Volume 33, Issue 8
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 875
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (218K)
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 877
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (337K)
Rapid Communications
-
Article type: Rapid Communications
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 879-881
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (544K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 883-887
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (994K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 889-895
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1176K) -
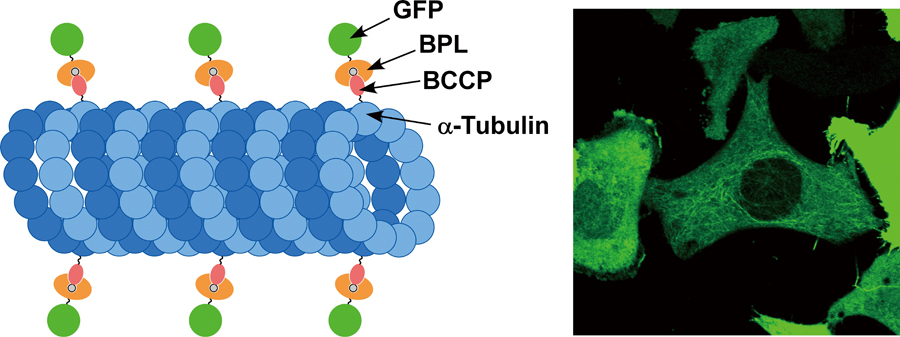
Labeling of Cytoskeletal Proteins in Living Cells Using Biotin Ligase Carrying a Fluorescent ProteinArticle type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 897-902
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (898K) -
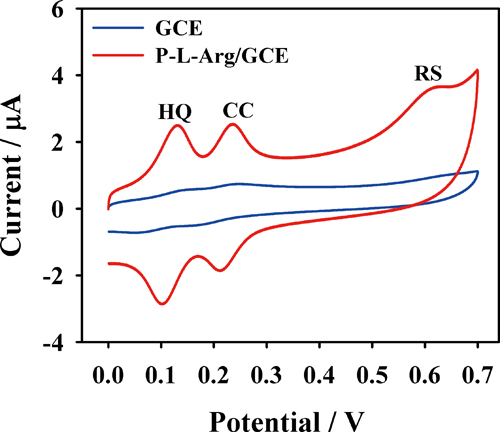
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 903-909
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1126K) -
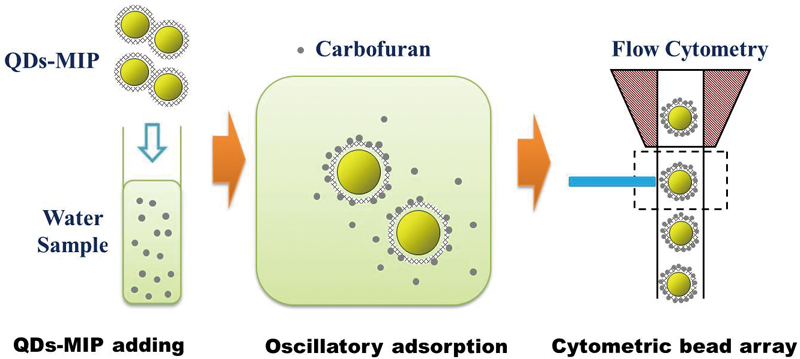
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 911-915
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1109K) -
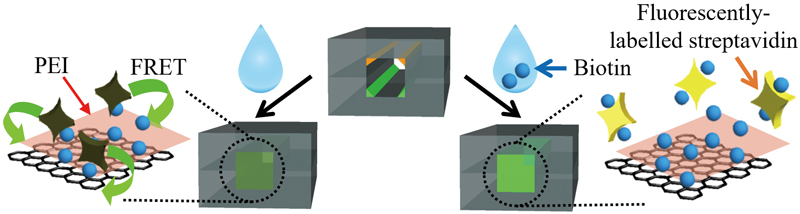
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 917-923
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1227K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 925-930
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1907K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 931-938
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (2207K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 939-944
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1067K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 945-951
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (2195K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 953-956
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1778K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 957-962
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (1607K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 963-967
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (824K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 969-972
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (606K) -
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 973-977
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (407K) -
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 979-982
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (557K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017Volume 33Issue 8 Pages 983
Published: August 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2017
Download PDF (3695K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|