacteria (LAB) from yogurt. This method is based on the process of destructions and denaturation of casein micelle aggregates by vortexing, and can supply samples containing only LAB. Recovered LAB were clearly observable by microscopy, meaning that morphological changes could be directly detected at the single-cell level. This method will be a helpful tool for the analyzing various LAB, including their enzyme activity and protein expression.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (433K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (433K)
-
Manish Kumar SHARMA, Pooja DHAKNE, Sidhartha NN, P Ajitha REDDY, Pinak ...Article type: Reviews
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1069-1082
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
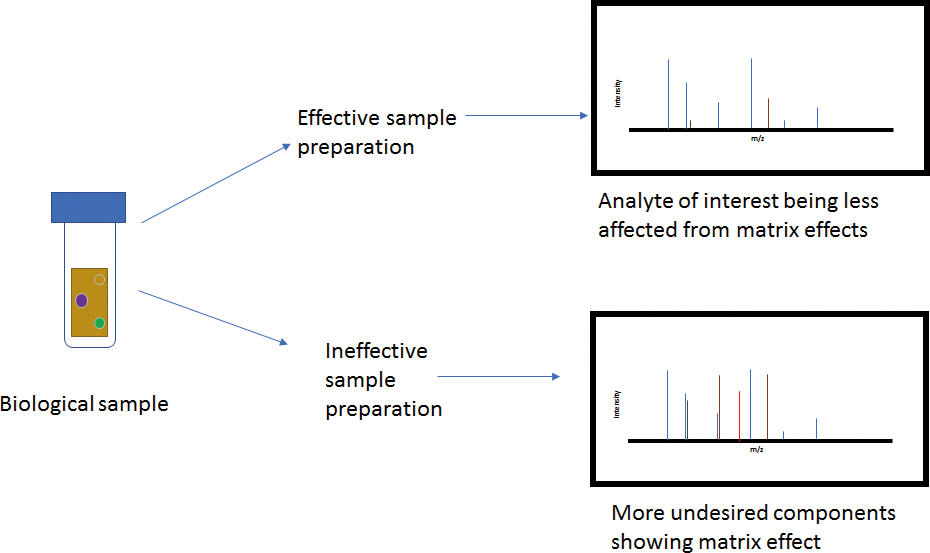
Advance online publication: May 17, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSample preparation is a highly important and integral part of bioanalysis for cleaning up the complex biological matrices and thereby minimizing matrix effect. Matrix effect can jeopardize the precise quantification and adversely affect the reliability of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry-based analytical results by alteration of analyte ionization. Matrix components result in suppression or enhancement of the intensity of analyte response. In spite of the high specificity and selectivity of tandem mass spectrometry, a relatively higher concentration of coeluted matrix elements present in biofluids may alter the efficiency of quantification of a bioanalytical method. Numerous literature reports different types of sample preparation techniques employed in bioanalysis. In this review, the strategies for selection of the appropriate sample clean-up technique in bioanalysis are discussed extensively. A paradigm shift in the arena of sample preparation and bioanalytical approaches involving the liquid chromatography–mass spectroscopic technique has been scrutinized. Current trends and possible future advancements in the field of biological sample extraction methods, including instrumental techniques are analyzed in detail.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (202K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (202K)
-
Rana SHARIATI, Behzad REZAEI, Hamid Reza JAMEI, Ali Asghar ENSAFIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1083-1088
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 24, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this article, a new optical sensor was developed using a molecularly imprinted polymers layer coated with new green carbon dots (CDs) for the determination of propranolol. First, the CDs were synthesized for the first time from Cedrus plant through the hydrothermal method. Then, a nanolayer molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was applied on the CDs (MIP-CDs) in the presence of propranolol as a template using a reverse microemulsion technique. Afterward, propranolol was removed from MIP-CDs nanocomposites using a mixture of ethanol and acetonitrile, and the obtained nanocomposite was used as a fluorescence sensor for propranolol determination. Under the optimal conditions, the sensor response was linear in the range of 0.8 – 65.0 nmol L−1 with a detection limit of 0.2 nmol L−1. The results confirmed that the sensor has some advantages such as cost-effectiveness, rapid response, high sensitivity and selectivity for propranolol determination.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (635K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (635K) -
Meichao ZHAO, Haruka SHINOZAKI, Hideyuki ITABASHI, Daisuke KOZAKI, Mas ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1089-1096
