All issues

Volume 30, Issue 6
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 629
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (690K)
Rapid Communications
-
Hiromu IKEDA, Yoshihiro YAYAMA, Akito HATA, Jumpei KAMIMOTO, Tatsuhiro ...Article type: Rapid Communications
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 631-635
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPeptide microarrays can be used to measure the activity of multiple protein kinases (PKs), which can be used to elucidate kinomics for drug discovery and diagnosis. Here we demonstrated a new microarray for ratiometric detection of the activity of PKs using peptide nucleic acid (PNA)-tagged peptides labeled with two different fluorophores, Cy3 and Cy5. We successfully detected cellular PK activities based on ratiometry, and applied the system for evaluation of an inhibitory drug. View full abstractDownload PDF (1794K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1794K)
Original Papers
-
Xun MAO, Anant GURUNG, Hui XU, Meenu BALODA, Yuqing HE, Guodong LIUArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 637-642
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this work, we present a simple and fast approach for simultaneous detection of nucleic acid and protein using gold nanoparticles (GNPs) and a lateral flow device (LFD). Sandwich-type immunoreactions and DNA hybridizations were performed simultaneously on the LFD by using DNA- and antibody-functionalized GNPs. The captured GNPs, due to the DNA hybridization and immunoreaction events on the LFD, produced characteristic red bands that could be used for the qualitative detections of DNA and/or protein. The proof of principle was demonstrated by using 60-mer DNA and rabbit IgG (R-IgG) model targets. The LFD was capable of detecting a minimum of 0.5 nM target DNA and 2 ng mL−1 IgG simultaneously in 15 min. The proposed LFD shows great promise for in-field and point-of-care testing of disease-related circulating nucleic acid and protein biomarkers in biological fluids.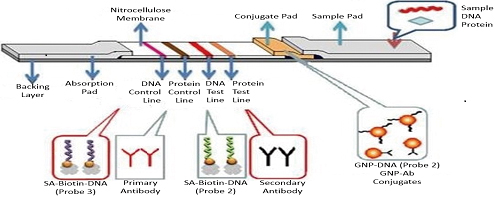 View full abstractDownload PDF (5853K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5853K) -
Hiroya KANO, Daichi TANOUE, Hiroaki SHIMAOKA, Kohei KATANO, Takeshi HA ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 643-648
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn inclusion complex consisting of a boronic acid fluorophore (C1-APB) and β-cyclodextrin (β-CyD) acts as a supramolecular sugar sensor whose response mechanism is based on photoinduced electron transfer (PET) from the excited pyrene to the boronic acid. We have investigated the PET process in C1-APB/CyD complexes by using time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) measurements at room temperature, and have succeeded in estimating the electron-transfer time to be about 1 ns. We have also studied the effects of CyDs on the PET process by comparing two kinds of CyDs (α-CyD, β-CyD) under different water–dimethyisulfoxide (DMSO) concentration conditions. We found that the CyDs interacting with the boronic acid moiety completely inhibits PET quenching and increases the monomer fluorescence intensity. View full abstractDownload PDF (4997K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4997K) -
Kazuharu SUGAWARA, Makoto OKUSAWA, Yusaku TAKANO, Toshihiko KADOYAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 649-655
