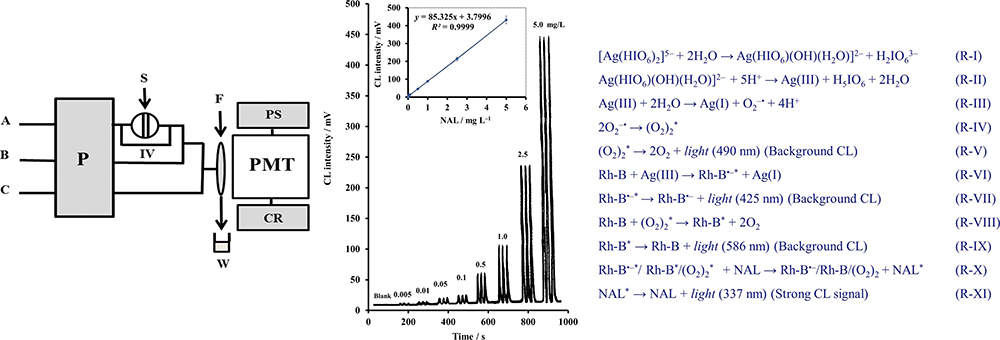
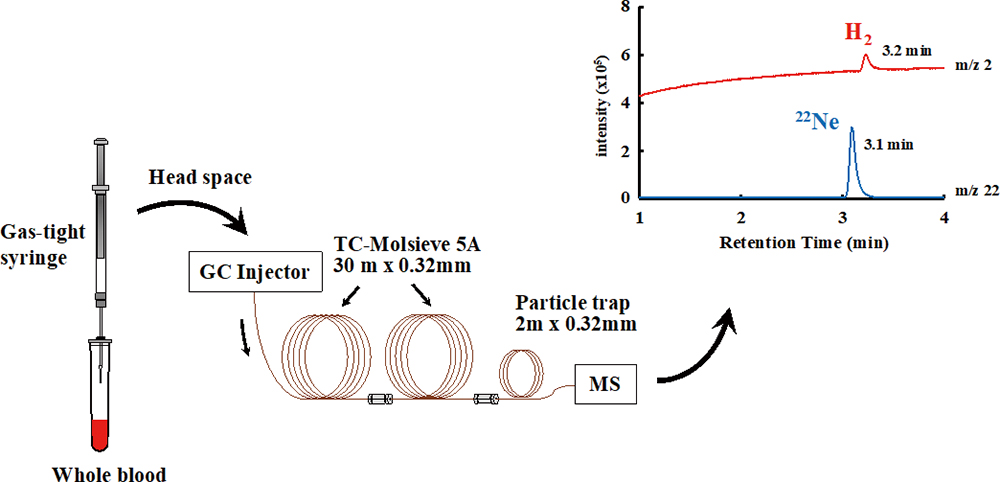
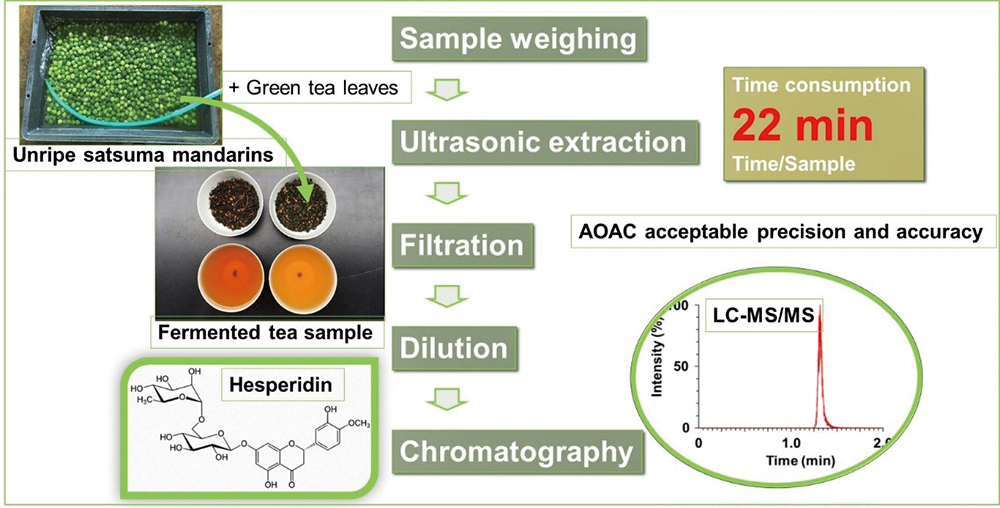
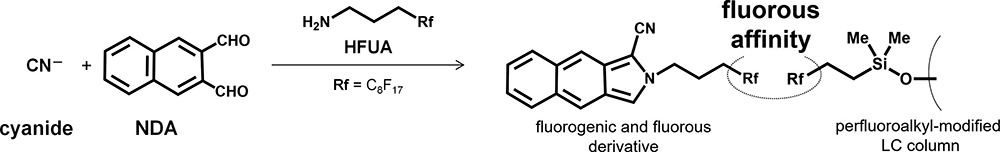
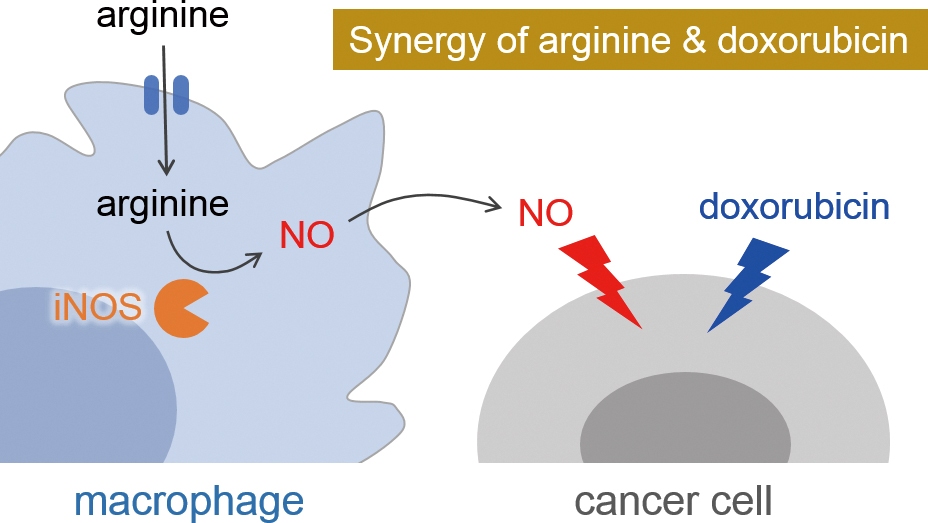
Volume 36, Issue 10
Displaying 1-24 of 24 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1151
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Download PDF (143K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1153-1155
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: September 18, 2020Download PDF (121K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1157-1163
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 10, 2020Download PDF (1185K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1165-1169
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 24, 2020Download PDF (3712K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1171-1176
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 01, 2020Download PDF (3216K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1177-1184
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 01, 2020Download PDF (884K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1185-1190
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: October 01, 2020Download PDF (414K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1191-1196
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 08, 2020Download PDF (280K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1197-1202
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 08, 2020Download PDF (651K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1203-1209
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 15, 2020Download PDF (9751K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1211-1215
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 15, 2020Download PDF (461K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1217-1222
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 15, 2020Download PDF (219K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1223-1230
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 22, 2020Download PDF (977K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1231-1236
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 29, 2020Download PDF (251K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1237-1241
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 29, 2020Download PDF (2211K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1243-1249
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 29, 2020Download PDF (177K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1251-1254
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 29, 2020Download PDF (166K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1255-1260
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 29, 2020Download PDF (440K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1261-1267
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 29, 2020Download PDF (2739K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1269-1274
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 19, 2020Download PDF (521K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1275-1278
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: June 19, 2020Download PDF (225K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1279-1283
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: July 03, 2020Download PDF (426K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1285-1288
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 01, 2020Download PDF (433K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2020Volume 36Issue 10 Pages 1289
Published: October 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2020
Download PDF (181K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|