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 14, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA method for extracting metals from solid samples was developed. The system had four flow channels (each containing a column packed with a solid sample), a single-flow peristaltic pump, and eight six-port valves. An extractant was passed into each channel for a specified period, then the valves were closed. We evaluated the system by performing a four-step sequential extraction procedure to extract heavy metals from a lake sediment sample. The four extractants were, in order of use, magnesium chloride, ammonium acetate, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, and hydrochloric acid. The concentrations of the analytes extracted agreed well with the concentrations determined using the batch method. The system was also successfully used to analyze heavy metals in a soil sample from a parking lot and fly ash from a domestic waste disposal facility. The total amount of extractant required per sample using the system was two-thirds of the amount required using the batch method.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1090K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1090K) -
Yu Lim HONG, Tae Hoon SEO, Hongje JANG, Young-Kwan KIMArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1097-1102
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 14, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe influence of oxidative debris (OD) on laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (LDI-TOF-MS) analysis using graphene oxide (GO) derivatives was systematically investigated. Specifically, the effects on LDI-TOF-MS analysis of small molecules and synthetic polymers were highlighted. The analytical efficiency of GO was significantly enhanced by removing OD from its surface and the working molecular weight range of GO was considerably extended for analysis of synthetic polymers and small molecules.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (398K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (398K) -
Yan TAN, Qianhui SONG, Wenfang LIU, Ming LI, Jian XIAO, Chuanpin CHENArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1103-1109
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 21, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA dual-channel microchip electrophoresis (ME) with in-channel amperometric detection was developed for cefoperazone and sulbactam determination simultaneously. In this study, a microelectrode detector was made of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) modified indium tin oxide (ITO)-coated poly-ethylene terephthalate (PET) film. The parameters including detection potential applied on working electrode, buffer concentration and pH value were optimized to improve the detection sensitivity and separation efficiency of cefoperazone and sulbactam. Under the optimal conditions, sensitive detection of cefoperazone and sulbactam was obtained with limits of detection (LODs) (S/N = 3) of 0.52 and 0.75 μg/mL, respectively. The plasma sample, which was from a patient with a brain injury taking Sulperazone, was successfully detected with a simple sample pretreatment process by dual-channel ME amperometric detection. This rapid and sensitive method possesses practical potential in clinical applications, and could provide a guidance for clinical rational drug use.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1660K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1660K) -
Atsuko KONISHI, Shigehiko TAKEGAMI, Tatsuya KITADEArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1111-1115
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 21, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPotentiometric glutathione (GSH) sensors were fabricated using a molecularly imprinted polymer prepared from GSH, methacrylic acid (MAA), and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as the template molecule, functional monomer, and cross-linker, respectively. Five GSH sensors were prepared with different ratios of GSH to MAA. Their potential responses were measured in a GSH aqueous solution using Ag/AgCl as the reference electrode. A GSH sensor prepared with a GSH:MAA ratio of 2:32 had the best responsivity, while the sensor synthesized from a non-imprinted polymer prepared without GSH (NIP sensor) showed a potential response value of almost zero after the addition of GSH. The ratio of the potential responses of the GSH sensor to the NIP sensor was 8.21. Additionally, the GSH sensor had good linearity over a GSH concentration range of 1 × 10−5 to 2 × 10−4 mol L−1. The GSH sensor provided good quantification and high specificity for GSH and is expected to be applicable for easy and direct determinations of GSH.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (248K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (248K) -