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSElectrodes modified with gallium(III) complexes were constructed to detect ovalbumin (OVA). For immobilization of a gallium(III)-nitrilotriacetate (NTA) complex, the electrode was first covered with collagen film. After the amino groups of the film had reacted with isothiocyanobenzyl-NTA, the gallium(III) was then able to combine with the NTA moieties. Another design featured an electrode cast with a gallium(III)-acetylacetonate (AA) complex. The amount of gallium(III) in the NTA complex was equivalent to one-quarter of the gallium(III) that could be utilized from an AA complex. However, the calibration curves of OVA using gallium(III)-NTA and gallium(III)-AA complexes were linear in the ranges of 7.0 × 10−11 – 3.0 × 10−9 M and 5.0 × 10−10 – 8.0 × 10−9 M, respectively. The gallium(III) on the electrode with NTA complex had high flexibility due to the existence of a spacer between the NTA and the collagen film, and, therefore, the reactivity of the gallium(III) to OVA was superior to that of the gallium(III)-AA complex with no spacer. View full abstractDownload PDF (995K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (995K) -
Joyce F. S. de SANTANA, Mônica F. BELIAN, André F. LAVORA ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 657-661
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis work describes an automated procedure to determine L-malic acid (MA) in wine samples using a multicommuted flow analysis. The MA quantification was based on an enzymatic reaction between MA and L-malate dehydrogenase (L-MDH) in the presence of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), producing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase (NADH), which was monitored at 340 nm. The L-MDH was immobilized on a surface of modified silica with amino groups in the presence of glutaraldehyde. For studying optimization, the system was maintained with 200 μL (288 U) of the L-MDH in 0.5 g of modified silica. Under the optimum experimental conditions, a linear response ranging from 0.1 to 1.5 g L−1 MA (R = 0.997 and n = 7), a detection (3σ criterion) and quantification (10σ criterion) limit estimated at 0.02 and 0.06 g L−1, respectively, a standard deviation relative of 1.8% (n = 7) for a sample of 0.5 g L−1 MA, a sampling rate of 67 samples per hour were achieved. Analyzing ten wines samples and applying the t-test to the results found and those obtained using reference procedures (HPLC) provided no significant differences at the 95% confidence level. View full abstractDownload PDF (651K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (651K) -
LiPing HU, Nan WU, Jing ZHENG, JingLi XU, Min ZHANG, PinGang HEArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 663-668
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA magnetic metal organic framework (MOF) composite was prepared. The composite was fabricated by incorporation of Fe3O4 nanoparticals with MOF. It was characterized and expected to offer a promising template for molecular immobilization and sensor fabrication because of its ordered structure and satisfying large specific surface area. The resulting composite was used to detect methyl parathion. Electrochemical measurements showed that the multifunctional composite of MOF provided an excellent matrix for the co-adsorption of methyl parathion. Owing to the ordered structure, the large surface area, excellent compatibility and magnetic property of the material, methyl parathion could be separated, accumulated and directly detected in the solution with high sensitivity. The differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) response was proportional to the concentration range from 5.00 × 10−6 to 5.00 × 10−3 g L−1 with the detection limit of 3.02 × 10−6 g L−1. The experimental results can lead to a widespread use of electrochemical sensors to detect organophosphorous pesticides contaminates and other substances. View full abstractDownload PDF (1216K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1216K) -