Sakura YOSHII, Masanobu MORI, Daisuke KOZAKI, Takayuki HOSOKAWA, Hidey ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1117-1122
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 21, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
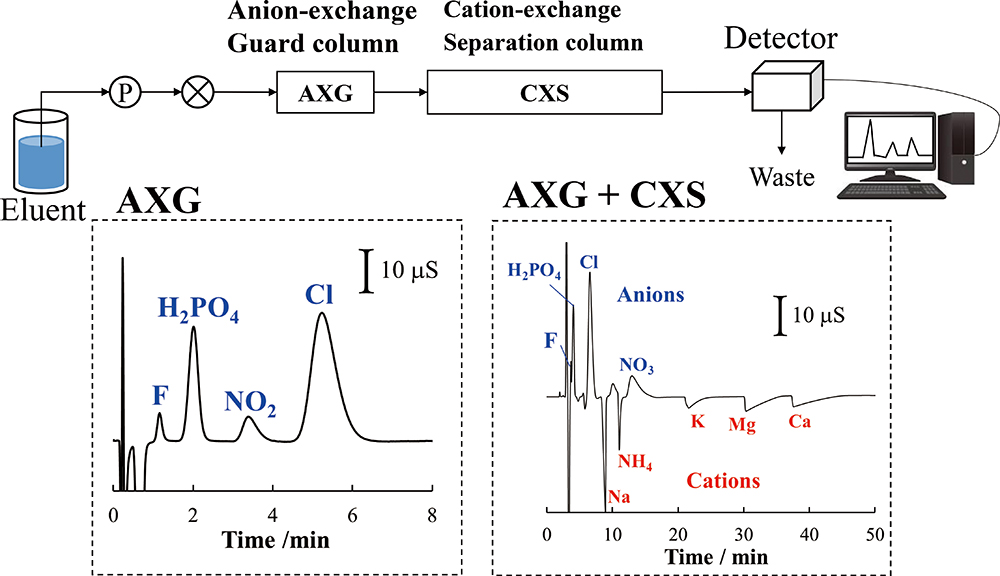
Supplementary materialThis study demonstrated that a guard column containing anion-exchange resin has the potential for use as a separation column for acid eluent. Specifically, a 1-cm long anion-exchange guard column with a 4.6-mm internal diameter provided good separation of monovalent inorganic anions, by elution of 8 mM tartaric acid or 4 mM malic acid. Using the guard column with acid eluent could be applied to evaluation of nitrite and nitrate ions in mountain and urban river water samples. When the guard column was connected in front of a cation-exchange separation column (15 cm long × 4.6 mm internal diameter) in a series, the system provided simultaneous separation of anions and cations in eluent of 8 mM tartaric acid and 0.5 mM 18-crown-6 ether by a single injection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1433K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1433K) -
Mao OTAKE, Yoshiaki UKITAArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1123-1127
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
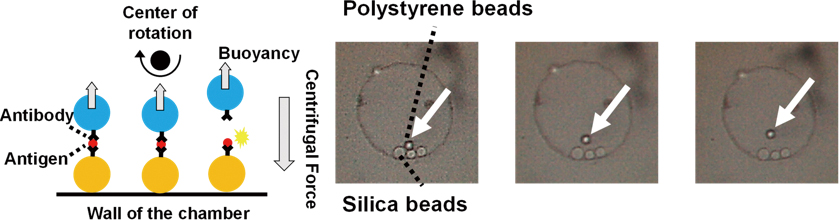
Supplementary materialMeasurement of single molecule interaction is performed by various micromanipulation techniques. However, a complex operation is required to perform the measurement, so the measurement throughput is low and a large amount of time is required for statistical analysis. In this paper, we propose a method for measuring intermolecular interactions that applies a tensile force to the intermolecular bond by using centrifugal force and can easily measure binding force. The binding force of an antigen–antibody reaction system was measured by the use of the proposed method as a proof of concept. The measured binding forces were distributed in the range of 19 – 133 pN. The values obtained by use of the proposed method were consistent with the conventional method. This result is promising for applications that require further development, such as the development of a biosensor as a novel measuring technique that is based on the intermolecular interaction measurement.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (629K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (629K) -
Toshiki OTAKA, Tatsumi SATO, Simpei ONO, Kohei NAGOSHI, Ryoji ABE, Tsu ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1129-1133
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: July 05, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSingle porous silica microparticles coated with a styrene-divinylbenzene polymer (SDB) impregnated with octyl(phenyl)-N,N-diisobutylcarbamoylmethylphosphine oxide (CMPO) were injected into an aqueous 3 mol/L nitric acid solution containing trivalent lanthanide (Ln(III)), as a high-level liquid waste model. We used the microcapillary manipulation-injection technique; and the extraction rate of Ln(III), as an Ln(III)-CMPO complex, into the single microparticles was measured by luminescence microspectroscopy. The extraction rate significantly depended on the Ln(III), CMPO, or NO3− concentration, and was analyzed in terms of diffusion in the pores of the microparticles and the complex formation of Ln(III). The results indicated that the rate-determining step in Ln(III) extraction was diffusion in the pore solution of the microparticles.