Jian-Rong CAI, Li-Na ZHOU, En HANArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 669-673
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA sensitive biosensor based on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and carbon nanosphere (CNS) immobilized on a glassy carbon electrode was developed for the detection of pesticides by the inhibition of AChE activity. The inhibition effect of the pesticides resulted in a decrease of current response of the acetylthiocholine chloride that was used as a substrate to obtain an electrochemical signal. When applied to the pesticides carbofuran and fenitrothion, the designed biosensor exhibited high sensitivity and low detection limits. The inhibition ratio of carbofuran and fenitrothion were linearly proportional to their concentrations ranging from 0.40 to 4.79 and 6.26 to 125.31 μg/L, respectively. The theoretical detection limits were found to be 0.082 μg/L for carbofuran and 2.61 μg/L for fenitrothion. Furthermore, as the biosensor offers good reproducibility and stability, it could be used for trace detection of pesticides in real samples. Compared with other AChE biosensors, the proposed biosensor was convenient and it exhibited extreme sensitivity to pesticides. View full abstractDownload PDF (637K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (637K) -
Chenchen XIAO, Liang MING, Yifeng TUArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 675-681
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn the present work, the micellar electrophoretic separation of five chlorophenols (CPs) on a functionalized poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) microchip with amperometric detection was performed. In order to achieve high resolution by controlling the electroosmotic flow (EOF) as well as signal detection by suppressing analytes adsorption, the microchannel was functionalized by poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA)/SiO2 nanospheres (NSs)/ poly(sodium-p-styrenesulfonate) (PSS), via an approach of layer-by-layer assembly. Five chlorophenols (2-chlorophenol, 4-chlorophenol, 2,4-dichlorophenol, 2,3-dichlorophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol) were efficiently separated in this microchannel (3.7 cm of length) within 120 s. A resolution of at least 2.4 was obtained with a 10 mM phosphate buffer solution (PBS) (pH 9.48) containing 20 mM sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and 50% (v/v) acetonitrile as a carrier under optimized conditions. A graphene-modified carbon microdisk electrode was used for high-sensitivity detection. Its characteristics were investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). For those CPs, linear ranges of 0.08 – 5, 0.06 – 5, 0.04 – 5, 0.04 – 5 and 0.30 – 20 μM and detection limits of 0.021, 0.026, 0.022, 0.019 and 0.054 μM were obtained, respectively. The method was successfully applied for the analysis of some wastewater samples with satisfactory recovery. View full abstractDownload PDF (693K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (693K)
Notes
-
Yoshito WAKUI, Toshishige M. SUZUKIArticle type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 683-686