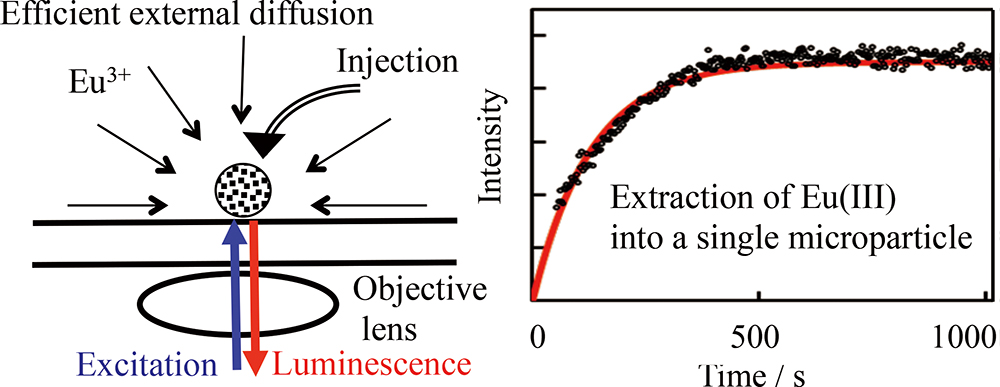 View full abstractDownload PDF (926K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (926K) -
Ze WANG, Bin DONG, Guodong FENG, Hongyan SHAN, Yanfu HUAN, Qiang FEIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1135-1140
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: July 05, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn the present study, we synthesized a water-soluble substance (Hemin-mPEG) at room temperature by using hemin and poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether (mPEG). It was found that the Hemin-mPEG maintained the excellent catalytic activity inherited from hemin, and was first used to catalyze a luminol–H2O2 chemiluminescence (CL) system to generate an intense and slow CL signal. The results of a mechanism research showed that the presence of Hemin-mPEG could promote the production of oxygen-relative radicals from H2O2 and dissolved oxygen in solution. Based on this mechanism, an ultra-sensitive, cheap and simply practical sensor for detecting glucose and H2O2 was developed. Under the most optimal experimental conditions, H2O2 and glucose detection results exhibited a good linear range from 0.002 to 3 μM and from 0.02 to 4 μM, respectively, and the detection limits were 1.8 and 10 nM, respectively. This approach has been successfully used to detect glucose in actual biological samples, and achieved good results.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (287K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (287K) -
Nobutoshi OTA, Genki N. KANDA, Hiroyuki MORIGUCHI, Yusufu AISHAN, Yiga ...Article type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1141-1147
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMicrofluidic devices are important platforms to culture and observe biological tissues. Compared with conventional setups, microfluidic devices have advantages in perfusion, including an enhanced delivery of nutrients and gases to tissues. However, explanted tissues can maintain their functions for only hours to days in microfluidic devices, although their observations are desired for weeks. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is a brain region composed of heterogeneous cells to control the biological clock system through synchronizing individual cells in this region. The synchronized and complicated cell–cell interactions of SCN cells are difficult to reproduce from seeded cells. Thus, the viability of explanted SCN contributes to the study of SCN functions. In this paper, we propose a new perfusion platform combining a PDMS microfluidic device with a porous membrane to culture an explanted SCN for 25 days. We expect that this platform will provide a universal interface for microfluidic manipulation of tissue explants.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1549K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1549K) -
Na LI, Shi Gang LIU, Yong Qin HE, Xi MAIArticle type: Original Papers
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1149-1153
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: July 05, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) technique was utilized as a tool for isoelectric point monitoring and iron(III) cation determination. The spectral properties of some amphoteric molecules (proteins and a DNA sequence) were investigated using the RRS technique. When the pH values were kept at around their isoelectric points, especially high RRS signals could be obtained, which were much stronger than those at other pH values. By using the C30 DNA sequence as a probe, the iron(III) cation can be detected rapidly. After iron(III) was added to a C30 solution, a significantly decreased RRS signal was obtained. The sensing process can be finished within 10 min with a detection limit of 0.9 μM. Thus, a sensitive, selective, and label-free method was successfully developed for iron(III) detection.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1722K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1722K)
-
Wenzhao ZHOU, Yan HONG, Xue ZOU, Lei XIA, Yan LU, Chengyin SHEN, Chaoq ...Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1155-1159
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 07, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialNitrogen-containing compounds are important components in human breath. However, their origins have not yet been clearly understood. In this study, a modified electrospray ionization (ESI) source coupling with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry has been used for breath analysis. Fourteen nitrogen-containing compounds were identified in mouth-exhaled breath, and 10 of them were from the oral cavity and oropharynx. Moreover, 8 of these nitrogen-containing compounds were recognized as endogenous metabolites. This result provides important clues for exploring the biological origins of these nitrogen-containing compounds. Observation of the ion suppression phenomenon also indicates that breath analysis should be carried out after clearing of the oral cavity and oropharynx, or directly through nose-breathing to eliminate the influence of those nitrogen-containing compounds from the oral cavity.
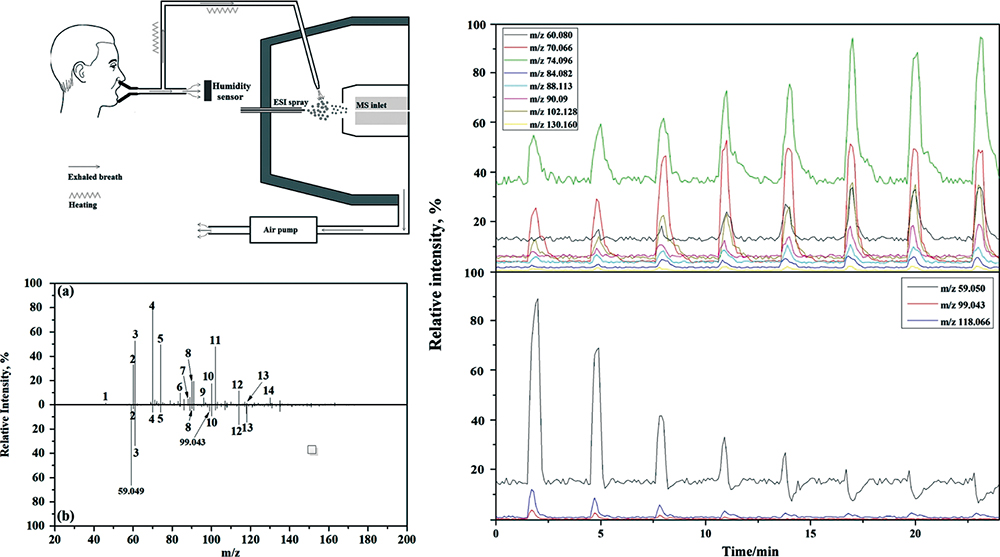 View full abstractDownload PDF (1741K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1741K) -
Shigehiro KAGAYA, Yuji MISHIMA, Issei OBATA, Makoto GEMMEI-IDE, Yoshin ...Article type: Notes
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1161-1164
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
Advance online publication: June 28, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialChelating resins immobilizing carboxymethylated polyethyleneimine (CM-PEI) with different carboxymethylation rates were prepared. The thermal decomposition behavior of CM-PEI resins was investigated using thermogravimetry–differential thermal analysis/photo ionization–quadrupole mass spectrometry (TG-DTA/PI-QMS) and ion attachment ionization–quadrupole mass spectrometry equipped with direct inlet probe (DIP/IA-QMS). The obtained results suggested that the carboxymethyl group decomposed at relatively low temperature (150 °C – 300 °C); the peak areas at m/z 45 and 59 in TG-DTA/PI-QMS and m/z 58, 70, and 72 in DIP/IA-QMS significantly increased with increasing carboxymethylation rate. These relationships should be useful for estimating the carboxymethylation rate of CM-PEI resin.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (816K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (816K)
-
Article type: Announcements
2019 Volume 35 Issue 10 Pages 1165
Published: October 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1092K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