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, a simple and effective method for the detection of trace amounts of arsenic in water samples was developed. Arsenic hydride generated by the reduction of a water sample was passed through a sensing filter retaining silver bis(2-ethylhexyl)dithiocarbamate complex. The original yellow color of the filter immediately turned reddish violet. The difference of color was observed by a reflection spectrophotometer. Sensing filters made of glass fiber gave the highest sensitivity. Addition of low volatile amines effectively stabilized the performance of the sensing filter. Common anions including phosphate ion did not interfere with the arsenic detection. Visual detection of 10 μg dm−3 was achieved in φ10 mm filter area using 60 cm3 of sample solution.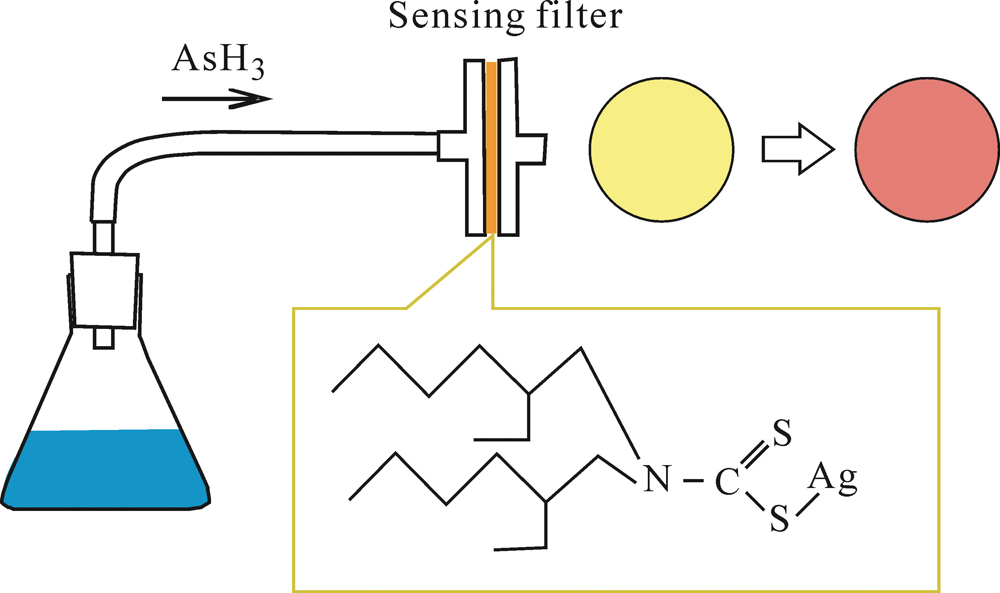 View full abstractDownload PDF (550K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (550K) -
Koichi KITAGUCHI, Naoya HANAMURA, Masaharu MURATA, Masahiko HASHIMOTO, ...Article type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 687-690
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA fluorocarbon and hydrocarbon organic solvent mixture is known as a temperature-induced phase-separation solution. When a mixed solution of tetradecafluorohexane as a fluorocarbon organic solvent and hexane as a hydrocarbon organic solvent (e.g., 71:29 volume ratio) was delivered in a capillary tube that was controlled at 10°C, the tube radial distribution phenomenon (TRDP) of the solvents was clearly observed through fluorescence images of the dye, perylene, dissolved in the mixed solution. The homogeneous mixed solution (single phase) changed to a heterogeneous solution (two phases) with inner tetradecafluorohexane and outer hexane phases in the tube under laminar flow conditions, generating the dynamic liquid–liquid interface. We also tried to apply TRDP to a separation technique for metal compounds. A model analyte mixture, copper(II) and hematin, was separated through the capillary tube, and detected with a chemiluminescence detector in this order within 4 min. View full abstractDownload PDF (1053K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1053K) -
Rania N. EL-SHAHENY, Koji YAMADAArticle type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 691-697
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe first stability-indicating HPLC method was developed and validated for azelastine HCl (AZL). The separation of AZL from its degradation products was achieved on a C18 column using acetonitrile-0.04 M phosphate buffer of pH 3.5 (32:68, v/v) as a mobile phase with UV-detection at 210 nm and naftazone as an internal standard. The method was rectilinear over the range of 0.2 – 20.0 μg mL−1 with a detection limit of 7.05 ng mL−1. The degradation behavior of AZL was studied under different ICH-recommended stress conditions along with a kinetic investigation; also, degradation products were identified by mass spectrometry. The method was applied for the quality control and stability assessment of AZL in eye drops and nasal spray. The obtained results were favorably compared with those obtained by a comparison method.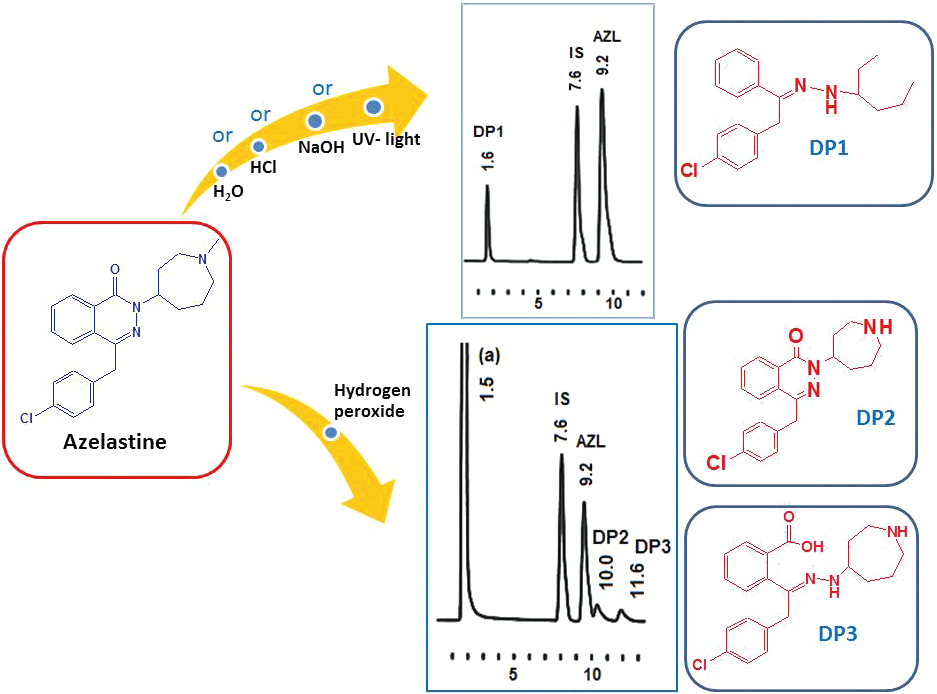 View full abstractDownload PDF (8703K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (8703K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014 Volume 30 Issue 6 Pages 699
Published: June 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2519K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|